Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2025; 31(7): 98448
Published online Feb 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.98448
Published online Feb 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.98448
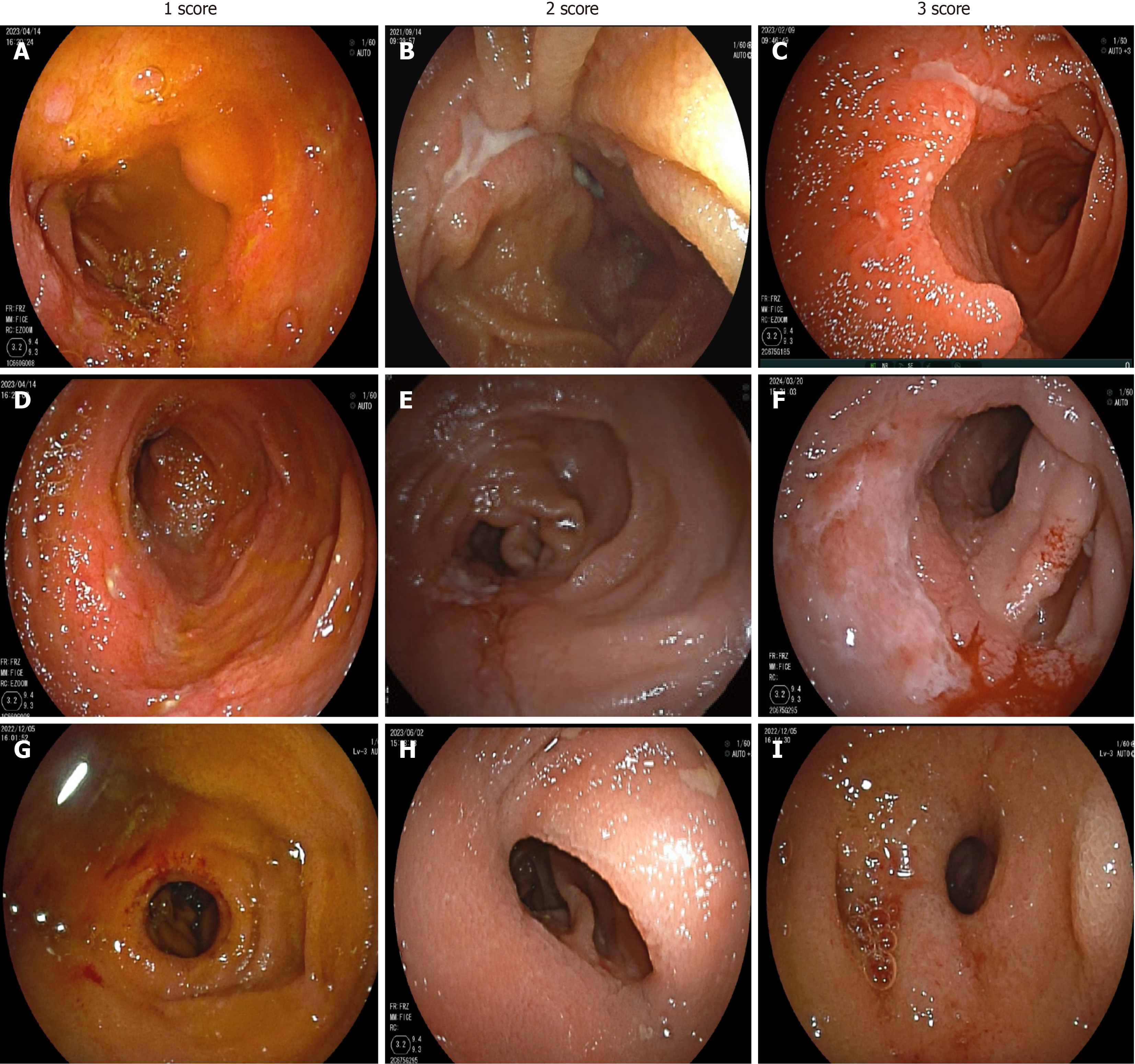
Figure 1 Representative of balloon-assisted enteroscopy images with modified Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s disease scores of 1, 2, or 3.
