Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2024; 30(18): 2379-2386
Published online May 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i18.2379
Published online May 14, 2024. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i18.2379
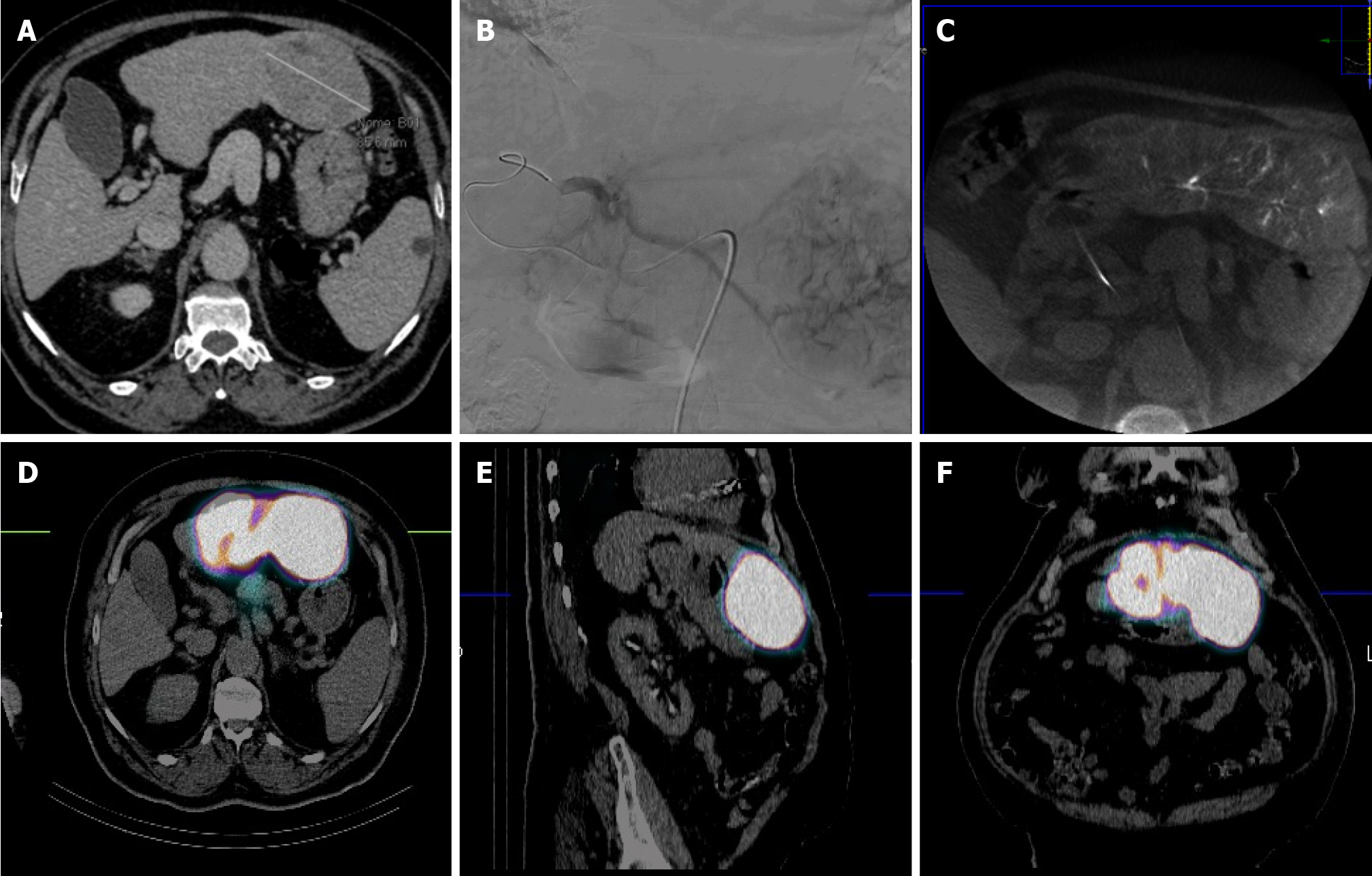
Figure 1 72-year-old man with hepatocellular carcinoma unfit for surgery due to comorbidities (alpha-fetoprotein 2235 ng/mL).
A: Computed tomography (CT) showing large hepatocellular carcinoma nodule (7 cm) located in S3; B and C: Angiography and cone beam CT demonstrating superselective catheterization of the segmental S3 artery with perfused nodule; D-F: Single-photon emission tomography combined with CT showing 99mTc-MAA uptake into S3 without uptake in the remaining liver parenchyma or other organs.
