Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2023; 29(1): 75-95
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.75
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.75
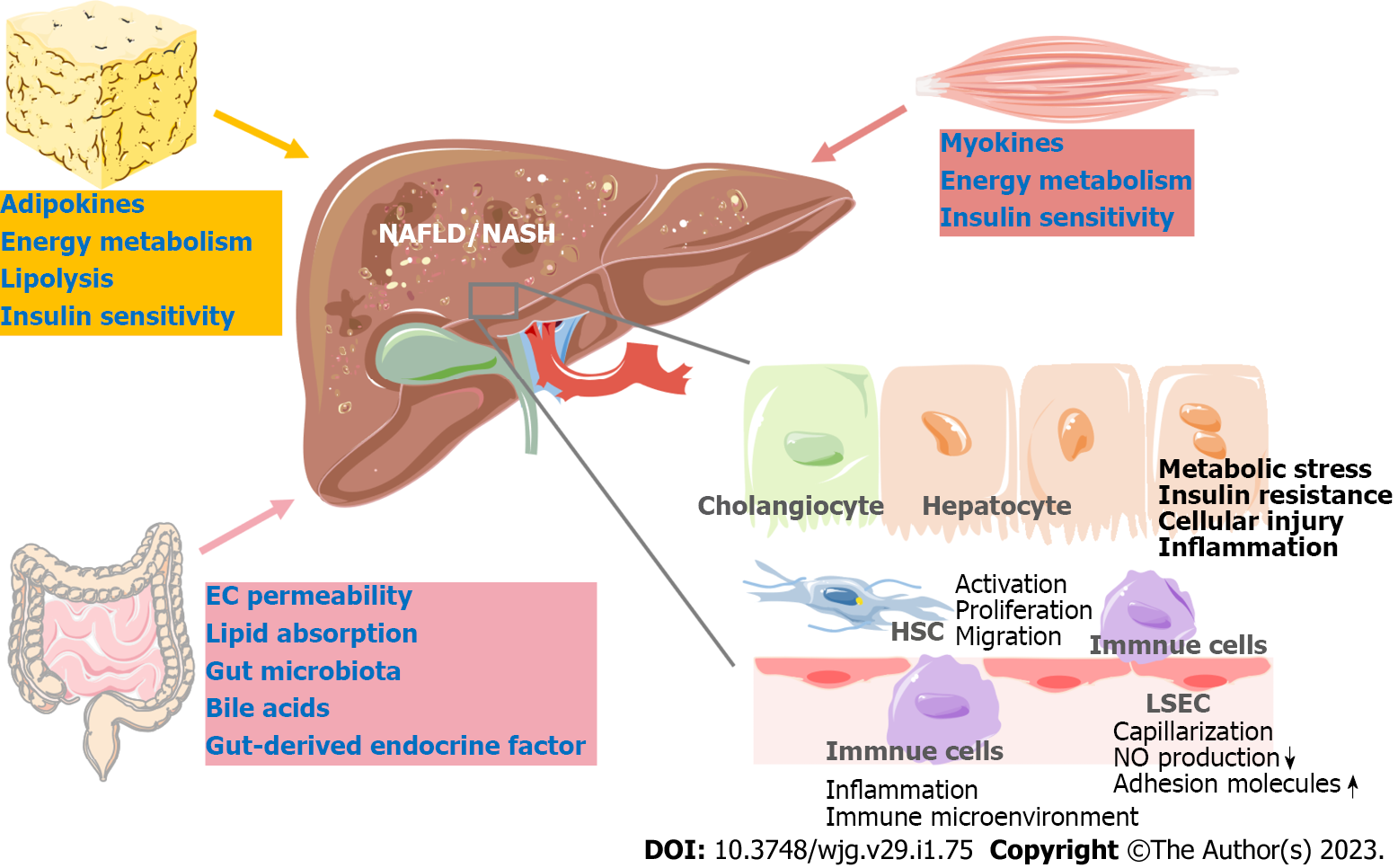
Figure 1 An overview of intrahepatic and extrahepatic targets for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis treatment.
In hepatocytes, strategies for treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) aim to improve metabolic disturbance and protect hepatocytes from injury. In the liver, the crosstalk network of nonparenchymal cells, including immune cells, hepatic stellate cells, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and hepatocytes, is an important target for NAFLD/NASH. Outside the liver, the gut, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle interact with the liver via various endocrine factors or affect whole-body energy metabolic homeostasis, which has been verified to be an extrahepatic target for NAFLD/NASH treatment. EC: Epithelial cell; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; LSEC: Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; NO: Nitric oxide.
- Citation: Wang GY, Zhang XY, Wang CJ, Guan YF. Emerging novel targets for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease treatment: Evidence from recent basic studies. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(1): 75-95
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i1/75.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.75