A: Small ulcers; B: Large ulcer; C: Very large ulcer; D: Ulcerated surface < 10%; E: Ulcerated surface 10%-30%; F: Ulcerated surface > 30%; G: Single stenosis which can be passed; H: Multiple stenosis which can be passed; I: Stenosis which could not be passed.
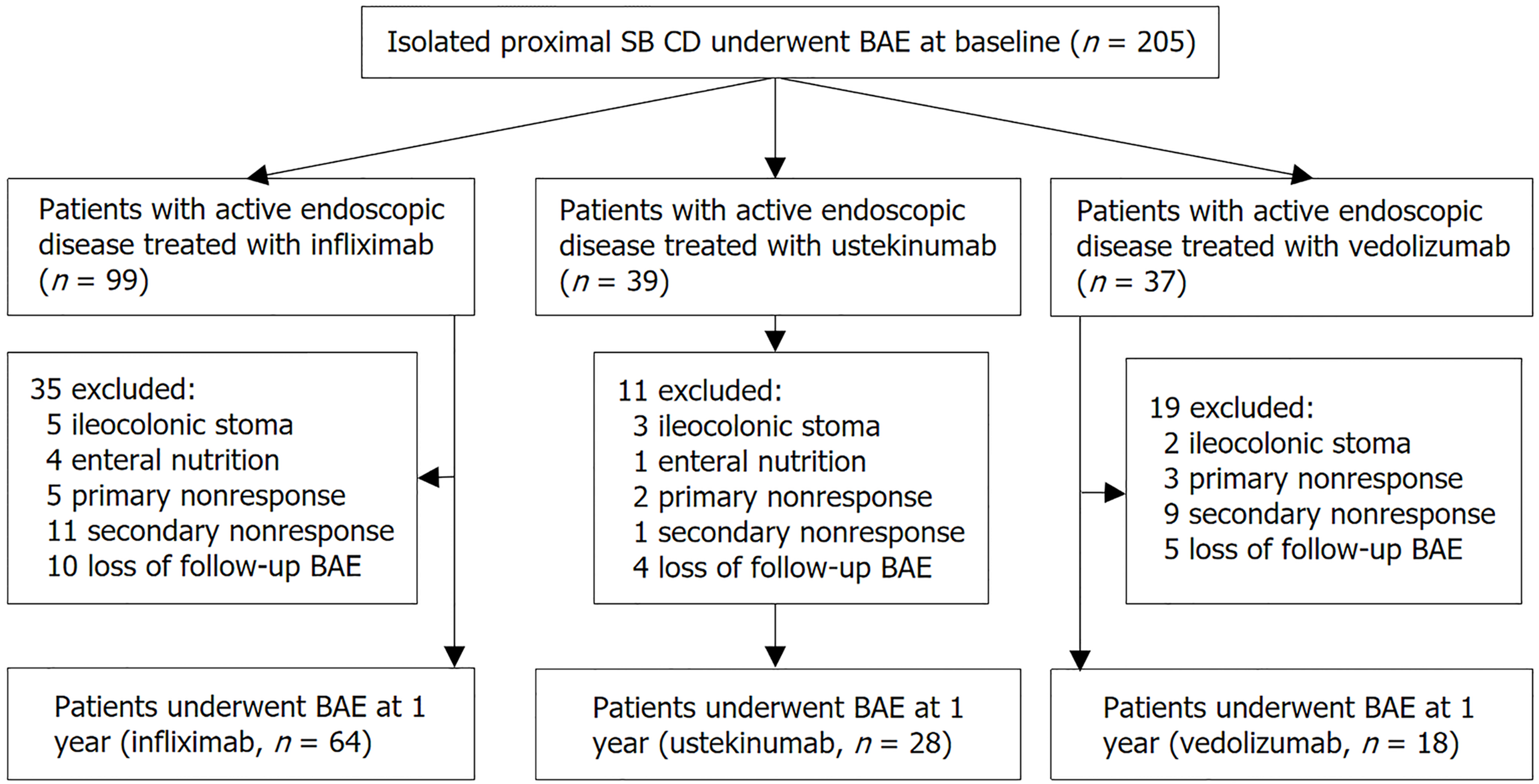
Figure 2 The flow of enrolled patients in this study.
Active endoscopic disease was defined as having a modified simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease ≥ 3, accompanied by any size ulcer. BAE: Balloon-assisted enteroscopy; SB: Small bowel; CD: Crohn’s disease; SES-CD: Simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease.