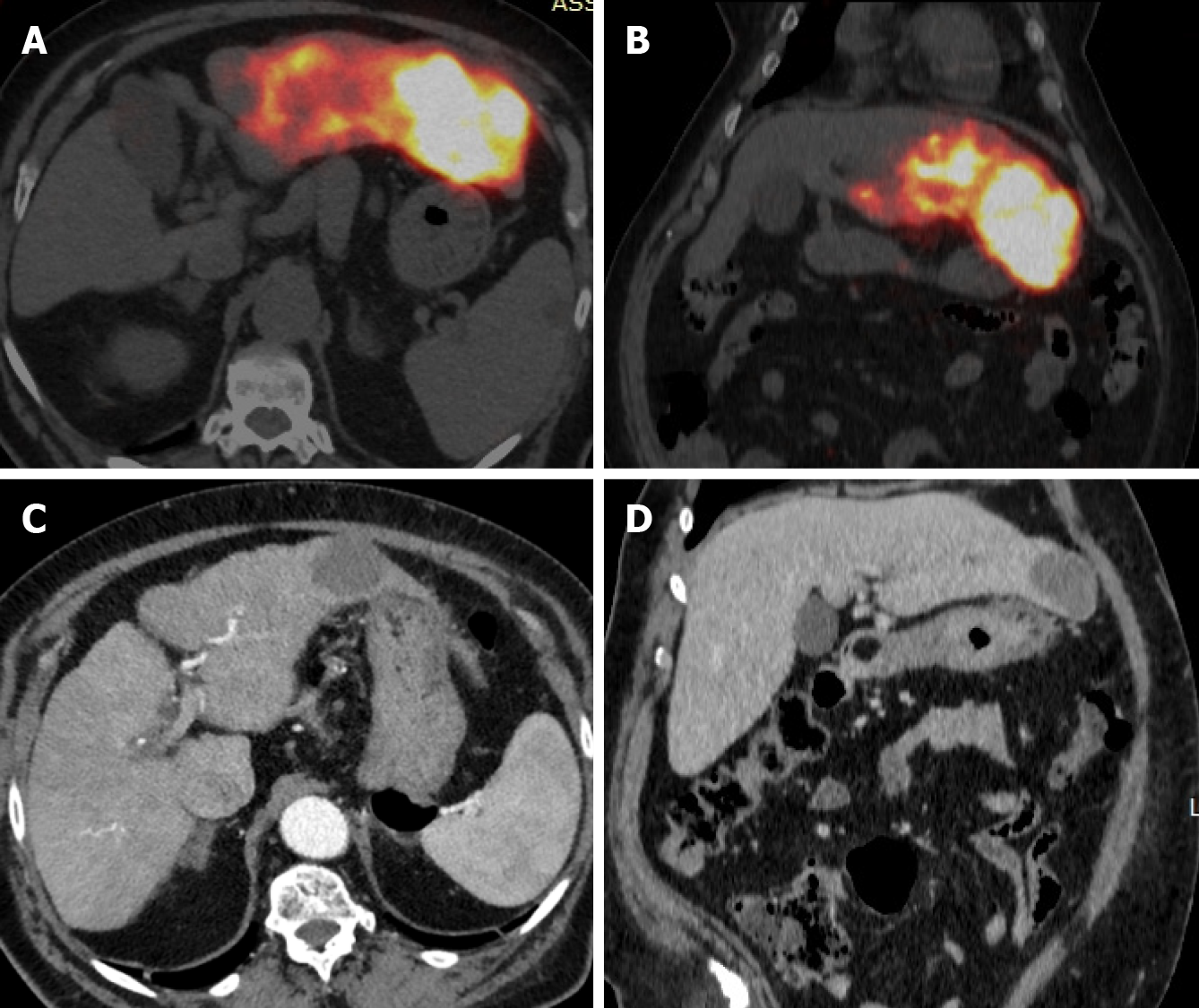
Figure 2 Same patient of figure 1.
A and B: Post-transarterial radioembolization, axial and coronal positron emission tomography-computed tomography (CT) views of the Y-90 dose distribution demonstrating high uptake in the tumor without any nontarget activity; C and D: Four-months follow-up CT scan (axial and coronal view) showing necrotic nodule with segmental S3 atrophy (alpha-fetoprotein 7 ng/mL).
- Citation: Inchingolo R, Cortese F, Pisani AR, Acquafredda F, Calbi R, Memeo R, Anagnostopoulos F, Spiliopoulos S. Selective internal radiation therapy segmentectomy: A new minimally invasive curative option for primary liver malignancies? World J Gastroenterol 2024; 30(18): 2379-2386
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v30/i18/2379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v30.i18.2379