Copyright
©The Author(s) 2000.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 2000; 6(5): 626-629
Published online Oct 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i5.626
Published online Oct 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i5.626
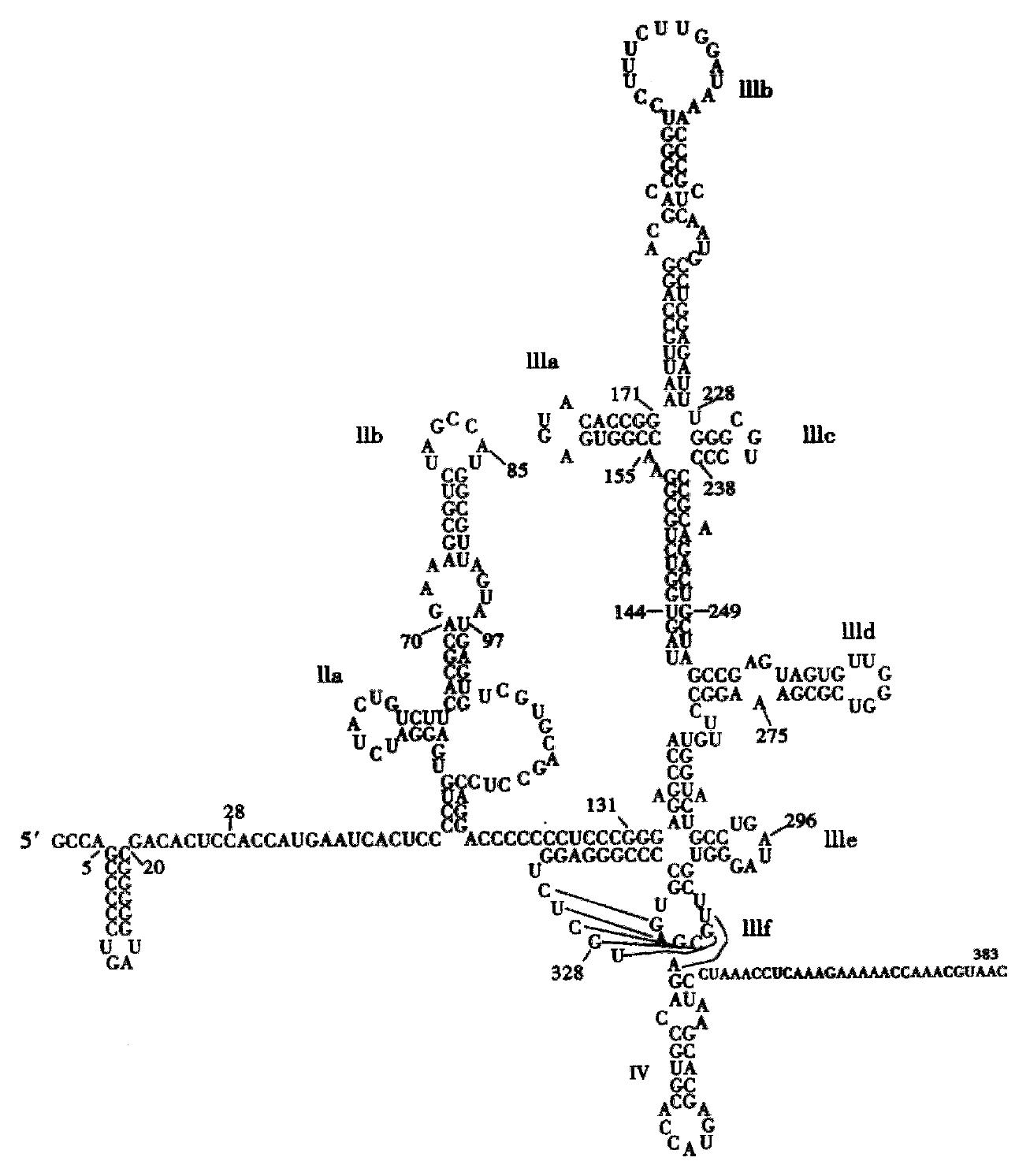
Figure 1 HCV 5’-non-coding region.
The pseudonot region and stem loop IV including the start AUG are indicated in bold font as optimum target sequences for ODN binding.
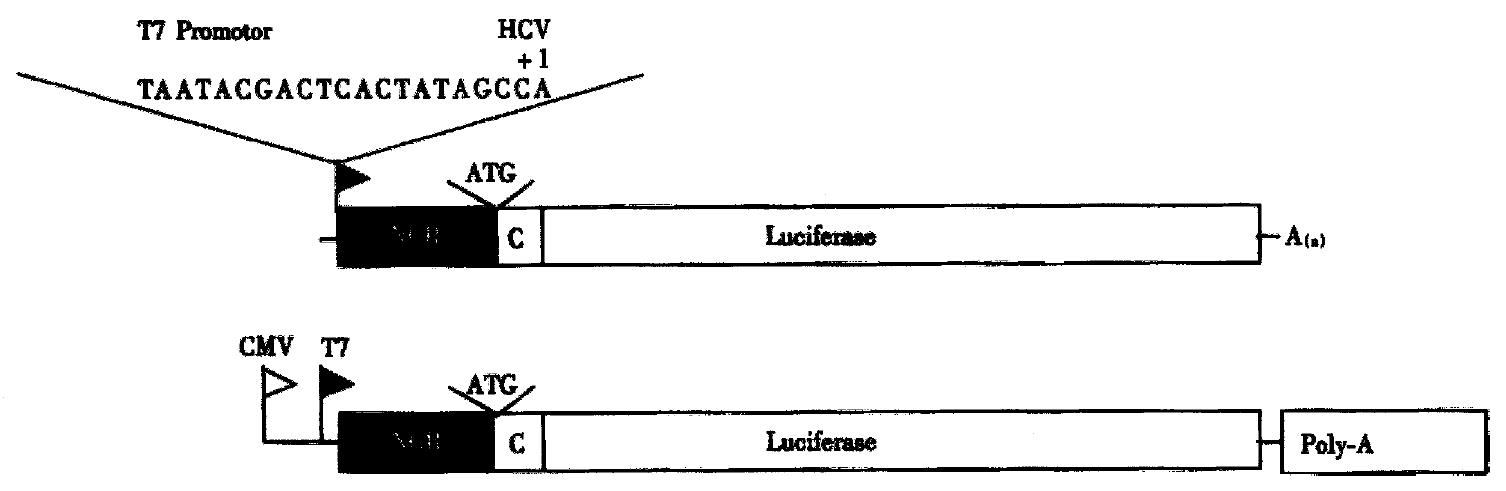
Figure 2 Plasmid constructs to analyze inhibition of HCV translation in vitro (upper) and in vivo (lower).
