Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2023; 29(9): 1509-1522
Published online Mar 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1509
Published online Mar 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1509
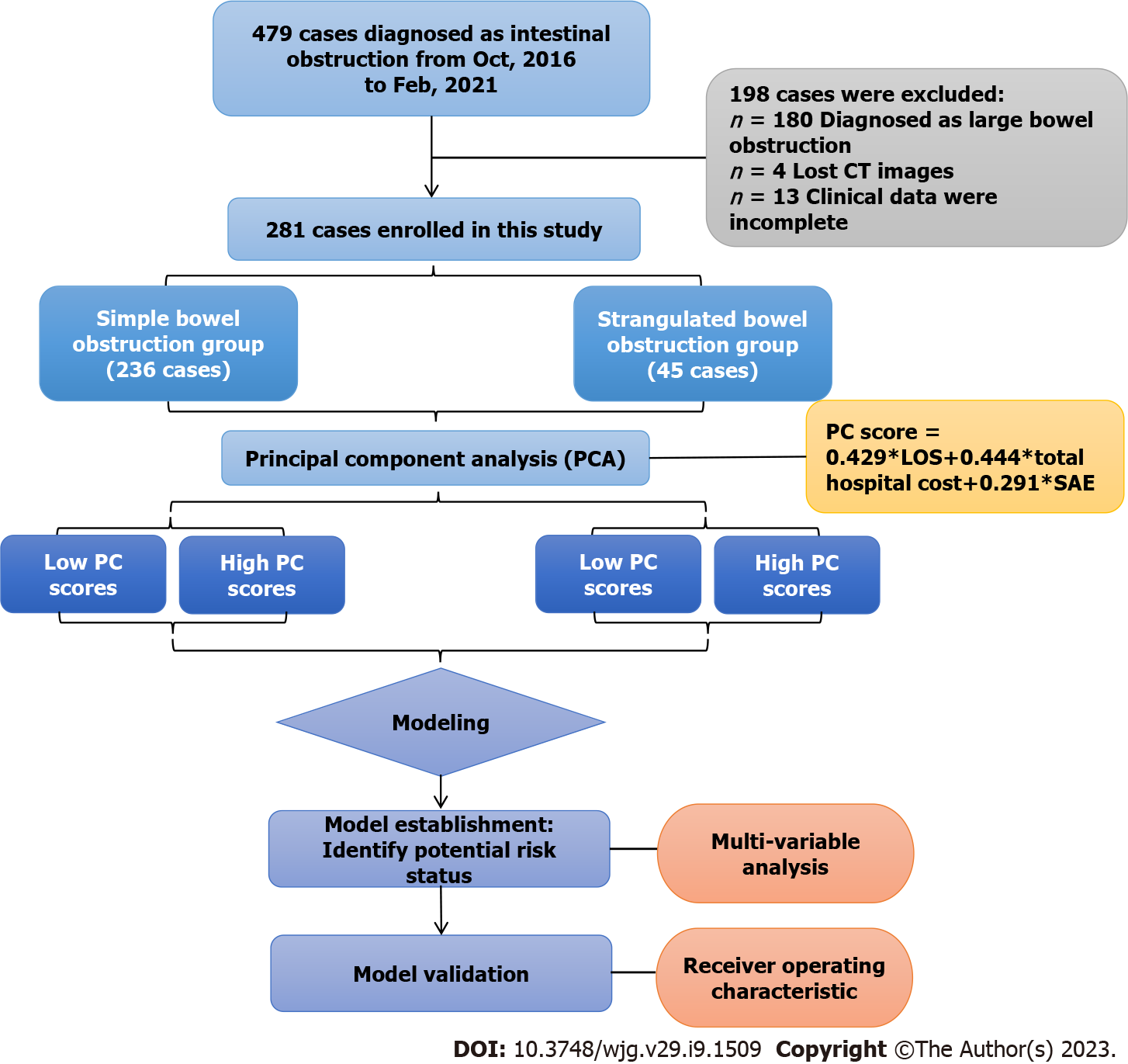
Figure 1 Workflow of this study.
CT: Computed tomography; PC: Principal component; LOS: Length of stay; SAE: Severe adverse event.
