Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2023; 29(1): 61-74
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.61
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.61
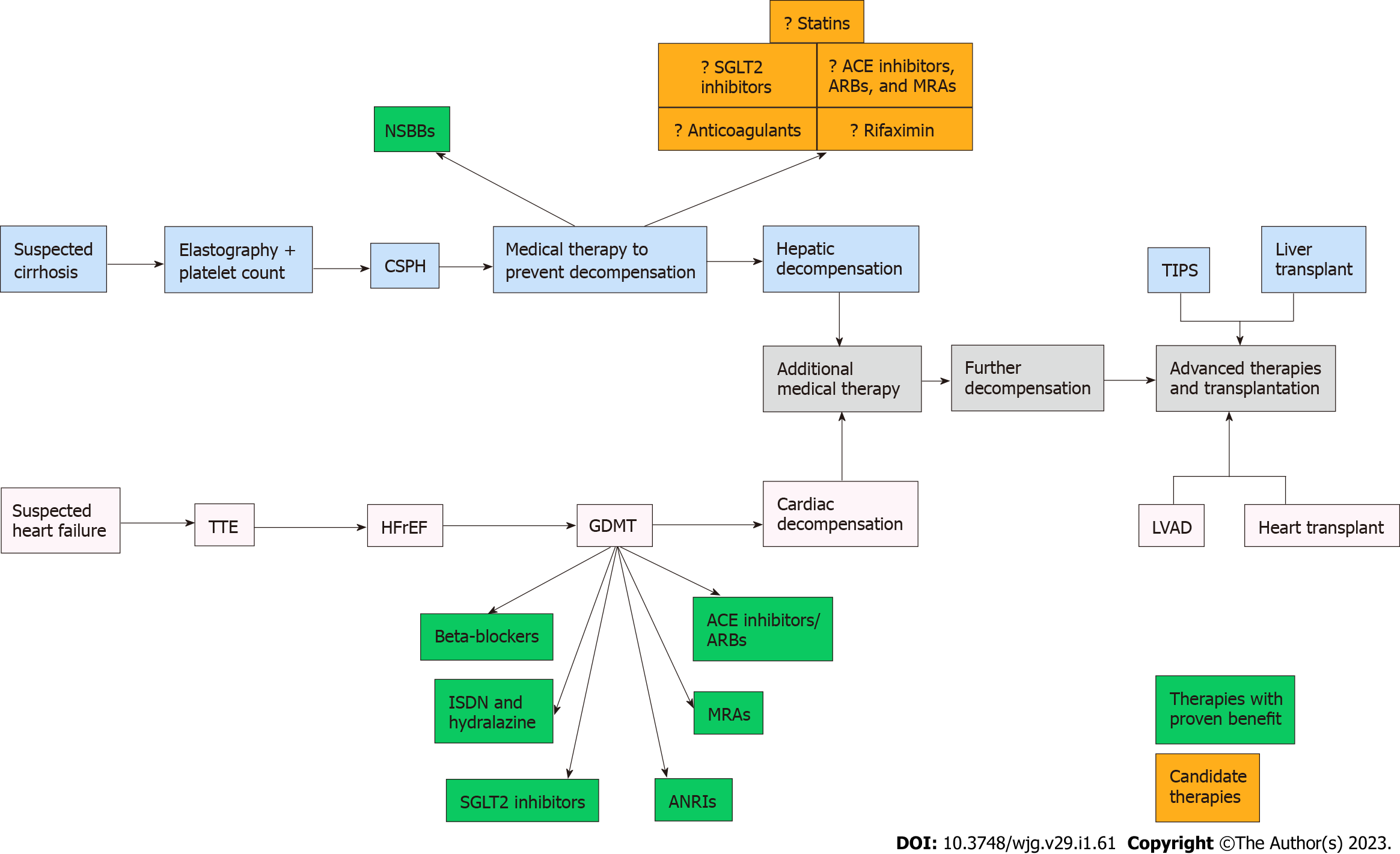
Figure 1 Management of cirrhosis in comparison to congestive heart failure.
ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; ANRI: Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor; ARB: Angiotensin receptor blocker; CSPH: Clinically-significant portal hypertension; GDMT: Guideline-directed medical therapy; HFrEF: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; LVAD: Left ventricular assist device; MRA: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; NSBB: Non-selective beta-blocker; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting; TTE: Transthoracic echocardiogram.
