Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2023; 29(1): 144-156
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.144
Published online Jan 7, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.144
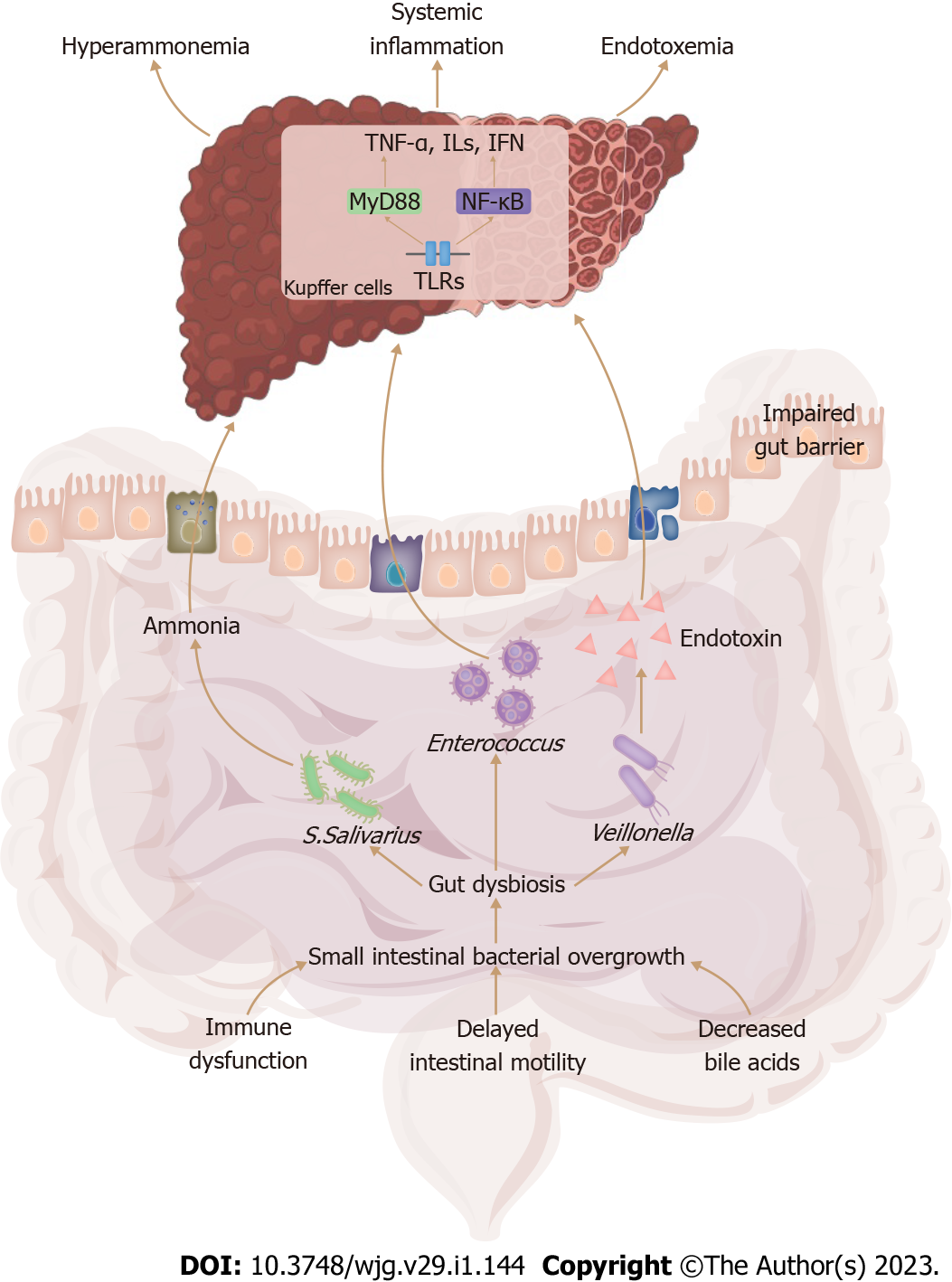
Figure 1 On the background of liver cirrhosis with hepatic dysfunction, dysbiotic gut microbiota and its byproducts including ammonia and endotoxin cross the impaired intestinal barrier, stimulate innate immune responses in the liver, and lead to systemic inflammation, hyperammonemia, and endotoxemia.
TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; ILs: Interleukins; IFN: Interferon.
