Copyright
©The Author(s) 1997.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 15, 1997; 3(1): 9-11
Published online Mar 15, 1997. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v3.i1.9
Published online Mar 15, 1997. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v3.i1.9
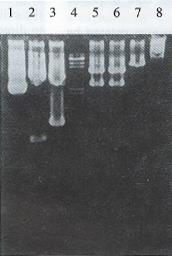
Figure 1 Identification of insertion of pgk + HSV-tk segment into the pMNM retroviral vector and plasmid pGEM 7Z-AFP.
Lane 1: plasmid pGEM. 7Z-AFP; Lane 2: pGEM. 7Z-AFP/Hind III 3.3 kb, 406 bp; Lane 3: pGEM. 7Z-AFP/EcoR I 3 kp, 727 bp; Lane 4: λDNA Hind III marker; Lane 5: pMNP-tk/BamH I 6.1 kb, 2.8 kb; Lane 6: pMNP-tk/EcoR I and Hind III 6.1 kb, 2.8 kb; Lane 7: pMNP-tk/EcoR I 8.9 kb; Lane 8: plasmid pMNP-tk.
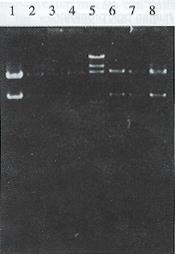
Figure 2 The orientation of human AFP enhancer core sequence was defined with Hind III and BamH I digestion of the colonies of pMNAP-tk.
Lane 1-4: right junction; Lane 5: λDNA Hind III marker; lane 6-8: reverse junction.
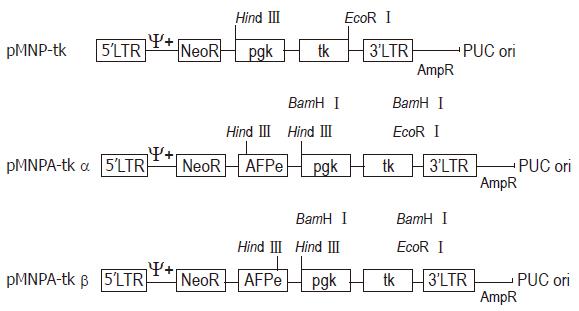
Figure 3 Structure of pMNP-tk, pMNAP-tkα, pMNAP-tkβ retroviral vectors.
LTR: Retroviral long terminal repeat sequence; NeoR: Neomycin phosphotransferase gene (for G418 selection); pgk: Human phosphoglycerokinase promotor; tk: Herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene; AFPe: Human α fetoprotein “home keeping” gene enhancer.
- Citation: Gao J, Cao GW, Qi ZT, Qiu XF, Wu ZD, Du P, Yang WG, Cui L. Construction of retroviral vector carrying HSV-tk gene under control of human AFP enhancer core sequence and human pgk promotor. World J Gastroenterol 1997; 3(1): 9-11
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v3/i1/9.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v3.i1.9