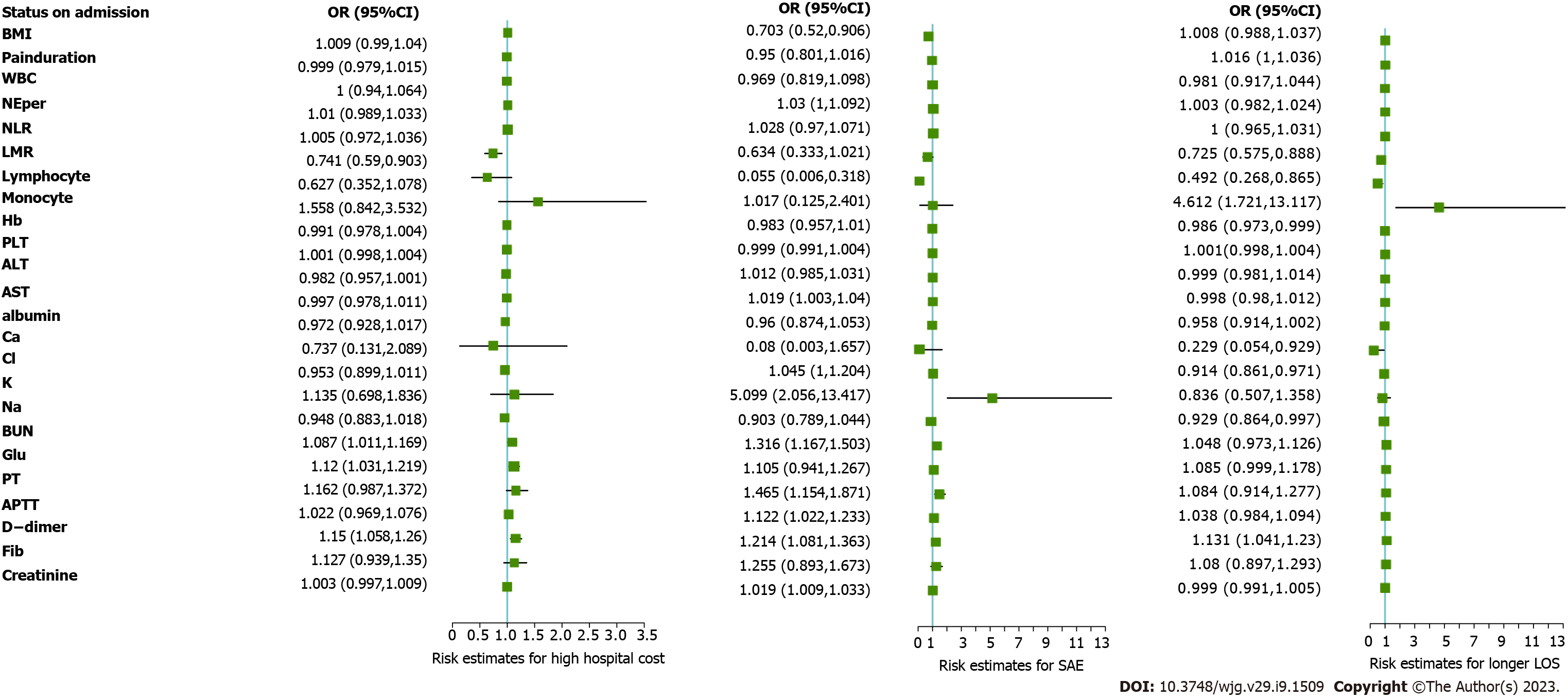
Figure 2 Risk factors for worse outcome of small bowel obstruction.
Risk estimates for high hospital cost; Risk estimates for severe adverse event; Risk estimates for longer length of stay. OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence interval; BMI: Body mass index; WBC: White blood cell; NE%: Neutrophil percentage; NLR: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; LMR: Lymphocyte to monocyte ratio; Hb: Hemoglobin; PLT: Platelet, ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; Ca: Calcium; Cl: Chloride; K: Potassiun; Na: Sodium; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; Glu: Glucose; PT: Prothrombin time; APTT: Activated partial thromboplastin time; DDI: D-dimer; Fib: Fibrinogen; SAE: Severe adverse event; LOS: Length of stay.