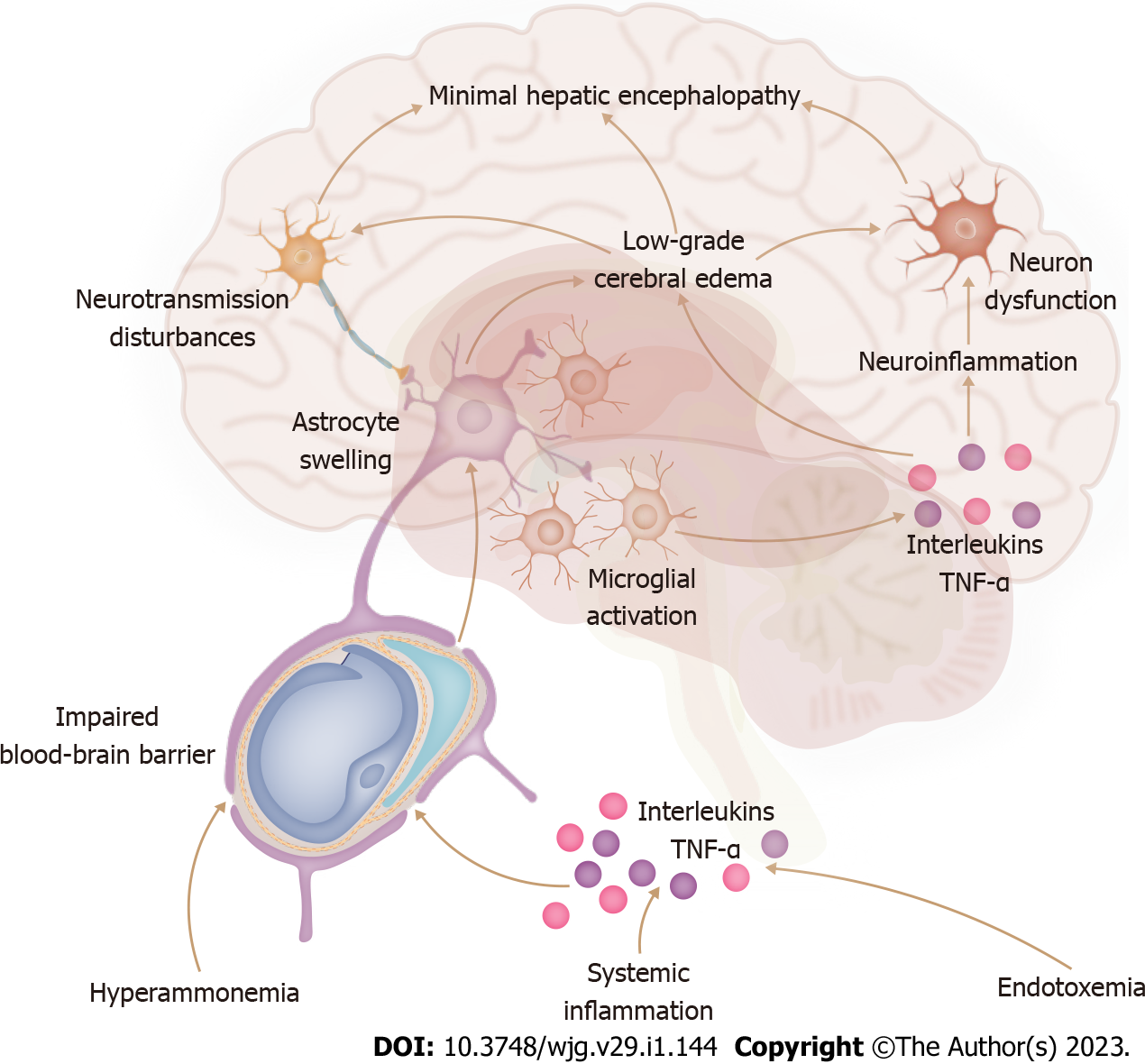
Figure 2 Systemic inflammation, hyperammonemia, and endotoxemia influence the permeability of the blood-brain barrier, resulting in neuroinflammation and low-grade cerebral edema, contributing to the pathogenesis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy.
TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
- Citation: Luo M, Xin RJ, Hu FR, Yao L, Hu SJ, Bai FH. Role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of minimal hepatic encephalopathy via the gut-liver-brain axis. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(1): 144-156
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i1/144.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i1.144