Copyright
©The Author(s) 1998.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 15, 1998; 4(5): 397-403
Published online Oct 15, 1998. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v4.i5.397
Published online Oct 15, 1998. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v4.i5.397
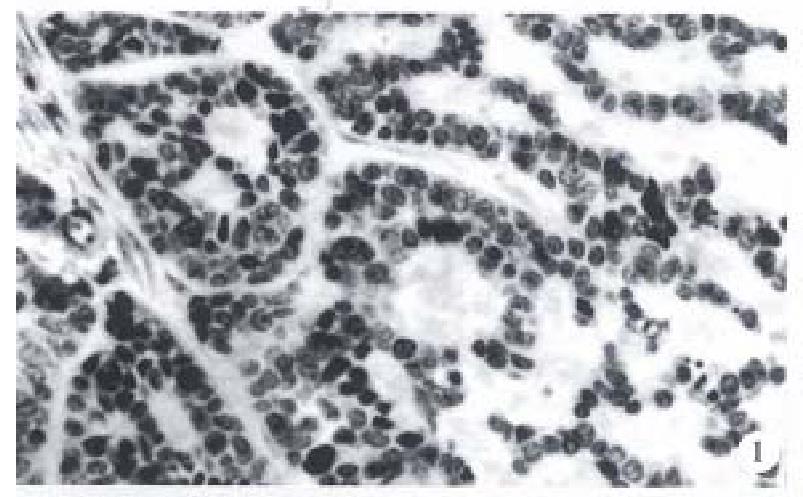
Figure 1 The basaloid cells arranged in the form of anastomosing trabeculae and microcystic structures.
H&E, × 200
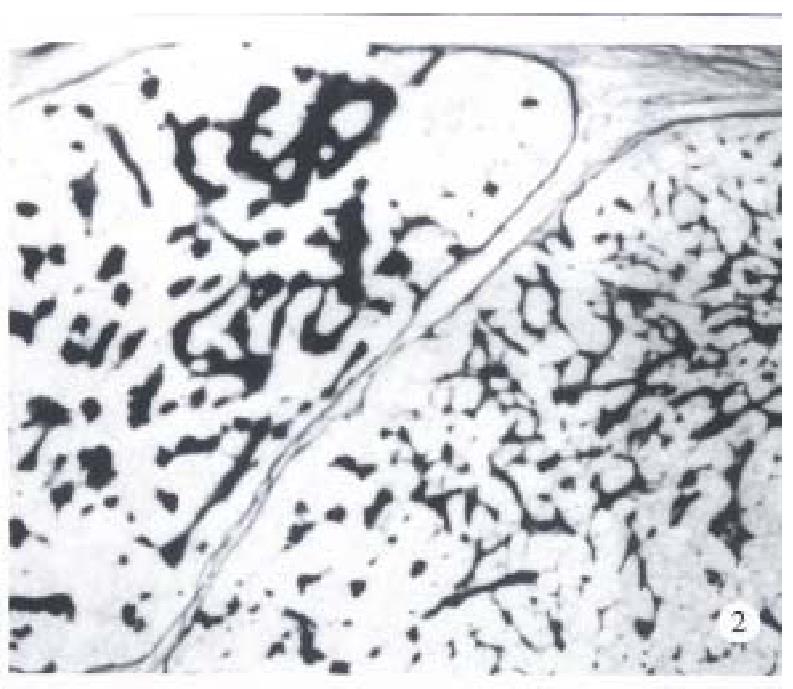
Figure 2 The intertrabecular and microcystic spaces filled with eosinophilic hyaline material which were PAS positive.
× 100
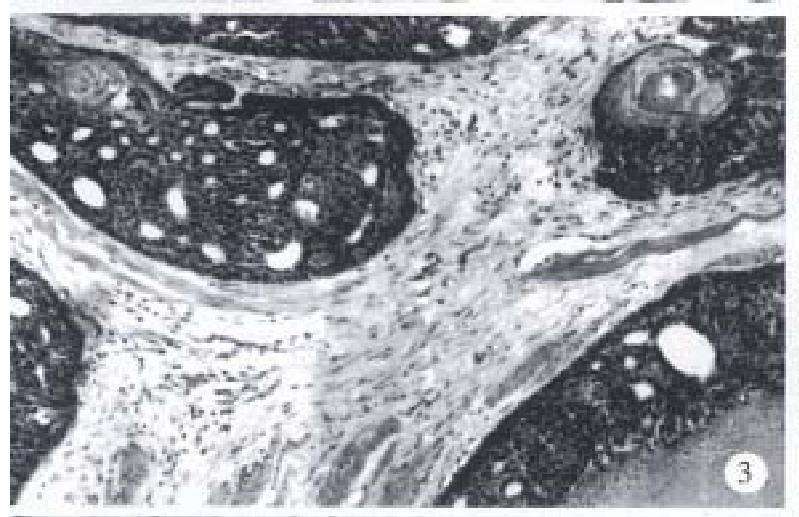
Figure 3 Focal squamous differentiation and keratinization and comedo necrosis were found in the basaloid lobules.
