Copyright
©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 15, 2001; 7(3): 389-393
Published online Jun 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.389
Published online Jun 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.389
Figure 1 Analysis of the PCR product of H.
pylori ureB gene by 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis. 1: 200 bp DNA ladder marker; 2: PCR product of ureB gene
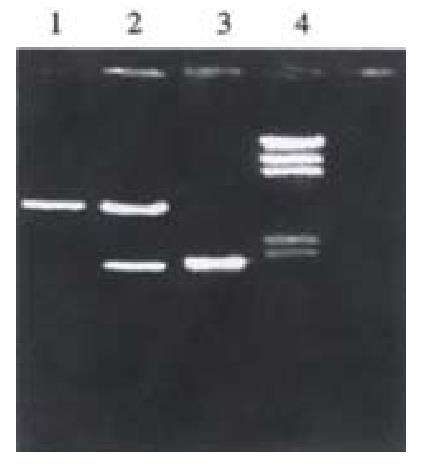
Figure 2 Identification of recombinant plasmids pPin-UreB digested with Hind III and EcoR V.
1: PCR product of ureB gene; 2: pPin-UreB plasmid digested by Hind III and EcoR V; 3: PinPointTM Xa-3 plasmid digested with Hind III and EcoR V; 4: λDNA/Hind III marker.
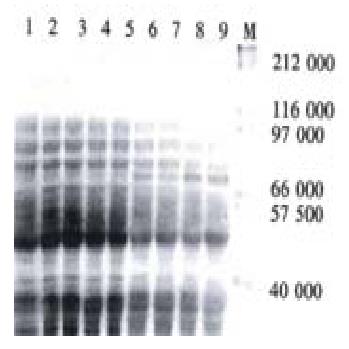
Figure 3 Analysis of expression product of recombinant plasmid pPin-UreB in E.
coli JM109 by 10% SDS-PAGE. 1, 2, 3: E. coli JM109; 4: E. coli JM109/PinPointTM Xa-3 before induction; 5: E. coli JM109/PinPointTM Xa-3 after induction with IPTG; 6, 7: E. coli JM109/pPin-UreB before induction; 8, 9; E. coli JM109/pPin-UreB after induction with IPTG; M: Molecular weight marker (212, 116, 97, 66.2, 57.5, 40) × 103.
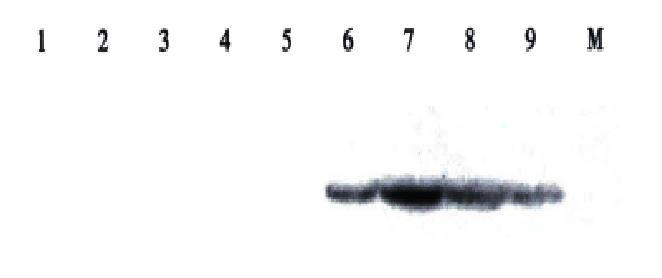
Figure 4 Analysis of recombinant fusion protein by Western-blotting.
1, 2, 3: E. coli JM109; 4: E. coli JM109/PinPointTM Xa-3 before induction; 5: E. coli JM109/PinPointTM Xa-3 after induction with IPTG; 6, 7: E. coli JM109/pPin-UreB before induction; 8, 9; E. coli JM109/pPin-UreB after induction with IPTG; M: Protein molecular weight marker (212, 116, 97, 66.2, 57.5, 40) × 103.
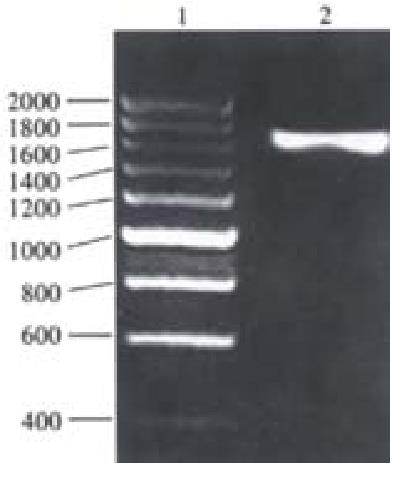
Figure 5 Determination of the purified rUreB by 10% SDS-PAGE.
1: Protein molecular weight marker; 2: The purified rUreB
- Citation: Wu C, Zou QM, Guo H, Yuan XP, Zhang WJ, Lu DS, Mao XH. Expression, purification and immuno-characteristics of recombination UreB protein of H. pylori. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(3): 389-393
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i3/389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.389