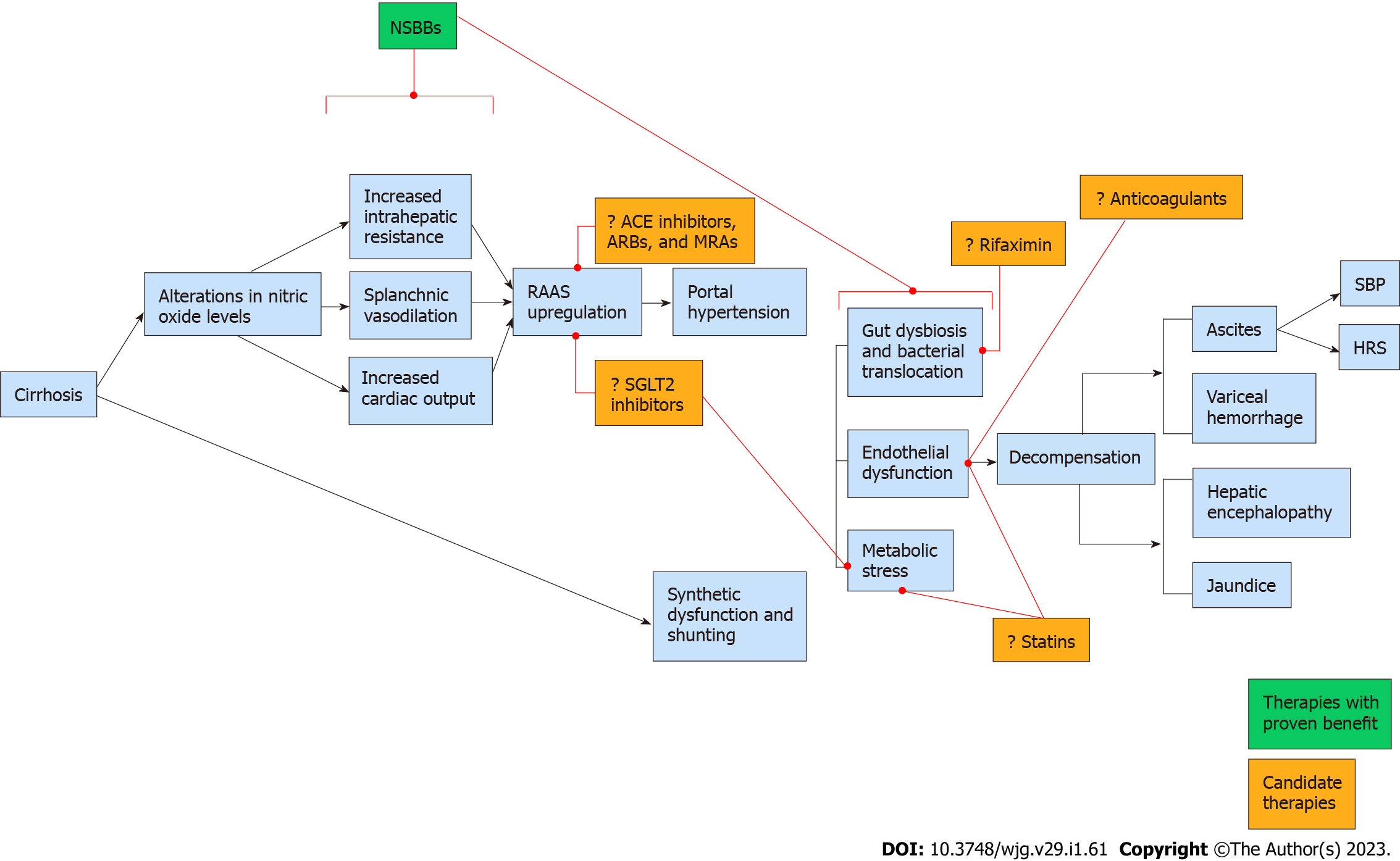
Figure 2 Therapeutic targets in the prevention of hepatic decompensation.
ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; ARB: Angiotensin receptor blocker; HRS: Hepatorenal syndrome; MRA: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; NSBB: Non-selective beta-blocker; RAAS: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; SBP: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; SGLT2: Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2.
- Citation: Lee S, Saffo S. Evolution of care in cirrhosis: Preventing hepatic decompensation through pharmacotherapy. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(1): 61-74
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i1/61.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.61