Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 15, 2003; 9(11): 2533-2538
Published online Nov 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2533
Published online Nov 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2533
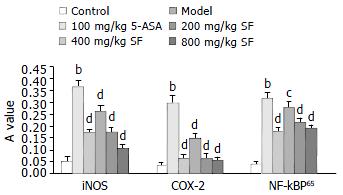
Figure 1 Effects of SF on the expressions of iNOS, COX-2 and NF-κB P65 in the colonic tissue of rats colitis induced by acetic acid (n = 8, ¯x ± s).
bP < 0.01, vs control group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, vs model group.
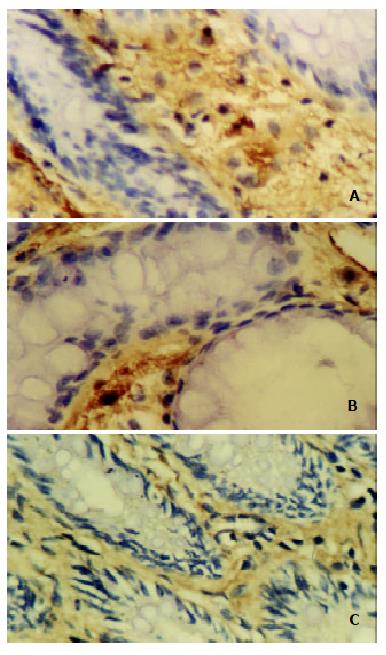
Figure 2 Expressions of iNOS (A), COX-2 (B) and NF-κB p65 (C) in the inflammatory areas of colonic tissue from rats with colitis induced by acetic acid enema, respectively.
The strongly positive signal were found. SP stain × 400.
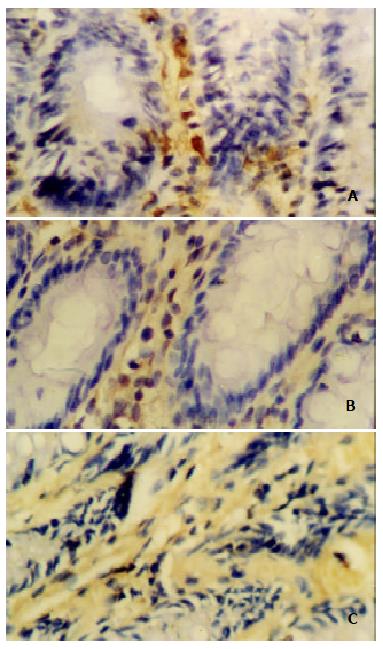
Figure 3 Expressions of iNOS (A), COX-2 (B) and NF-κB p65 (C) were significantly decreaed in the colonic tissue from rats with colitis induced by acetic acid enema after treasted with 800 mg•kg-1 ASP, respectively.
The weakly positive staining could be found. SP stain × 400.
- Citation: Dong WG, Liu SP, Yu BP, Wu DF, Luo HS, Yu JP. Ameliorative effects of sodium ferulate on experimental colitis and their mechanisms in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(11): 2533-2538
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i11/2533.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2533