Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2024; 30(7): 652-662
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.652
Published online Feb 21, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.652
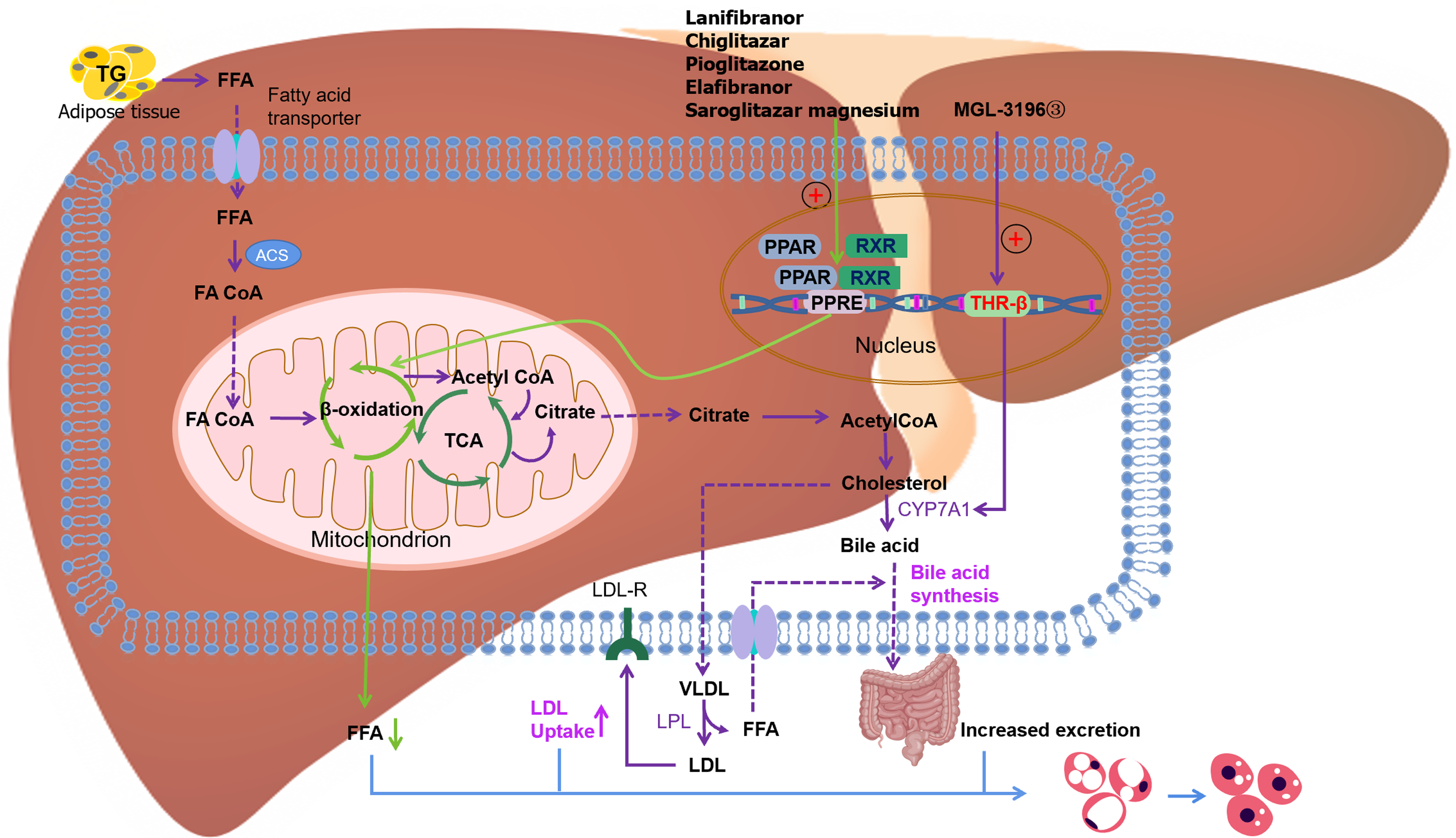
Figure 1 Signaling pathways of proliferator-activated receptor alpha and thyroid hormone receptor-beta and drugs targeting these pathways.
PPAR: Proliferator-activated receptor; TG: Triglyceride; FFA: Free fatty acid; ACS: Acyl coenzyme A synthetase; FA CoA: Fatty acyl coenzyme A; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; PPRE: PPAR reaction element; THR: Thyroid hormone receptor-beta; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; LDL-R: Low-density lipoprotein receptor; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein.
