Copyright
©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2001; 7(3): 435-439
Published online Jun 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.435
Published online Jun 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.435
Figure 1 (A) AI at different time intervals after radiation of various doses of X-rays and (B) fast-neutron-rays.
AI of cells induced by X-rays and fast-neutron-rays of various doses gradually increased with the increase of dose and time. (C) Comparison of AI between X-rays and N-rays. At the same point of time, AI of cells induced by fast-neutron-rays was higher than that induced by X-rays.
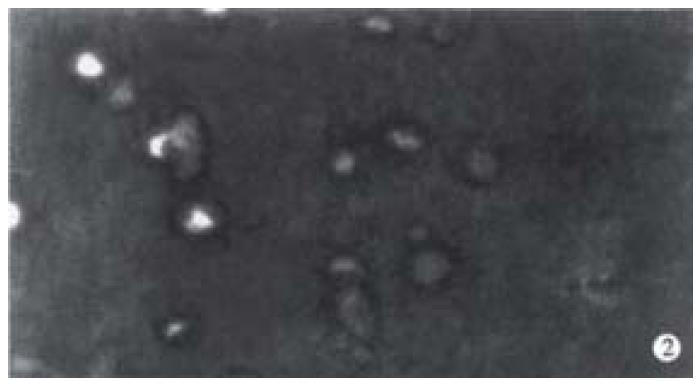
Figure 2 Hoechest 33342 fluorescence staining of cells radiated by fast-neutron-rays shows the special morphological features of apoptotic cells: cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, lunated margination.
Figure 3 Effect of X-rays on DNA fragmentation in HR 8348 cells.
Cells were incubated for 6 h after radiation by X-rays. DNA fragmentation was examined by agrose gel analysis, as described in Materials and methods. A, 885 bp and 585 bp DNA marker; B, Control; C, 2 Gy; D, 8 Gy; E, 10 Gy.
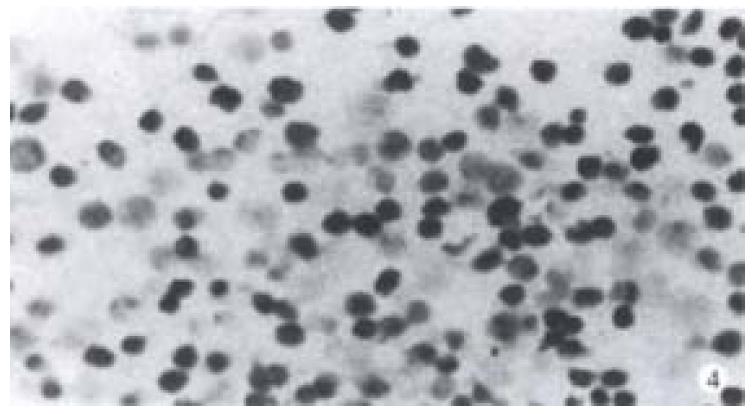
Figure 4 Positive nuclear staining of cells irradiated by 8 Gy X-rays with TUNEL was observed.
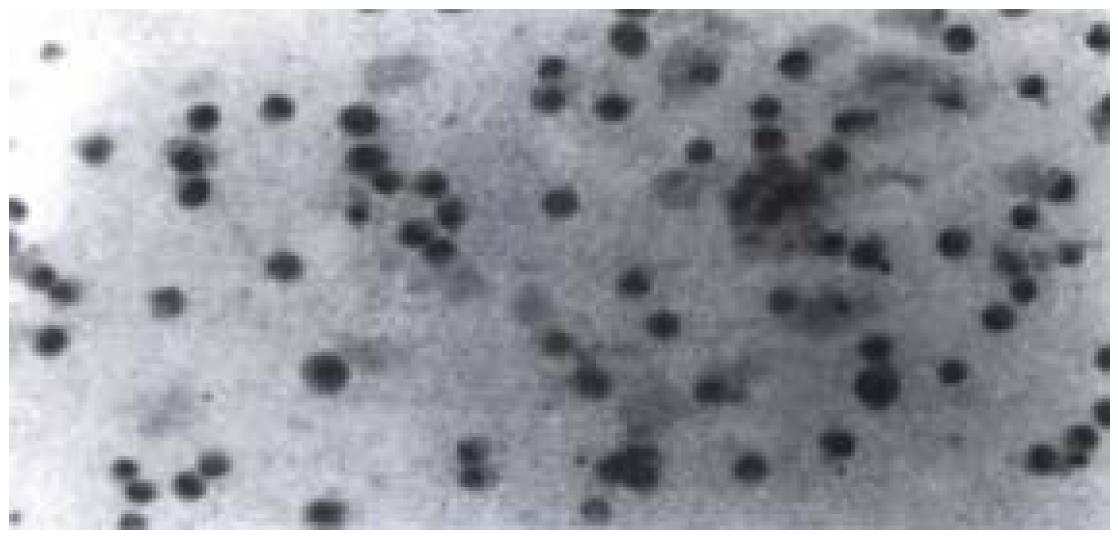
Figure 5 p53 positive nuclear staining of cells irradiated by 8 Gy X-rays with immunohistochemistry staining was seen.
Nuclei of cells appeared in light yellow.
- Citation: Wang LP, Liang K, Shen Y, Yin WB, Hans G, Zeng YJ. Neutron-induced apoptosis of HR8348 cells in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(3): 435-439
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i3/435.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.435