Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2023; 29(38): 5374-5382
Published online Oct 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i38.5374
Published online Oct 14, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i38.5374
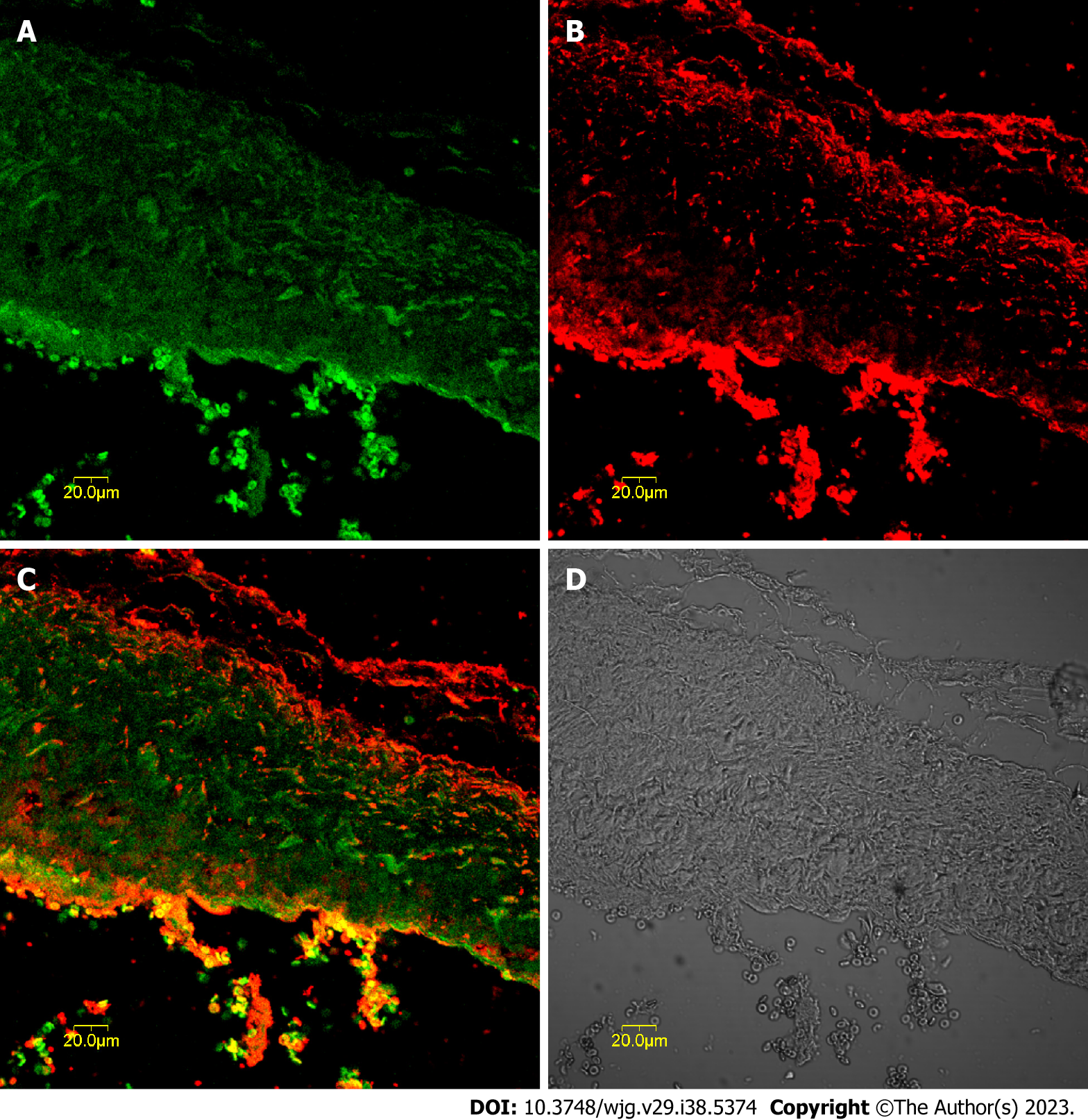
Figure 1 Expression of tyrosine kinase receptor and cholecystokinin-A receptors in gallbladder tissue sections determined by immunofluorescence.
A: Tyrosine kinase receptor-positive cells (green) in the muscularis layer of the gallbladder; B: Cholecystokinin-A receptor-positive cells (red) were mainly located in the muscularis layer of the gallbladder; C: Synthetic micrographs of A and B; D: Phase-contrast micrograph of A and B.