H&E, × 100
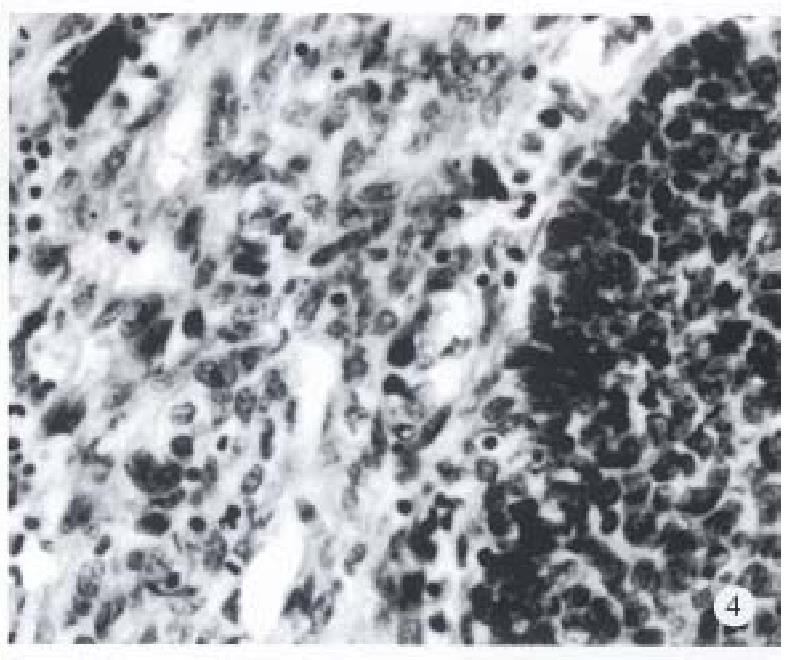
Figure 4 Basaloid cell carcinoma with spindle cell component.
H&E, × 200
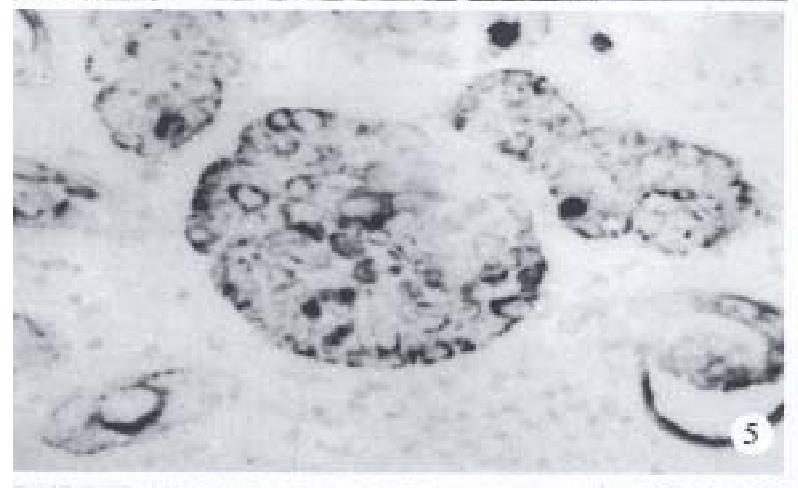
Figure 5 Immunohistochemical studies (S-P method) show positivity in the basaloid components for cytokeratin (Pan).
× 200
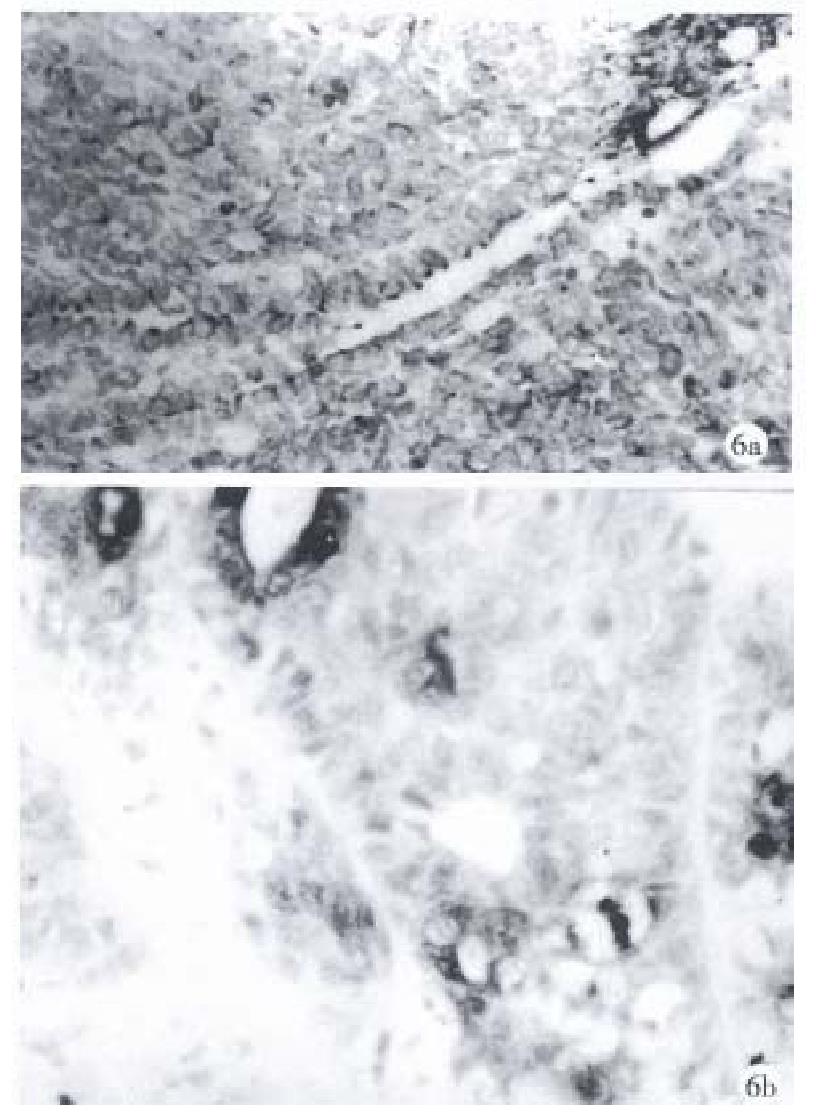
Figure 6 The basaloid components in case 15 are diffusely and strongly positive staining for (a) vimentin and (b) S-100 protein.
