Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2025; 31(1): 100750
Published online Jan 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.100750
Published online Jan 7, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.100750
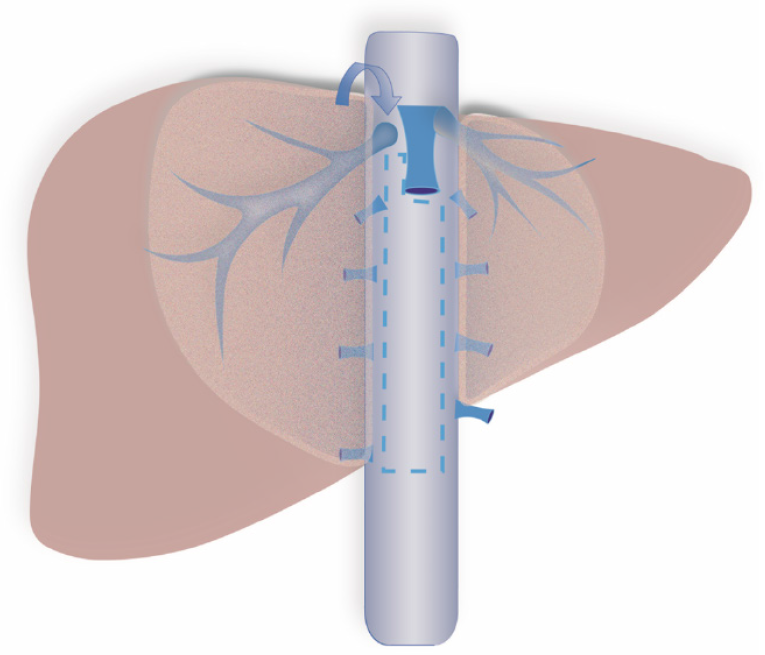
Figure 1
Schematic of the avascular area of the retrohepatic tunnel.
Figure 2 The surgical procedure of conventional laparoscopic segment VII resection.
A: Dissecting the ligaments surrounding the liver; B and C: Dissecting short hepatic veins of the third hepatic hilum; D and E: Unexpected intraoperative hemorrhaging of short hepatic veins; F and G: Transection of the liver parenchyma to improve surgical vision; H: Disclosing the bleeding point; I-L: Hemostatic process during surgery. IVC: Inferior vena cava; SHV: Short hepatic veins.
Figure 3 Computed tomography image of the liver tumor and the surgical procedure for S7 and S8.
A: Computed tomography image of the liver tumor located S7 and S8 (arrow); B: Schematic of the surgical procedure; C: The hepatic pedicle of S8 dorsal is located on the dorsal side and left of the right anterior hepatic pedicle; D: Clamping the S8 dorsal branches and the S7 pedicles; E: Marking the dorsal and ventral boundaries of segment 8 and the boundaries of segments 6 and 7; F: Transecting the parenchyma along the stain or ischemic demarcation line; G: Transecting the G7 and dorsal side of G8; H and I: Transecting liver parenchyma along the ventral avascular area of the inferior vena cava; J and K: Addressing the short hepatic vein, right hepatic vein and Makuuchi ligament. RHV: Right hepatic vein; AFV: Anterior fissure vein; IVC: Inferior vena cava; G8d: G8 dorsal.
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver tumor and the surgical procedure for S7.
A: Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver tumor located S7 (arrow); B: Schematic of the surgical procedure; C: Dissecting the G7 and then clamp it; D: Marking the surgical resection boundary; E: Transecting the liver parenchyma along the indocyanine green staining demarcation line and right hepatic vein; F: Transecting the G7; G: Transecting liver parenchyma along the ventral avascular area of the inferior vena cava; H-K: Addressing the short hepatic vein, Makuuchi ligament and right posterior inferior vein. RHV: Right hepatic vein; IVC: Inferior vena cava; SHV: Short hepatic veins.
Figure 5 Computed tomography and 3-dimensional reconstruction image of the liver tumor and the surgical procedure of laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy for tumors invading the right adrenal gland and inferior vena cava.