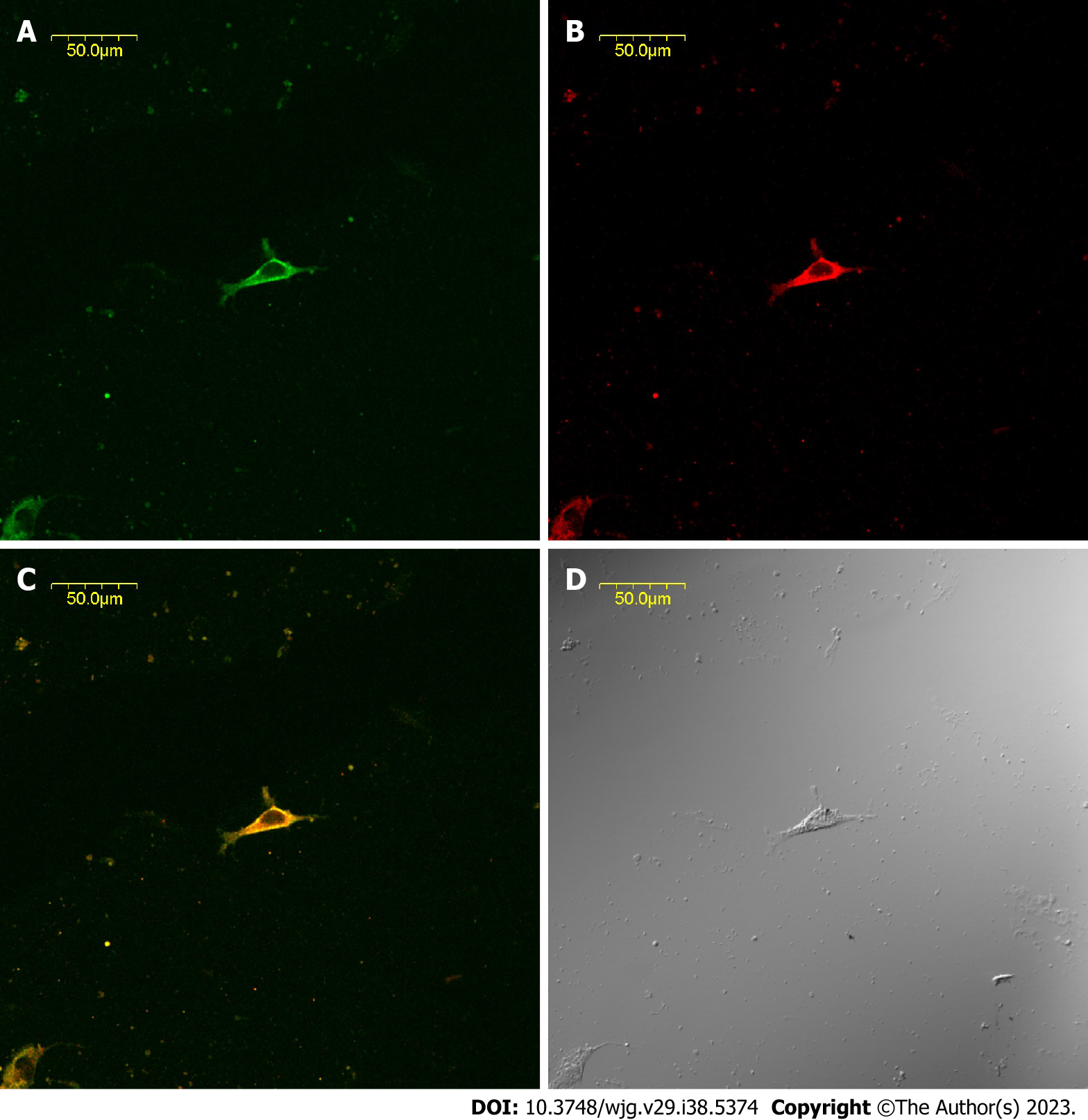
Figure 2 Expression of tyrosine kinase receptor and cholecystokinin-A receptors in common bile duct cultured cells determined by immunofluorescence.
A: Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLCs) are tyrosine kinase receptor-positive (green); B: ICLCs express cholecystokinin-A receptors (red); C: Synthetic micrographs of A and B; D: Phase-contrast micrographs of A and B.
