Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2025; 31(12): 99846
Published online Mar 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i12.99846
Published online Mar 28, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i12.99846
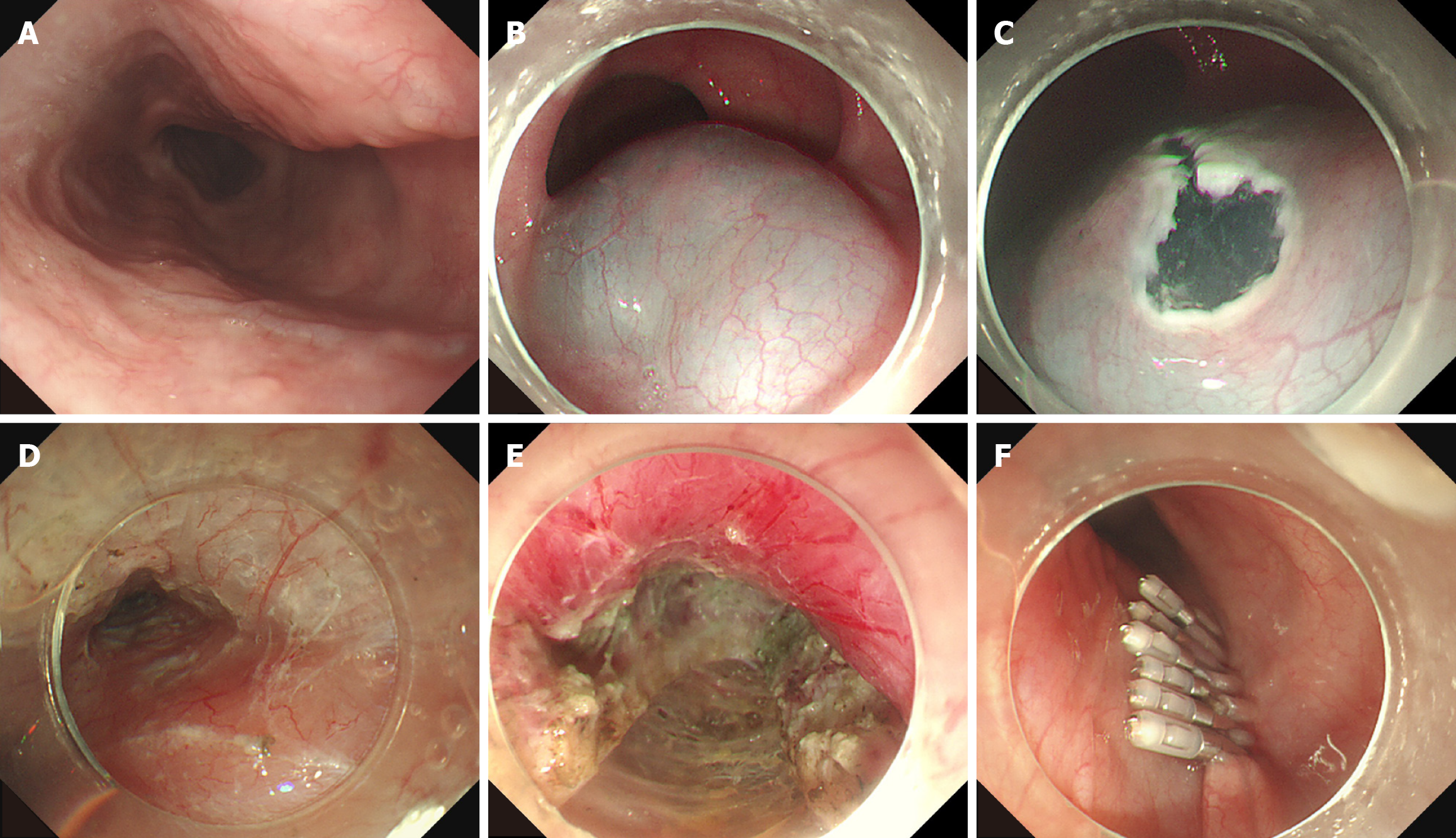
Figure 1 The procedure of peroral endoscopic myotomy.