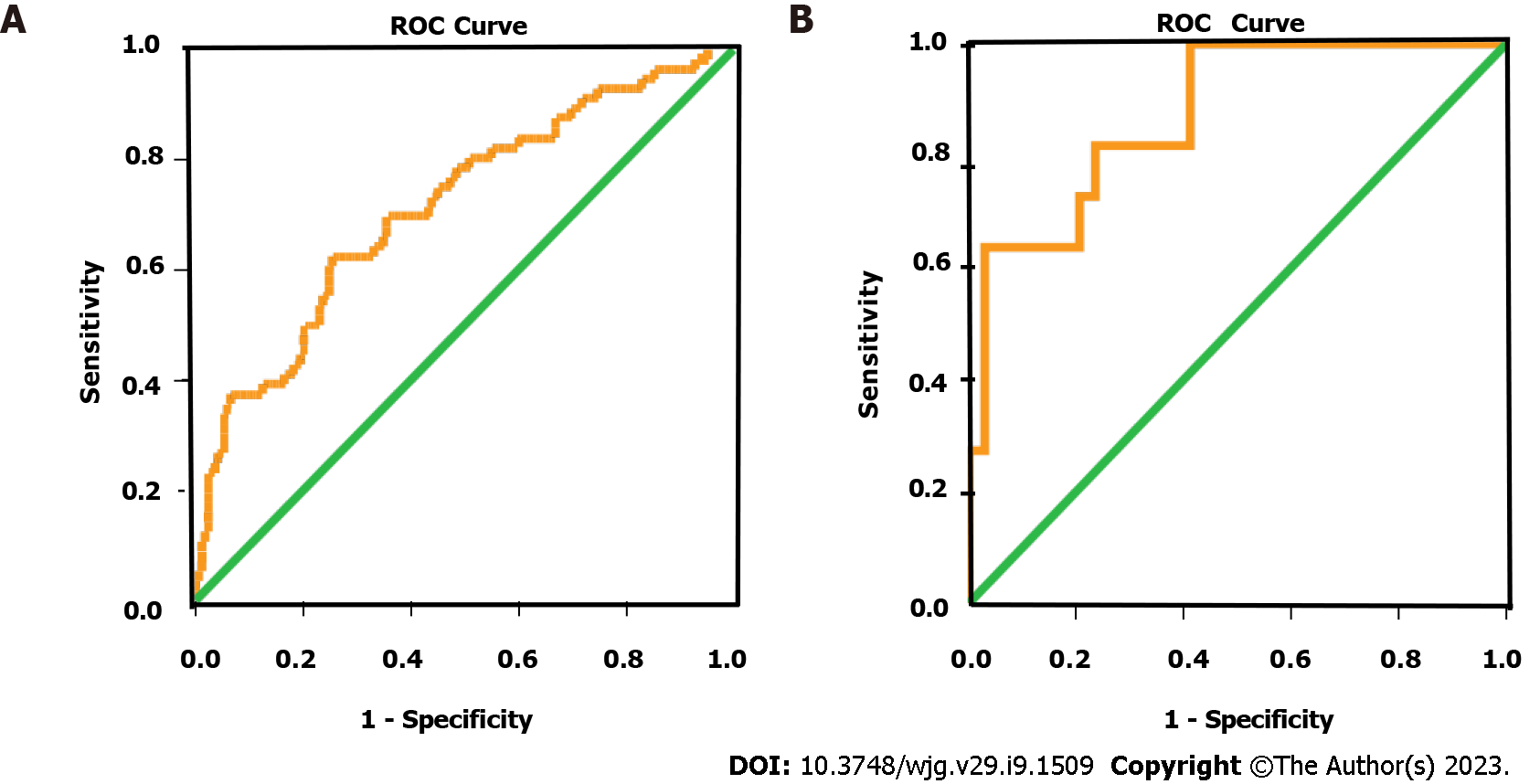
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve for high principal component score prediction.
The areas under the curve were 0.715 (95%CI: 0.635-0.795), 0.874 (95%CI: 0.762-0.986), respectively. A: Receiver operating characteristic curve of simple small bowel obstruction group for high principal component score prediction. B: Receiver operating characteristic curve of strangulated small bowel obstruction group for high principal component score prediction. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic.
