Copyright
©The Author(s) 2002.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2002; 8(5): 797-803
Published online Oct 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.797
Published online Oct 15, 2002. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.797
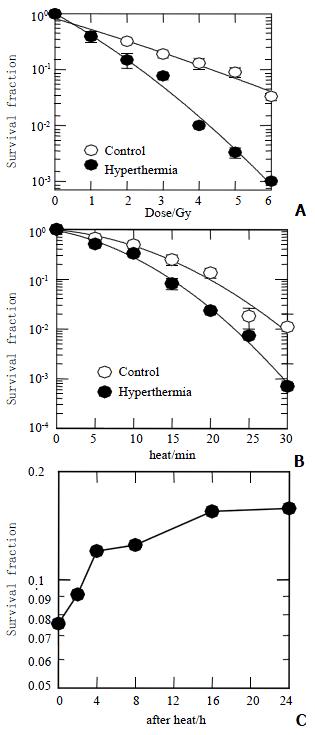
Figure 1 Survival fraction of HepG2.
A: Exposure to X-rays combined with (close circles) or without (open circles) 45.5 °C for 15 min; B: Heat-induced clonogenic cell death as a function of time combined with (close circles) or without (open circles) 3 Gy of X-rays; C: Irradiated with 3 Gy of X-rays at different hours after heat of 15 min at 45.5 °C.
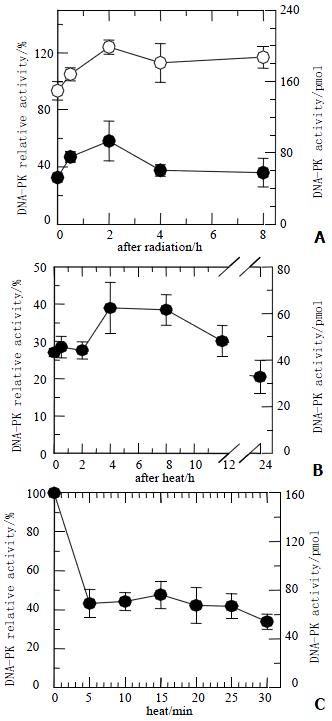
Figure 2 DNA-PKcs activity of HepG2 cells.
A: Cells were heated at 45.5 °C for 20 min and then received 40 Gy of X-rays (closed circles) or irradiated with 40 Gy of X-rays only (open circles). At various periods, DNA-PKcs activity in heated cells was inhibited, and kept at low level about 30%. The DNA-PKcs activity in both groups showed slight increase; B: After heated at 45.5 °C for 20 min, DNA-PKcs activity was still inhibited at various periods; C: DNA-PKcs activity was inhibited after exposure to heat at 45.5 °C for 5 min, even though the heat time was prolonged, DNA-PKcs activity levels still remained unchanged.
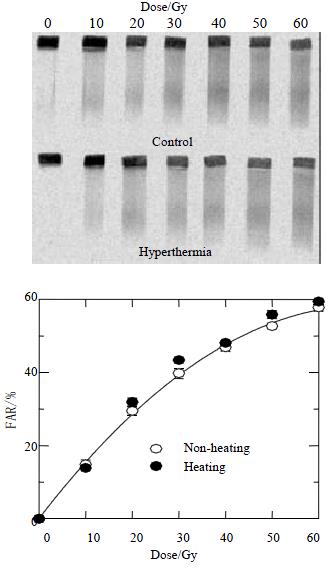
Figure 3 Dose response curves for HepG2 cells received radiation combined with or without hyperthermia.
The upper panel shows a typical gel scanned with 14C-TdR, while the lower panel shows quantitative data as described in the Methods. The FAR increases almost linearly with dose up to 30 Gy but bends downward at higher doses. Similar increases in FAR as a function of dose are observed in radiation alone or combined with hyperthermia, suggesting similar yields of DNA DSBs.
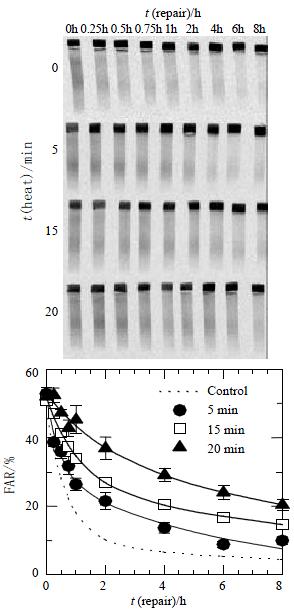
Figure 4 DNA DSBs repair kinetics in HepG2 cells.
Cells were irradiated with 40 Gy and prepared for AFIGE after various periods of incubation at 37 °C to allow for repair. The upper panel in the Figure shows a typical AFIGE gel, while the lower panel shows its quantification as described in the materials and Methods. The rejoining of DNA DSBs was decreasing with the increase of the lengths of hyperthermic time at 45.5 °C.
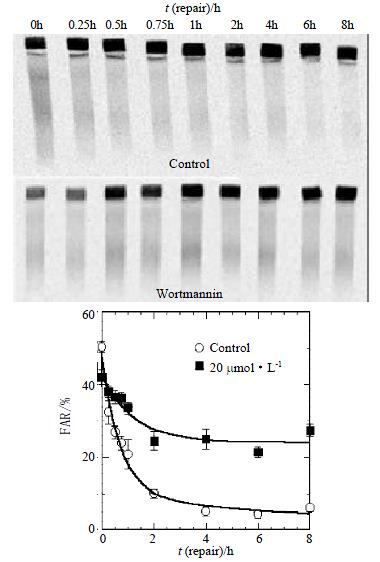
Figure 5 The kinetics of DNA DSBs rejoining after treatment with Wortmannin.
The slow rejoining component is strikingly high. The deficiency of DNA DSBs rejoining was found in Wortmannin treatment cells after 2 h.
- Citation: Zeng ZC, Jiang GL, Wang GM, Tang ZY, Curran WJ, Iliakis G. DNA-PKcs subunits in radiosensitization by hyperthermia on hepatocellular carcinoma hepG2 cell line. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8(5): 797-803
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v8/i5/797.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v8.i5.797