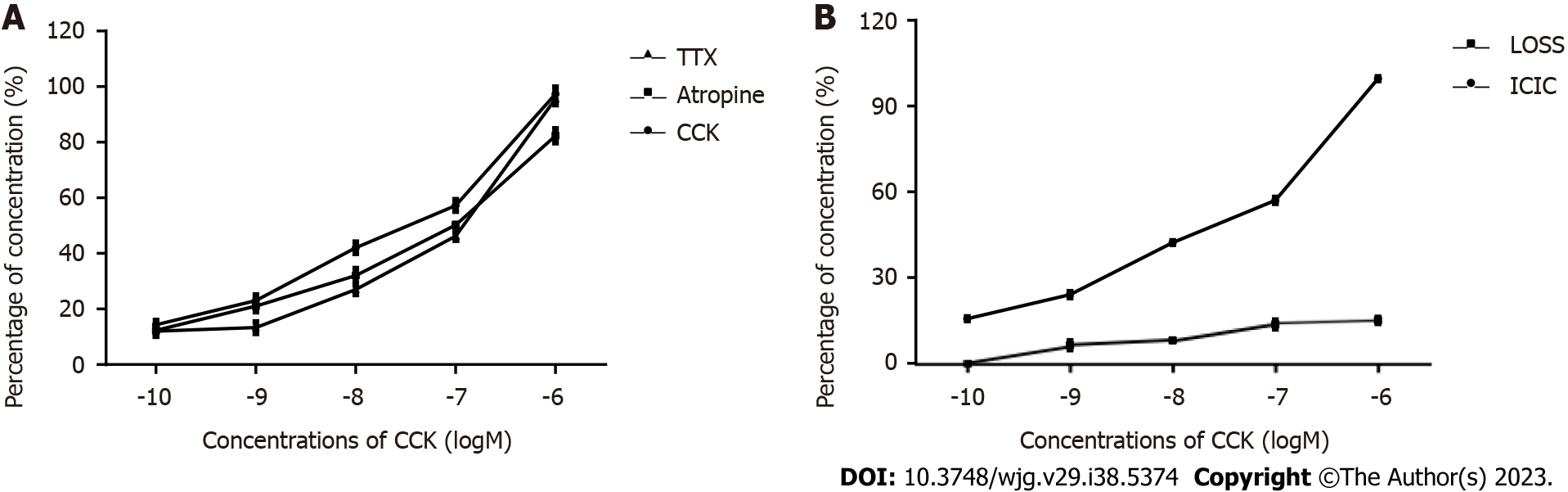
Figure 3 Response of common bile duct muscle strips with interstitial Cajal-like cells and interstitial Cajal-like cell-removed common bile duct muscle strips to cholecystokinin octapeptide.
A: Response of common bile duct muscle strips with interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLCs) to cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8); B: Response of ICLC-removed common bile duct muscle strips to CCK-8. ICLC: Interstitial Cajal-like cell; CCK: Cholecystokinin; TTX: Tetrodotoxin.
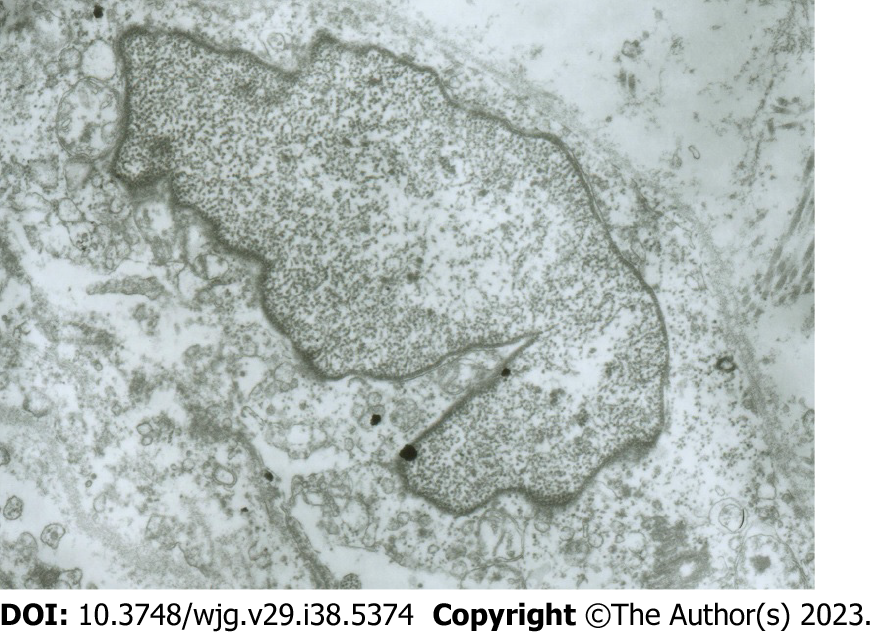
Figure 4 Electron microscopy images of damaged interstitial Cajal-like cells.
Interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLCs) in common bile duct notably changed after incubation with methylene blue and light treatment. The ICLCs were swollen, the cytoplasm was loose, the number of mitochondria was reduced, the caveolae disappeared, and the cell membrane was damaged.
- Citation: Xu D, Ma SL, Huang ML, Zhang H. Expression and functional study of cholecystokinin-A receptors on the interstitial Cajal-like cells of the guinea pig common bile duct. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(38): 5374-5382
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i38/5374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i38.5374