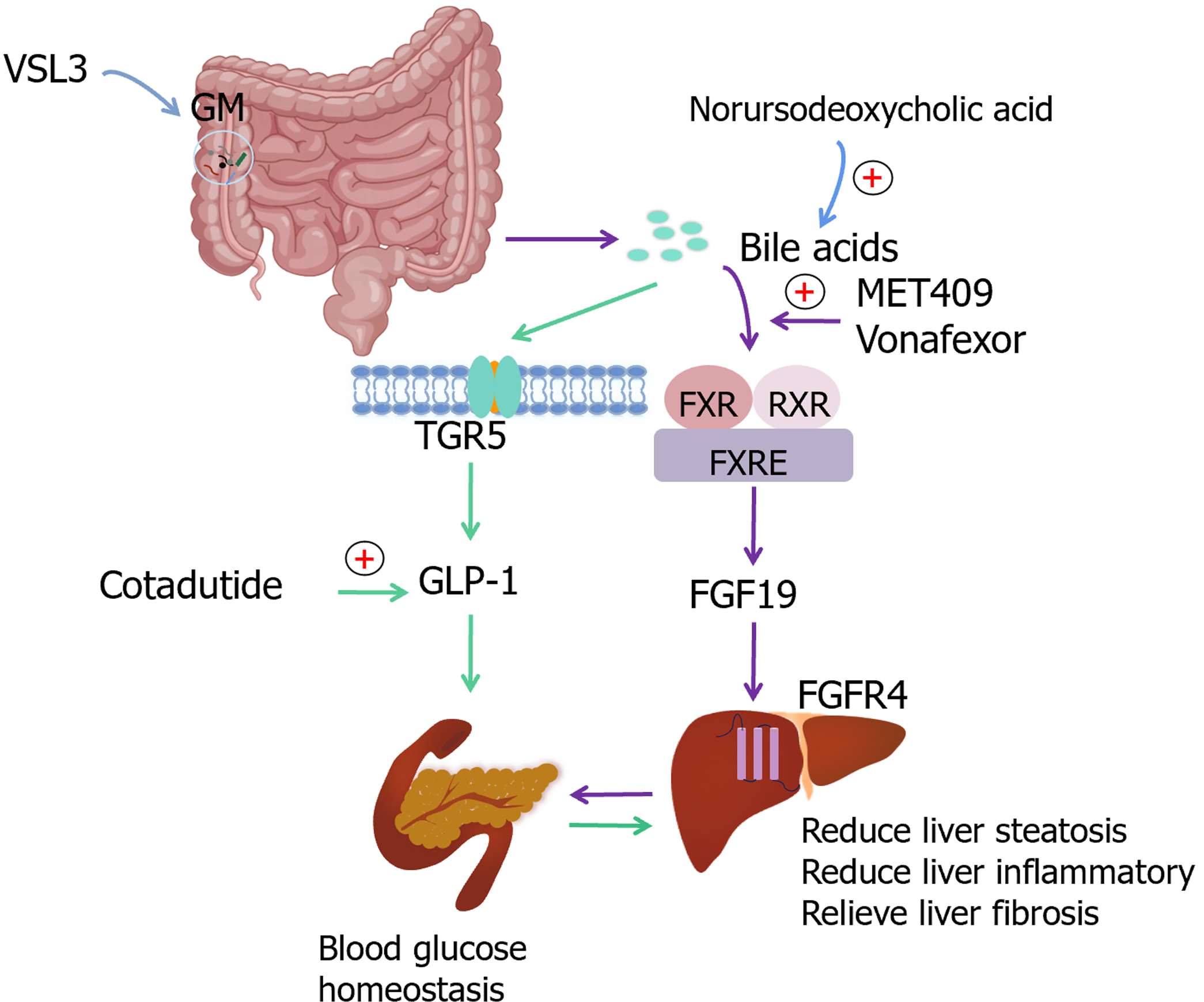
Figure 2 Targets related to lipids, bile acids, glucose homeostasis and intestinal microbiota in age-related metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
GM: Gut microbiota; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; FXRE: FXR reaction element; FGF19: Fibroblast growth factor 19; FGFR4: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; TGR5: Takeda G protein–coupled receptor 5; GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1.
- Citation: He QJ, Li YF, Zhao LT, Lin CT, Yu CY, Wang D. Recent advances in age-related metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(7): 652-662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i7/652.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.652