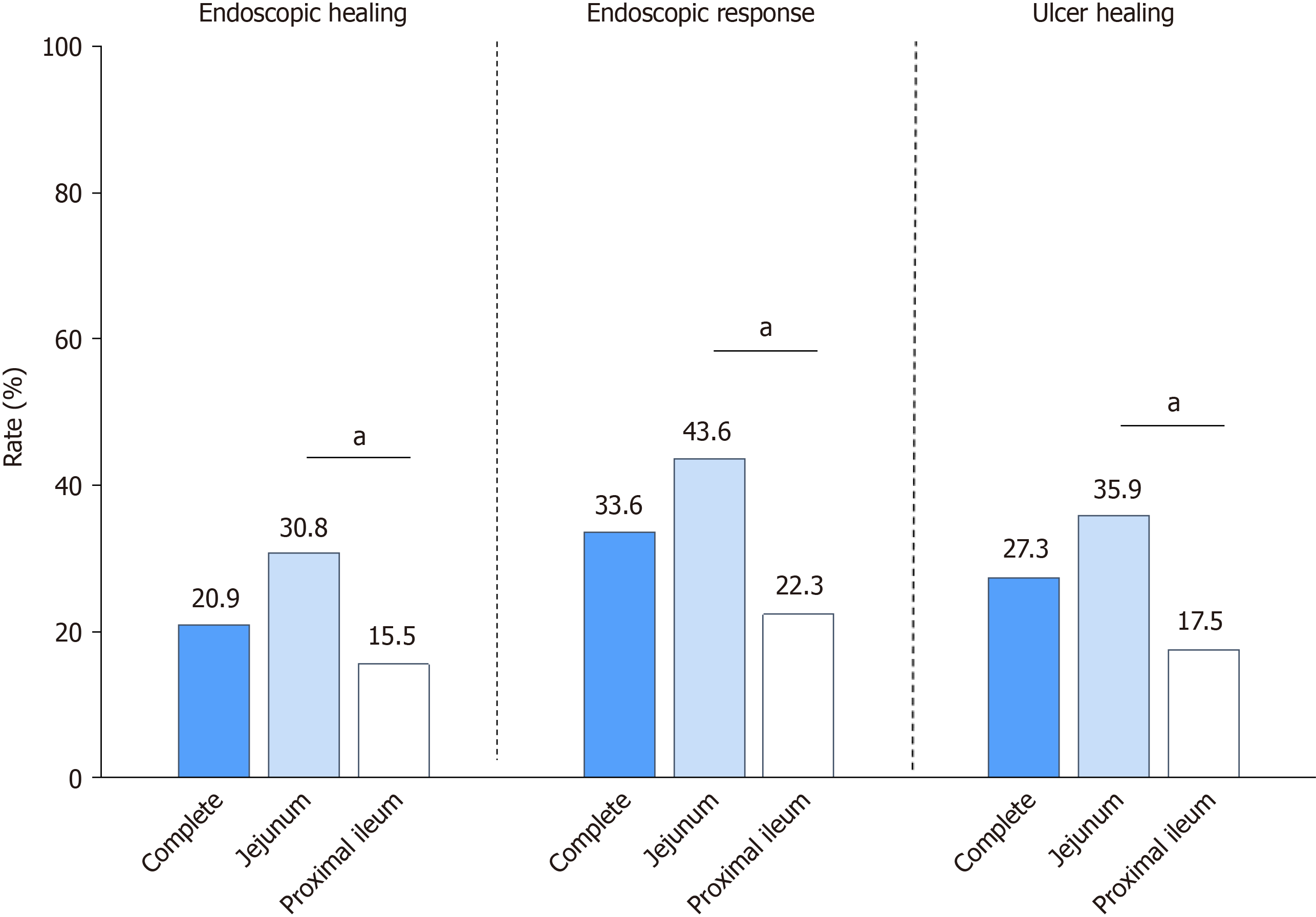
Figure 3 The rates of endoscopic healing, endoscopic response, and ulcer healing in patients with isolated proximal small bowel Crohn’s disease after 1 year of biologic therapy.
aP < 0.05.
