Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2023; 29(11): 1745-1756
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1745
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1745
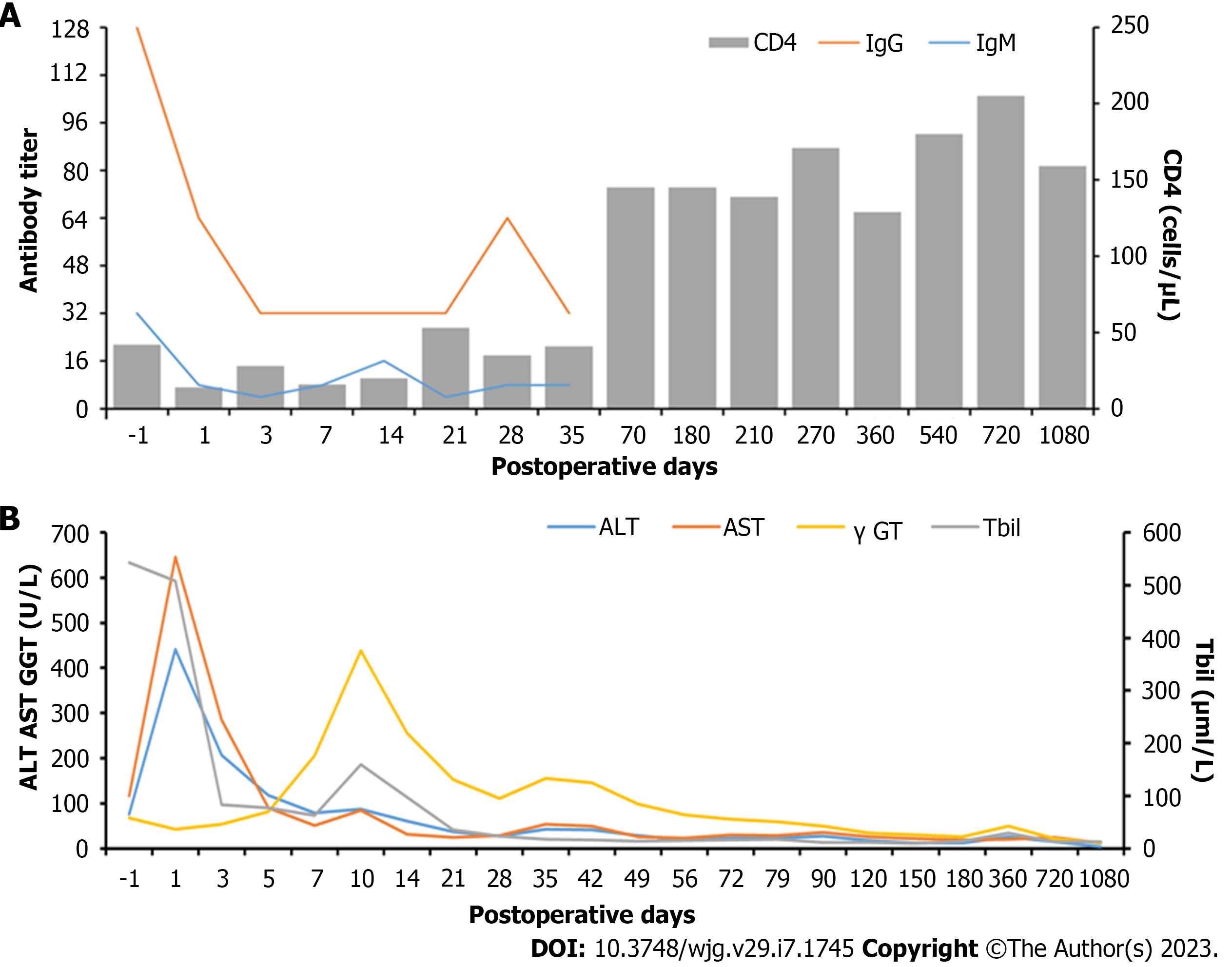
Figure 1 Dynamic changes in immunological indicators and liver function in case 1.