× 200
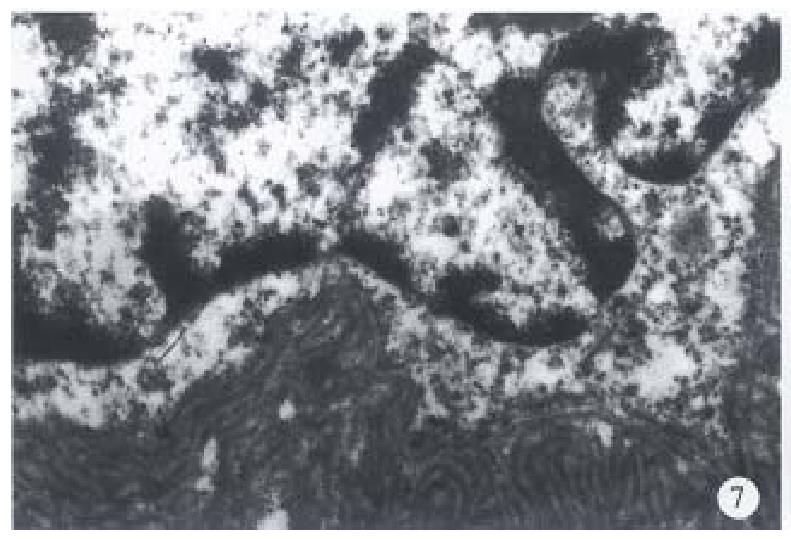
Figure 7 Electron microscopic photograph of esophage al BSC demontrating replicated basal lamina in fingerprint-like pattern filled in the intertrabecular and intercellular spaces.
× 20000
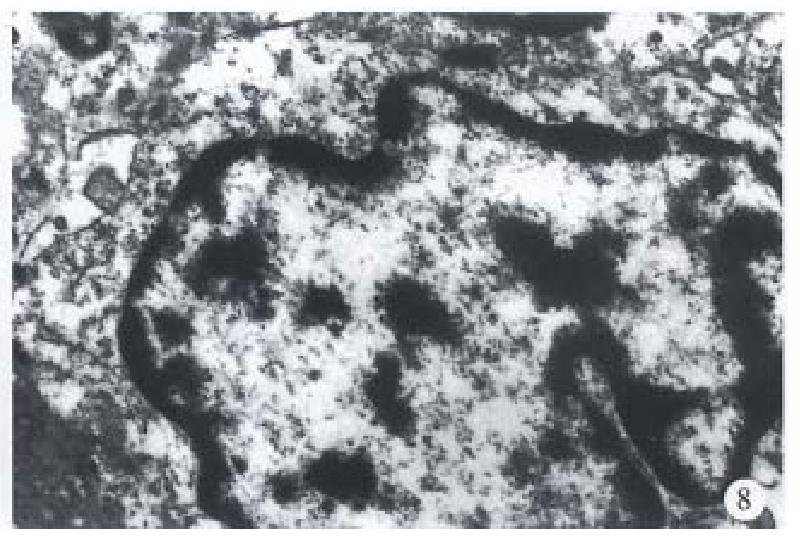
Figure 8 Electron microscopicphotograph of esophageal BSC demonstrating well-formed intercellular desmosomes.
× 16000
- Citation: Zhang XH, Sun GQ, Zhou XJ, Guo HF, Zhang TH. Basaloid squamous carcinoma of esophagus: a clinicopathological, immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study of sixteen cases. World J Gastroenterol 1998; 4(5): 397-403
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v4/i5/397.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v4.i5.397