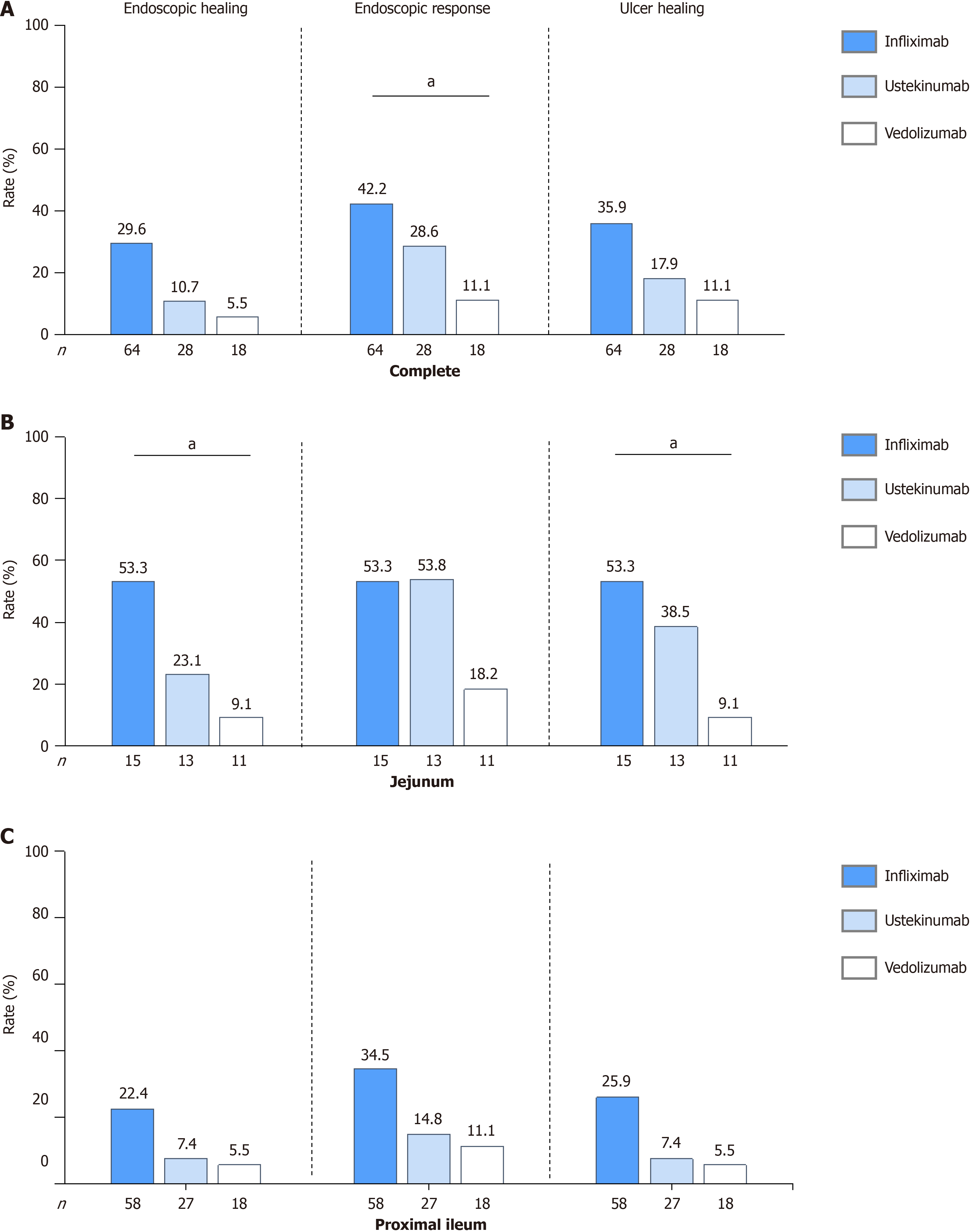
Figure 4 The ability of infliximab, ustekinumab, and vedolizumab to achieve endoscopic outcomes in patients with isolated proximal small bowel Crohn’s disease after 1 year of therapy.
A: Complete; B: Jejunum; C: Proximal ileum. aP < 0.05.