A: Trends of anti-A immunoglobulin M (IgM)/immunoglobulin G (IgG) titers and CD4(+) T cell counts over time; B: Trends of liver enzymes over time after liver transplantation. γGT: γ-glutamyltransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; Tbil: Total bilirubin.
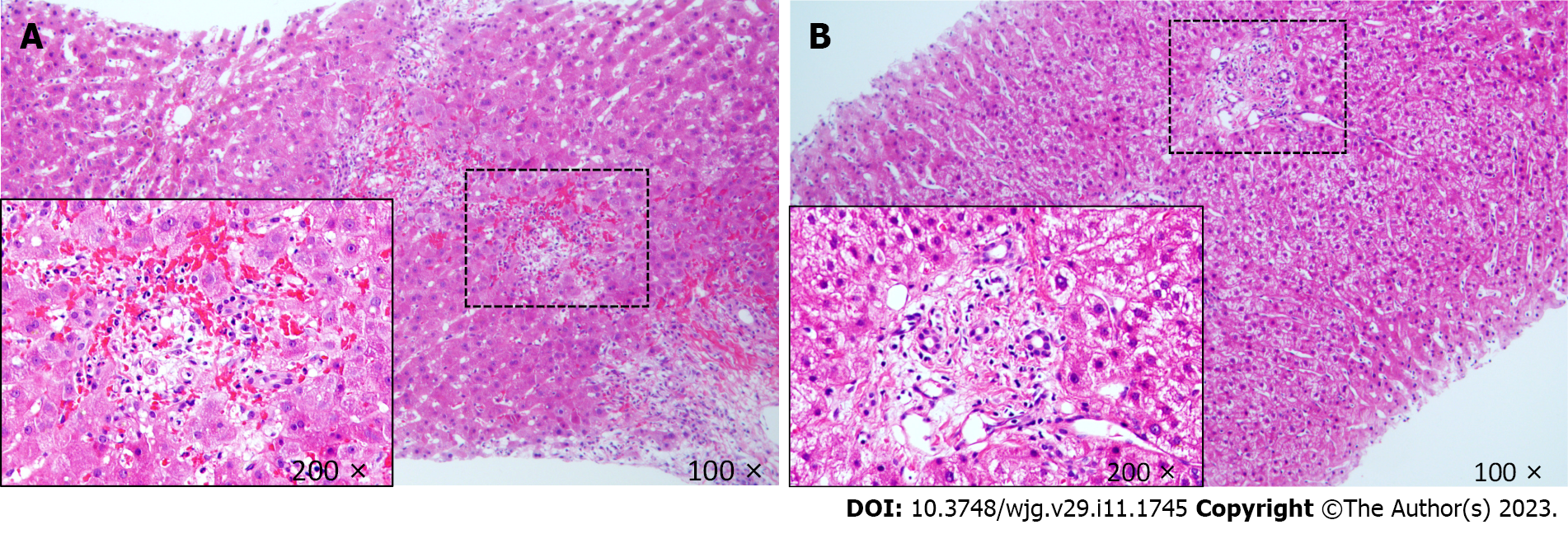
Figure 2 Pathological results of liver allograft biopsy.
A: Patient 1. The pathology results of liver allograft biopsy showed mild portal inflammation, mild venous endothelial inflammation, mild small bile duct inflammation and capillary bile duct cholestasis suggesting mild acute cellular rejection (Banff rejection activity index score, 4); B: Patient 2. The pathology results suggested chronic interlobular cholangitis with bile duct sclerosis and the possibility of early chronic rejection.