A: Preoperative screening for the morphological characteristics of the esophagus was performed by endoscopy; B: A sufficient submucosal injection was performed to separate the mucosal layer and submucosal layer; C: An entry incision, inverse T-shaped incision, was established; D: The submucosal tunnel was established; E: Progressive myotomy was completed; F: The tunnel opening was closed with metallic clips.
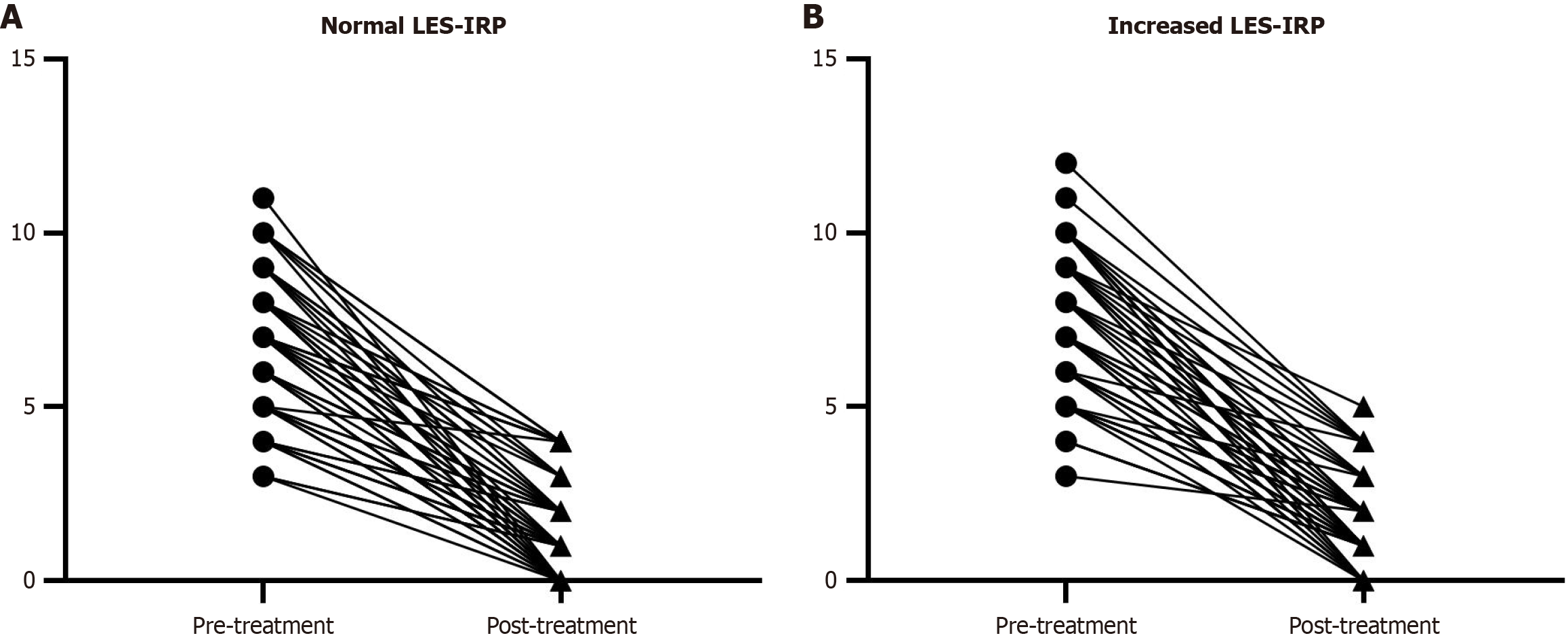
Figure 2 The Eckardt scores of the two groups before and after peroral endoscopic myotomy.
A: Eckardt scores of the normal lower esophageal sphincter integrated relaxation pressure (LES-IRP) group before and after peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM); B: Eckardt scores of the increased LES-IRP group before and after POEM. LES-IRP: Lower esophageal sphincter integrated relaxation pressure.
- Citation: Li X, Zhang XB, Shao JK, Zhang B, Li LS, Zhu RQ, Zou JL, Wang JF, Zhao X, Wu QZ, Chai NL, Linghu EQ. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia and patients with normal lower-esophageal-sphincter integrated relaxation pressure: A propensity-score-matched retrospective study. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(12): 99846
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i12/99846.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i12.99846