Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2025; 31(1): 99960
Published online Jan 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.99960
Published online Jan 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.99960
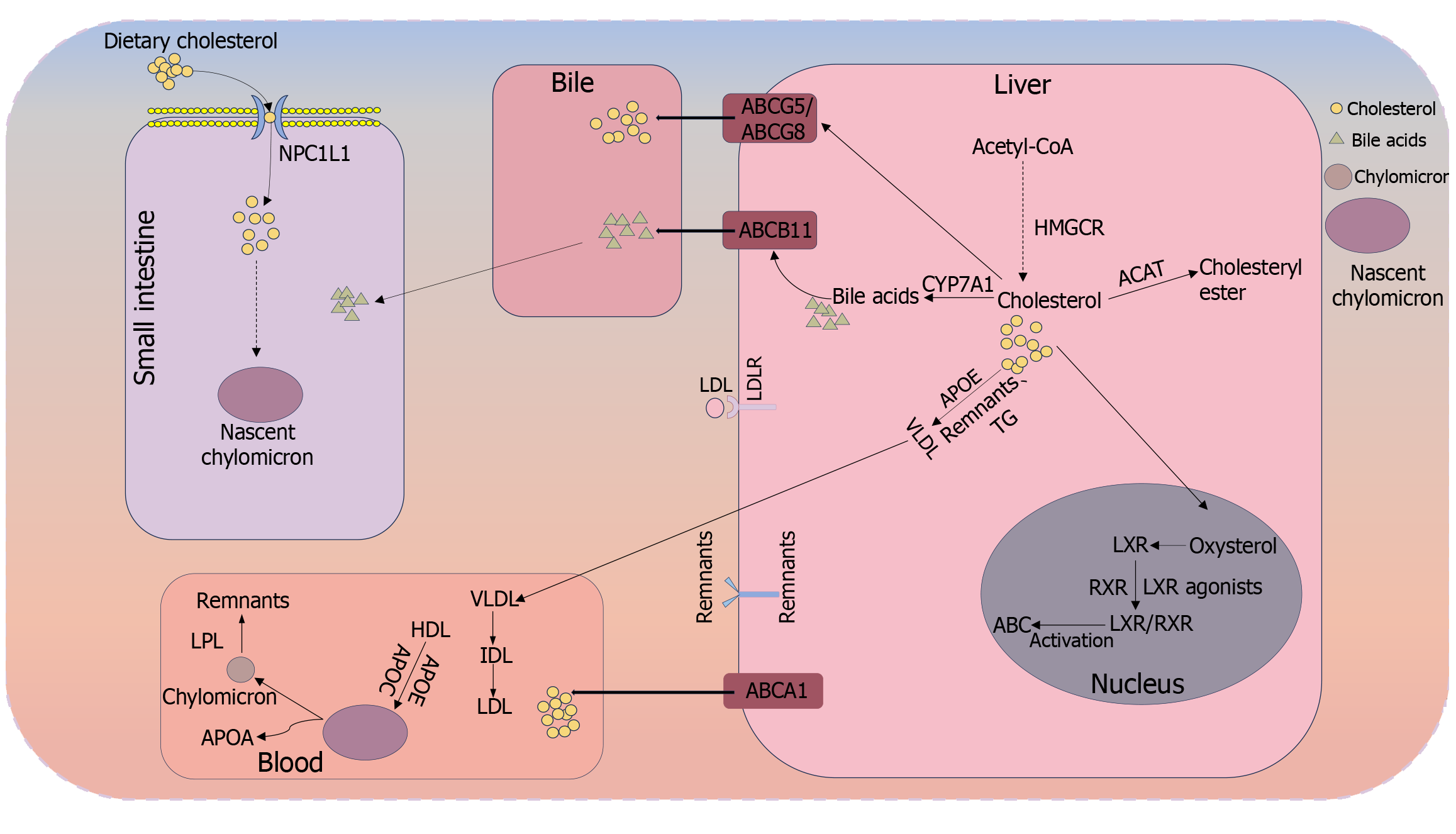
Figure 1 Cholesterol metabolic pathway.
Cholesterol is synthesized directly in the liver or taken up by the epithelial cells of the small intestine. Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 (NPC1 L1) in the small intestine absorbs dietary cholesterol into cells through endocytosis, which is transformed into nascent chylomicrons and then enters the blood. Under the action of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), nascent chylomicrons are transformed into chylomicrons, and then the chylomicrons decompose most of the triglycerides under the action of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), and the rest of the chylomicron remnants are used in the liver. The cholesterol directly produced in the liver is converted into bile acid by CYP7A1 and transported into the bile duct under the action of ABCB11. Some of the cholesterol is formed into cholesterol ester under the action of ACAT. Some of the excess cholesterol enters the bile duct through transport by ABCG5/ABCG8, and some enters the blood through transport by ABCA1. CoA: Coenzyme A; LXR: Liver X receptor.
- Citation: Zheng L, Ye ZY, Ma JJ. Effect of cholesterol metabolism on hepatolithiasis. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(1): 99960
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i1/99960.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.99960