Copyright
©The Author(s) 2003.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 15, 2003; 9(11): 2464-2468
Published online Nov 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2464
Published online Nov 15, 2003. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2464
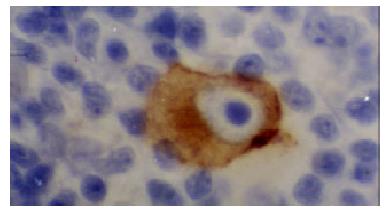
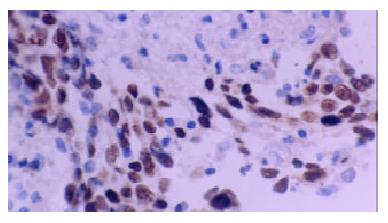
Figure 1 Positive-control of LMP1 from lymphoma of Hodgkin’ disease.
The cytoplasm of R-S cell showed clear positive signal.
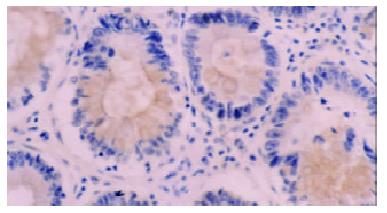
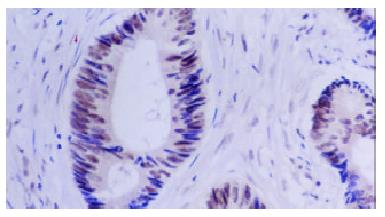
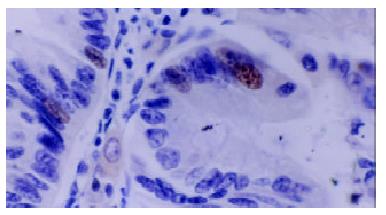
Figure 2 immunohistochemical staining with anti-LMP1 antibody of adenoma specimen with dysplasia.
The positive signals were localized at cytoplasm and membranes.
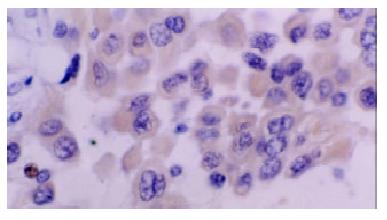
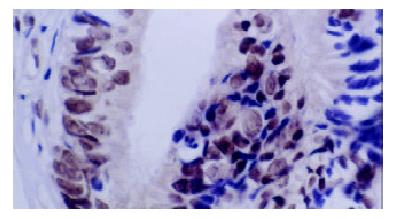
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining with anti-LMP1 antibody of colorectal carcinoma cells.
The positive signals were localized at cytoplasm. But no clear positive signals localized at membranes.
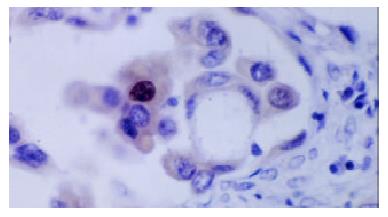
Figure 4 Metastatic colorectal carcinoma cells in lymphatic.
The cytoplasm of neoplasm cells showed LMP1 positive, the nucleic showed positive signals too.
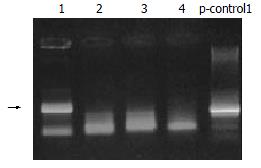
Figure 5 The electrophoresis photo of PCR.
Arrow points to the positive lane.
Figure 6 Positive control of EBER1 from a NPC specimen.
Clear and strong hybridization signals (yellow nuclear grains) were shown in nuclei of the tumor cells. DAB and hematoxylin counterstaining, × 200.
Figure 7 In situ hybridization with EBER1 (from an carcinomatous adenoma).
Positive signals were shown in nuclei of the tumor cells. DAB and hematoxylin counterstaining, × 200.
Figure 8 In situ hybridization with EBER1 (from a colorectal carcinoma).
Clear and strong hybridization signals were shown in nuclei of the tumor cells. DAB and hematoxylin counterstaining, × 400
Figure 9 In situ hybridization with EBER1 (from a colorectal carcinoma, too).
Interspersed positive signals were shown in neoplasm cells. DAB and hematoxylin counterstaining, × 400.
- Citation: Liu HX, Ding YQ, Li X, Yao KT. Investigation of Epstein-barr virus in Chinese colorectal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9(11): 2464-2468
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v9/i11/2464.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v9.i11.2464