Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2023; 29(20): 3216-3221
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3216
Published online May 28, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3216
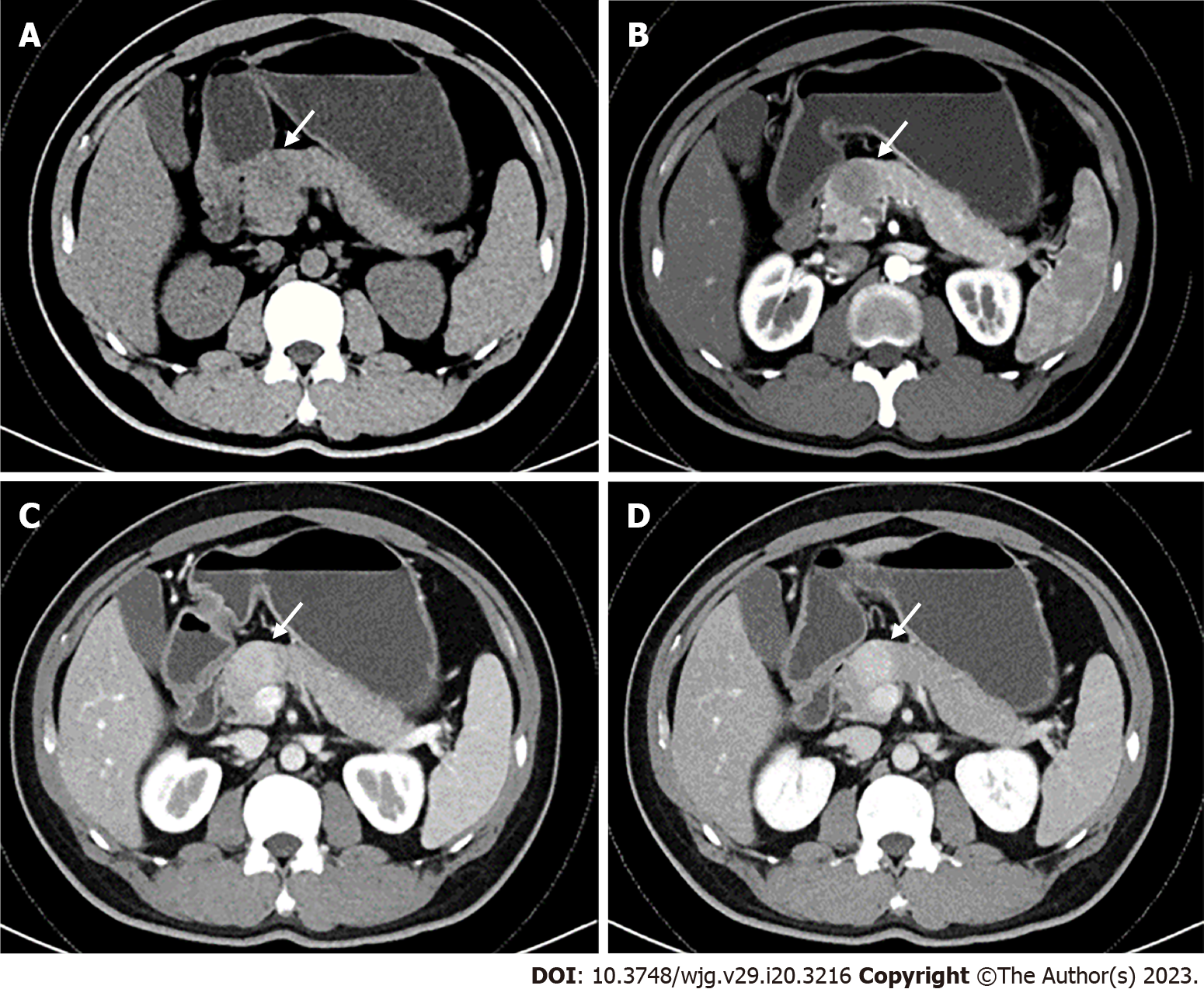
Figure 1 Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography.
A: Axial non-contrast showed a low-density mass in the neck of the pancreas; B: Arterial phase indicated a distinct hypoattenuating mass; C and D: Venous phase revealed persistent hyperenhancement of the mass (magnetic resonance imaging is similar to computed tomography in enhancement mode and characteristics).
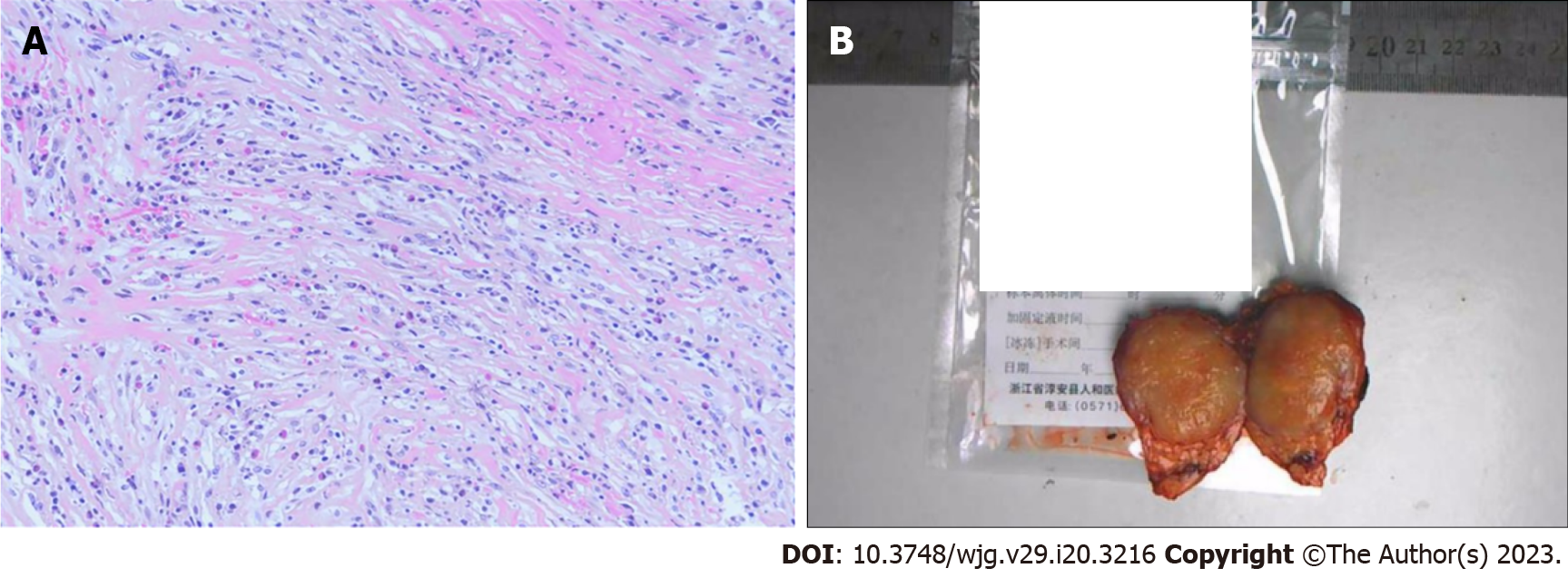
Figure 2 Histopathological image and resected tumor specimen.
A: Spindle-shaped myofibroblasts accompanied by large amounts of plasma cells. B: The resected specimen showing a well-defined neoplasm (some information has been excluded due to patient privacy).
- Citation: Liu JB, Gu QB, Liu P. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the pancreatic neck misdiagnosed as neuroendocrine tumor: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(20): 3216-3221
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i20/3216.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i20.3216