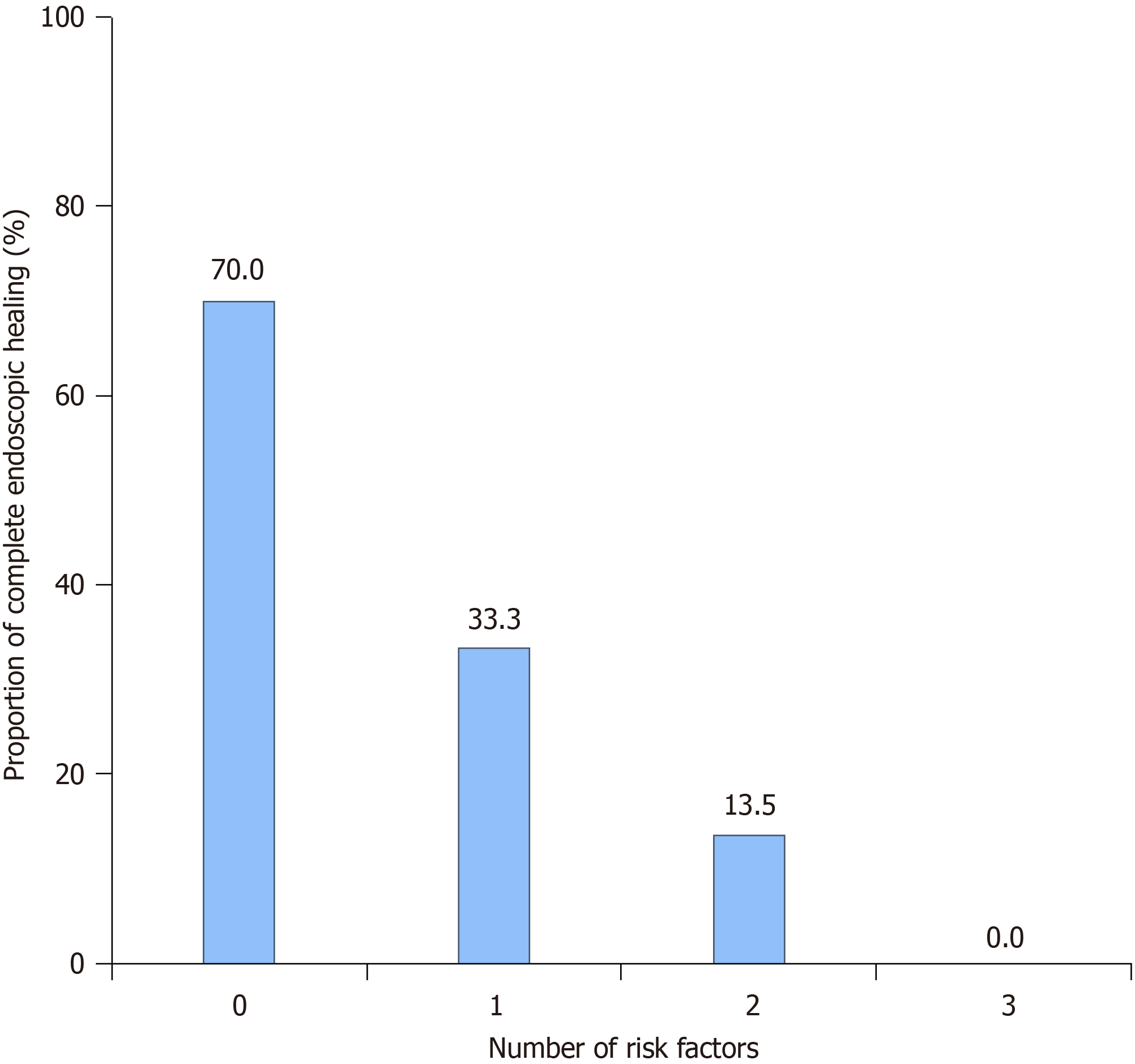
Figure 5 The likelihood of achieving complete endoscopic healing is stratified by the number of risk factors.
Stricturing or penetrating behavior, prior exposure to biologics, and moderate-to-severe endoscopic disease were identified as risk factors for achieving complete endoscopic healing.
- Citation: Huang ZC, Wang BY, Peng B, Liu ZC, Lin HX, Yang QF, Tang J, Chao K, Li M, Gao X, Guo Q. Effectiveness of biologics for endoscopic healing in patients with isolated proximal small bowel Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(7): 98448
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i7/98448.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.98448