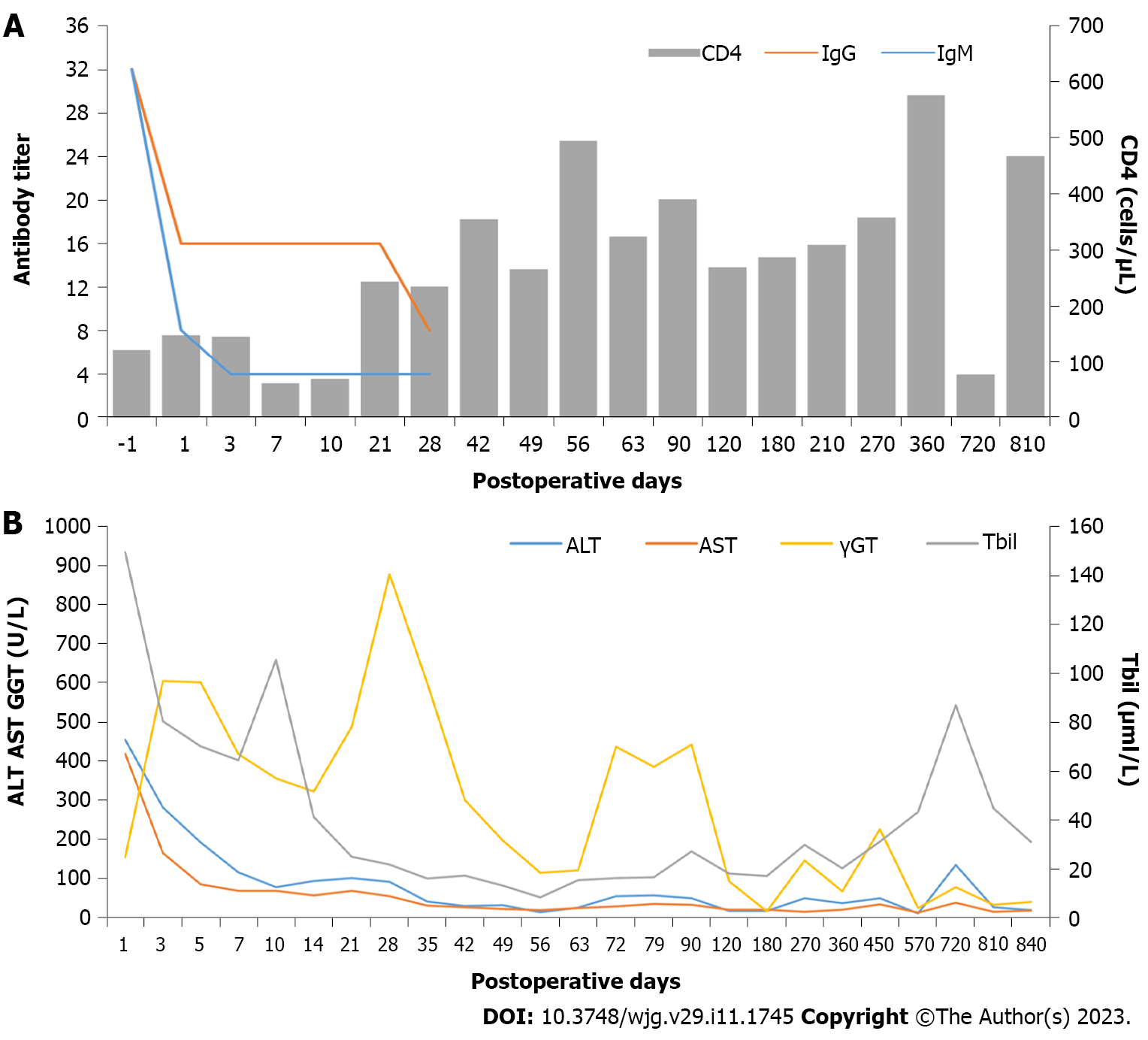
Figure 3 Dynamic changes in immunological indicators and liver function of case 2.
A: Trends of anti-A immunoglobulin M (IgM)/immunoglobulin G (IgG) titers and CD4(+) T cell counts over time; B: Trends of liver enzymes over time after liver transplantation. γGT: γ-glutamyltransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; Tbil: Total bilirubin.
- Citation: Tang JX, Zhang KJ, Fang TS, Weng RH, Liang ZM, Yan X, Jin X, Xie LJ, Zeng XC, Zhao D. Outcomes of ABO-incompatible liver transplantation in end-stage liver disease patients co-infected with hepatitis B and human immunodeficiency virus. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(11): 1745-1756
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i11/1745.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1745