A and B: Computed tomography and 3-dimensional reconstruction images reveal that the tumor invaded the right adrenal gland and inferior vena cava (IVC, arrow); C: Blunt dissection for exposing the avascular area in the retrohepatic tunnel; D-F: Splitting the liver parenchyma along the surface of the IVC in a caudal to cranial direction to expose the root of the middle hepatic vein; G and H: Transection of the short hepatic veins of the third hepatic hilum; I: Transection of right hepatic vein; J: The excision of the tumor and the involved right adrenal gland and IVC and subsequent repair of the IVC; K: Transection of the Makuuchi ligament. AT: Anterior trunk; PP: Posterior pedicle; IVC: Inferior vena cava; MHV: Middle hepatic vein; SHV: Short hepatic vein; RHV: Right hepatic vein.
Figure 6 Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver tumor and the surgical procedure of laparoscopic posterior and anterodorsal segment resection.
A: Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver tumor located on the posterior and anterodorsal segments (arrow); B: Schematic of the surgical procedure, with labels 1, 2, and 3 representing the different surgical steps; C: Transection of posterior pedicle; D: Blunt dissection for exposing the avascular area in the retrohepatic tunnel; E and F: Splitting the liver parenchyma on the surface of the inferior vena cava; G: Manifesting anterior fissure vein; H-J: Exposing and transecting the root of the right hepatic vein; K-M: Transection of short hepatic veins of the third hepatic hilum; N: Transection of Makuuchi ligament. RHV: Right hepatic vein; AFV: Anterior fissure vein; IVC: Inferior vena cava; PP: Posterior pedicle; SHV: Short hepatic vein.
Figure 7 Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver tumor and the surgical procedure of laparoscopic segment VII/VI resection.
A: Magnetic resonance imaging of the liver tumor located at S6 and S7 (arrow); B: Schematic of the surgical procedure, with labels 1, 2 and 3 representing the different surgical steps; C: Blunt dissection for exposing the avascular area in the retrohepatic tunnel; D: Splitting S1 on the surface of the inferior vena cava; E: Transection of posterior pedicle after splitting S1; F-I: Splitting the liver parenchyma along the surface of the inferior vena cava in a caudal to cranial direction to expose the root of the right hepatic vein; J: Transection of V7; K: Transection of short hepatic veins of the third hepatic hilum; L: Transection of the Makuuchi ligament. RHV: Right hepatic vein; IVC: Inferior vena cava; PP: Posterior pedicle; AFV: Anterior fissure vein; SHV: Short hepatic vein.
Figure 8 Computed tomography image of the liver tumor and the surgical procedure of laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy.
A: Computed tomography image of the liver tumor located S4 (arrow); B: Schematic of the surgical procedure, with labels 1, 2, and 3 representing the different surgical steps; C: Blunt dissection for exposing the avascular area in the retrohepatic tunnel; D: Splitting S1 on the surface of the inferior vena cava; E-H: Splitting the liver parenchyma along the surface of the inferior vena cava in a caudal to cranial direction to expose the root of the middle hepatic vein; I and J: Transection of short hepatic veins of the third hepatic hilum; K: Transection of left hepatic vein. MHV: Middle hepatic vein; LHV: Left hepatic vein; IVC: Inferior vena cava; SHV: Short hepatic vein.
Figure 9 Computed tomography image of the liver tumor and the surgical procedure of laparoscopic right hemihepatectomy.
A: Computed tomography image of the liver tumor located on S5 and S8 (arrow); B: Schematic of the surgical procedure, with labels 1, 2, and 3 representing the different surgical steps; C: Blunt dissection with laparoscopic vessel forceps for exposing the avascular area in the retrohepatic tunnel; D-F: The liver parenchyma was split along the surface of the inferior vena cava using an ultrasonic scalpel in a caudal to cranial direction; G: Exposing the root of the middle hepatic vein; H and I: Transection of the short hepatic vein of the third hepatic hilum; J: Transection of ventral branch of S8 vein; K: Transection of right hepatic vein. RHV: Right hepatic vein; MHV: Middle hepatic vein; IVC: Inferior vena cava; V8v: Ventral branch of S8 vein.
- Citation: Huang K, Chen Z, Xiao H, Hu HY, Chen XY, Du CY, Lan X. Laparoscopic liver resection utilizing the ventral avascular area of the inferior vena cava: A retrospective cohort study. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(1): 100750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i1/100750.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.100750