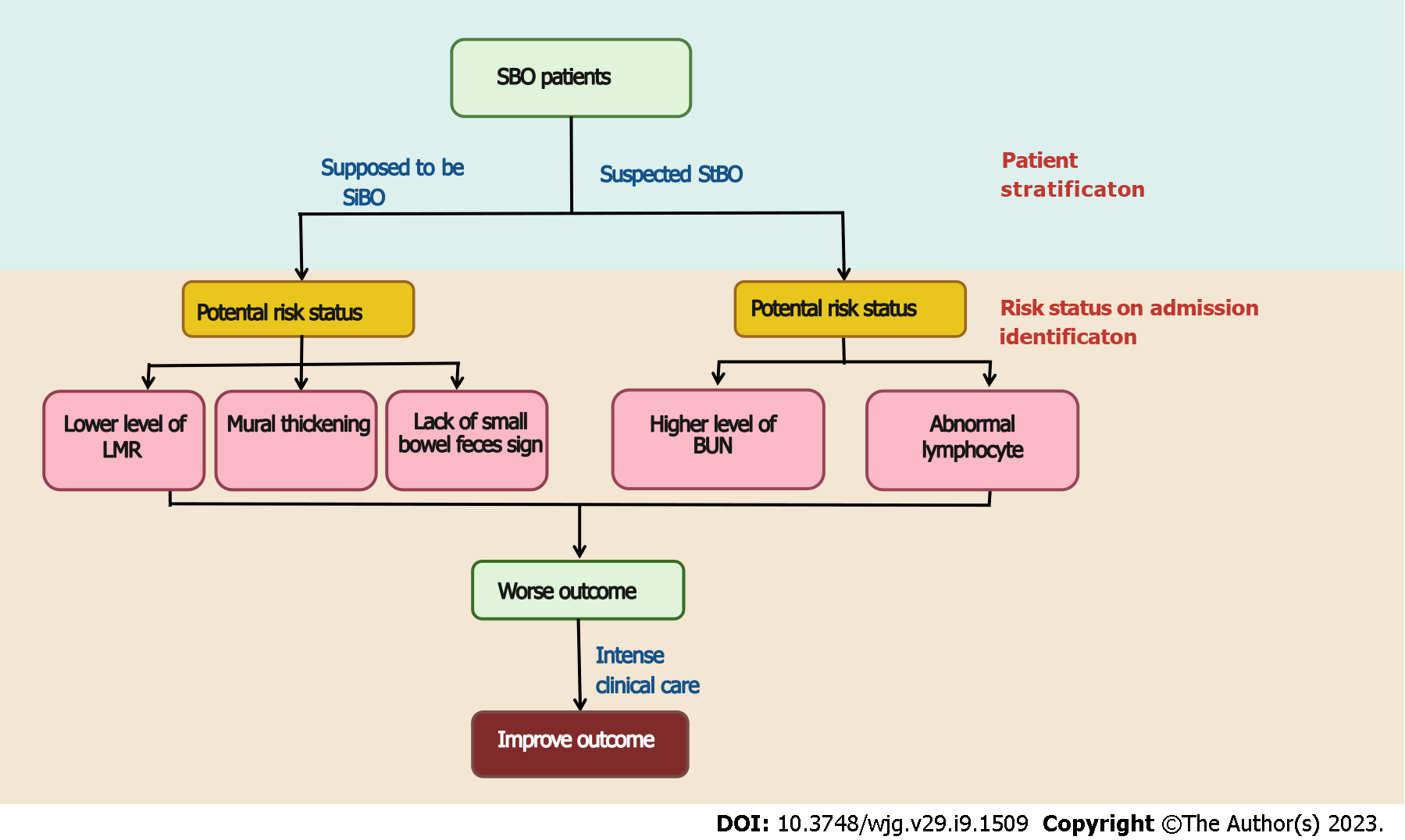
Figure 4 Proposal early clinical intensive care for small bowel obstruction patients on admission.
SBO: Small bowel obstruction; SiBO: simple small bowel obstruction; StBO: Strangulated small bowel obstruction; LMR: Lymphocyte to monocyte ratio; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen.
- Citation: Xu WX, Zhong QH, Cai Y, Zhan CH, Chen S, Wang H, Tu PS, Chen WX, Chen XQ, Zhang JR. Comprehensively evaluate the short outcome of small bowel obstruction: A novel medical-economic score system. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(9): 1509-1522
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i9/1509.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i9.1509