Expression is directed either by the T7-promoter or the CMV immediate early promoter.
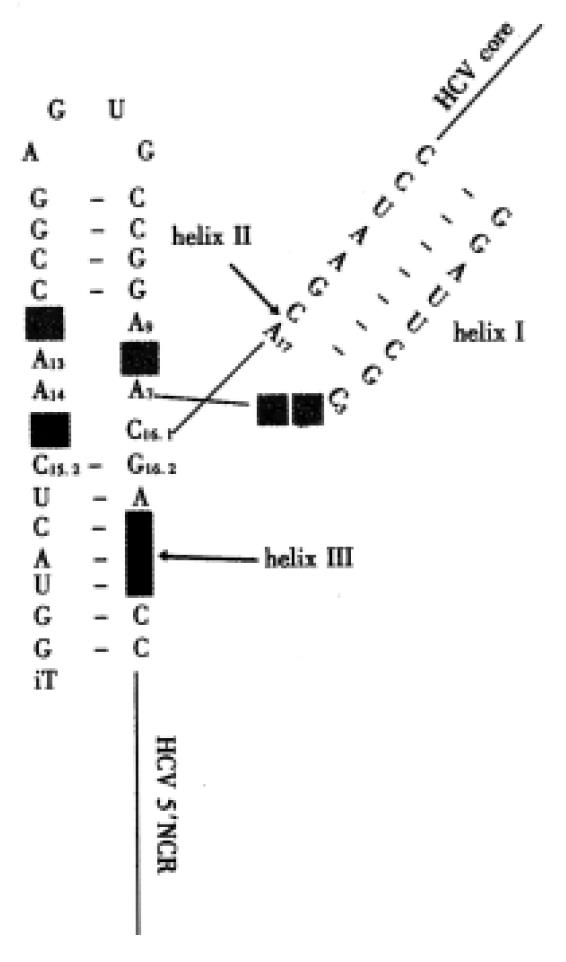
Figure 3 Modified hammerhead RZ and HCV target sequence.
The G16.2,C16.1, A17 recognition site (nts. 346-348), in which cleavage occurs, is marked by an arrow. All nucleotides are 2’-O-ally l-ribonucleotides except G5, A6, G8 and G12 (light gray), which are unmodified ribonucleotides. The position of the A to l exchange (medium gray) and the start AUG of the HCV template are indicated.
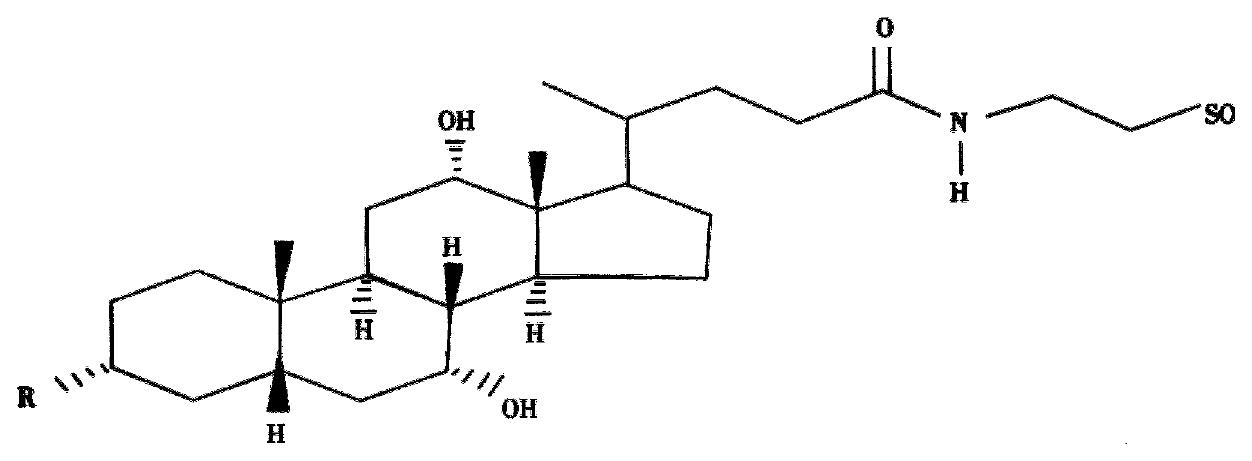
Figure 4 Schematic representation of a taurocholic acid-coupled antisense oligodeoxynucleotide.
R: oligodeoxynucleotide 5’-end.
- Citation: Caselmann WH, Serwe M, Lehmann T, Ludwig J, Sproat BS, Engels JW. Design, delivery and efficacy testing of therapeutic nucleic acids used to inhibit hepatitis C virus gene expression in vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol 2000; 6(5): 626-629
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v6/i5/626.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v6.i5.626