Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2025; 31(7): 102632
Published online Feb 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.102632
Published online Feb 21, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.102632
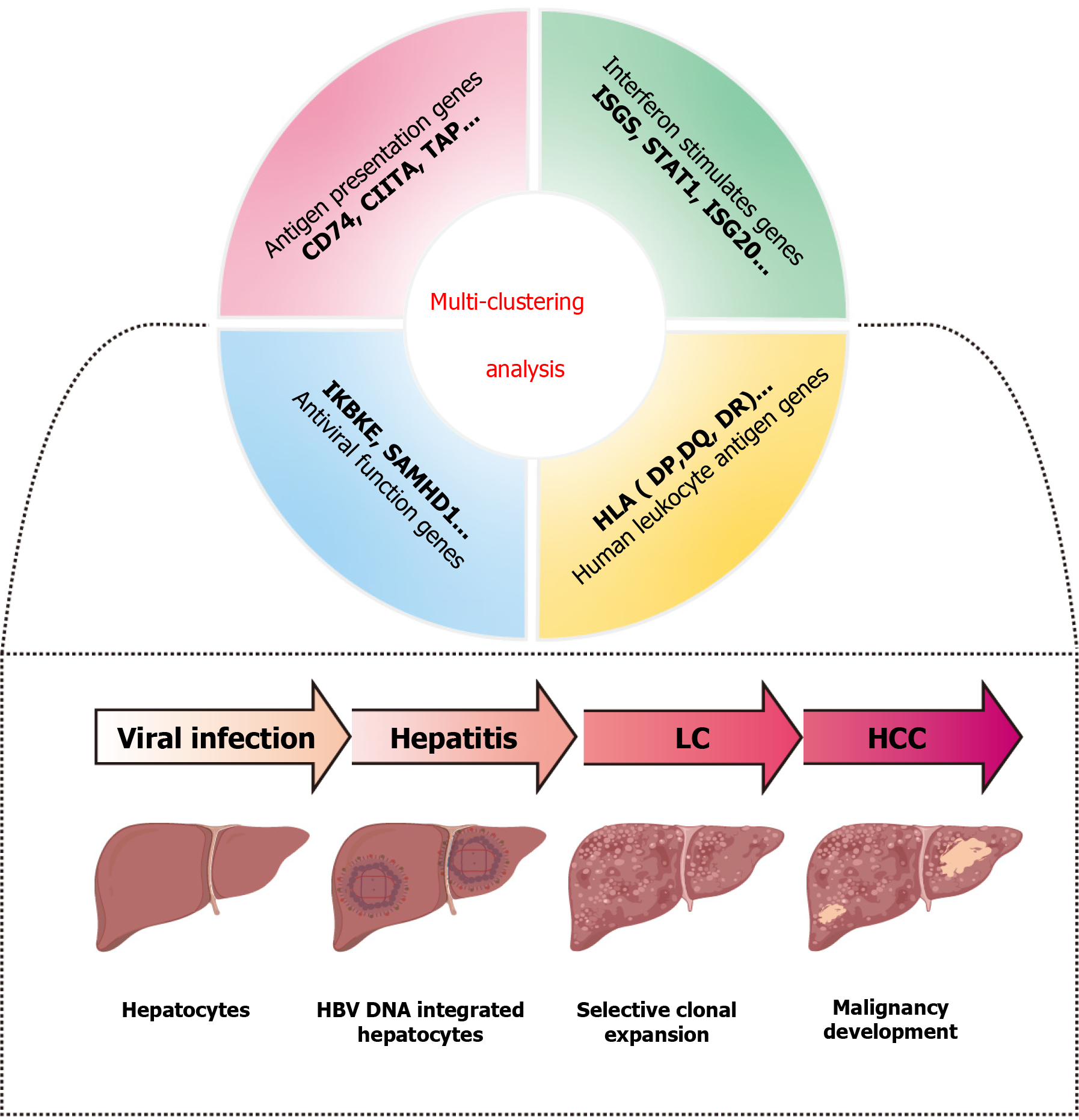
Figure 1 Machine learning revealed the complex relationship between different genotypes and hepatitis B virus liver diseases.
CD74: Leukocyte differentiation antigen 74; CIITA: Class II transactivator; TAP: Transporters associated with antigen processing; ISGS: Interferon-stimulated genes; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; ISG20: Interferon-stimulated gene 20; IKBKE: Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon; SAMHD1: Sterile alpha motif and HD domain-containing protein 1; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Li S, Xi Y, Dong XY, Yuan WB, Tang JF, Zhou CF. Evaluating the scope of human leukocyte antigen polymorphisms influencing hepatitis B virus-related liver cancer and cirrhosis through multi-clustering analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(7): 102632
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i7/102632.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i7.102632