Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2022; 28(47): 6702-6715
Published online Dec 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6702
Published online Dec 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6702
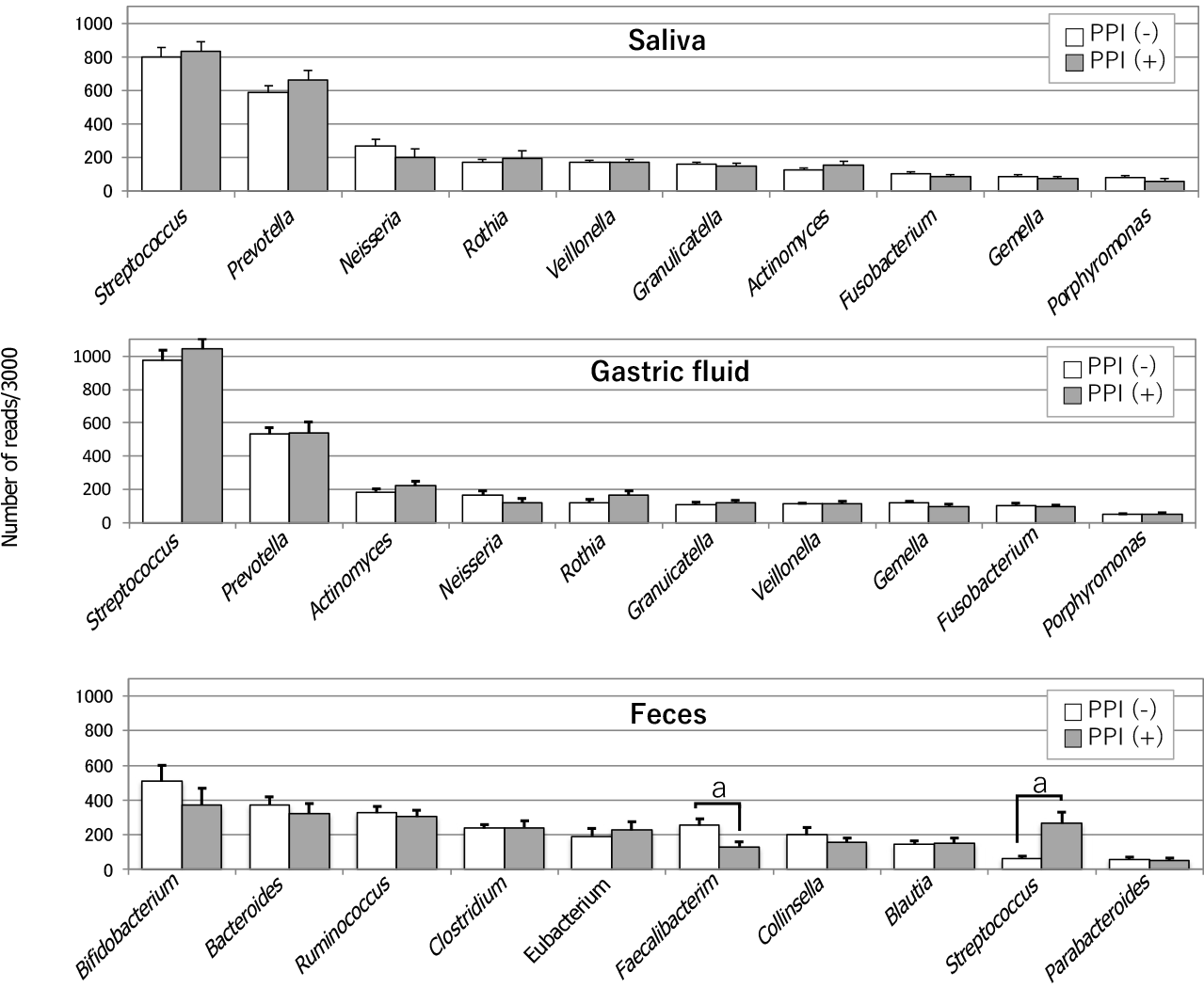
Figure 1 Comparison of the microbiota in the saliva, gastric fluid and feces, and the influence of proton-pump inhibitors.
Bacterial compositions at the genus level in saliva (top), gastric fluid (median) and feces (bottom) are shown. The average of read numbers of the top 10 major genera are indicated in each group. Open and filled bars represent proton-pump inhibitor (PPI)-nonusers and PPI-users, respectively. Asterisks show a significant difference according to Student t-test. aP < 0.05. PPI: Proton-pump inhibitor. Citation: Tsuda A, Suda W, Morita H, Takanashi K, Takagi A, Koga Y, Hattori M. Influence of Proton-Pump Inhibitors on the Luminal Microbiota in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2015; 6: e89. Copyright ©Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. 2015. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
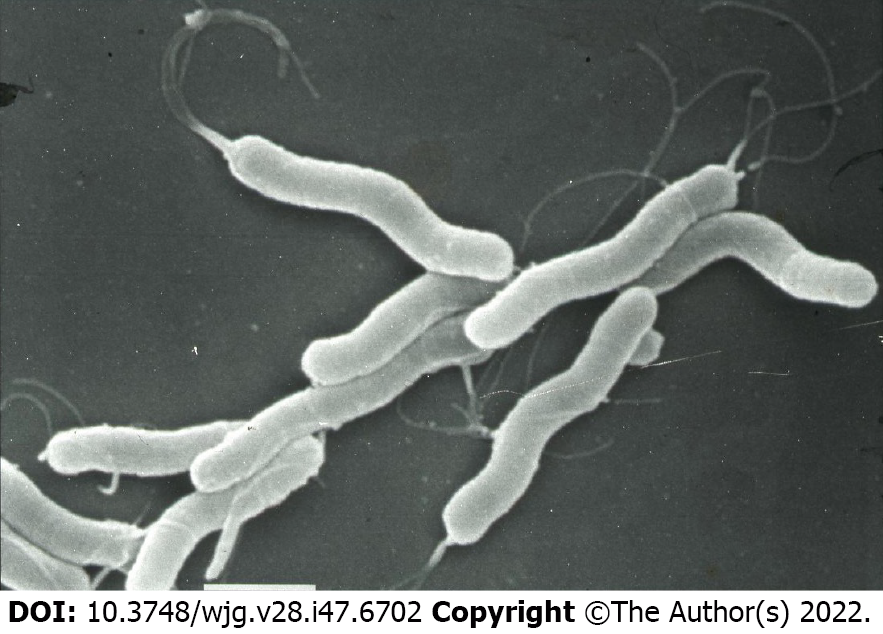
Figure 2 Observation of Helicobacterpylori by scanning electron microscopy.
The bar at the bottom shows 1 μm.
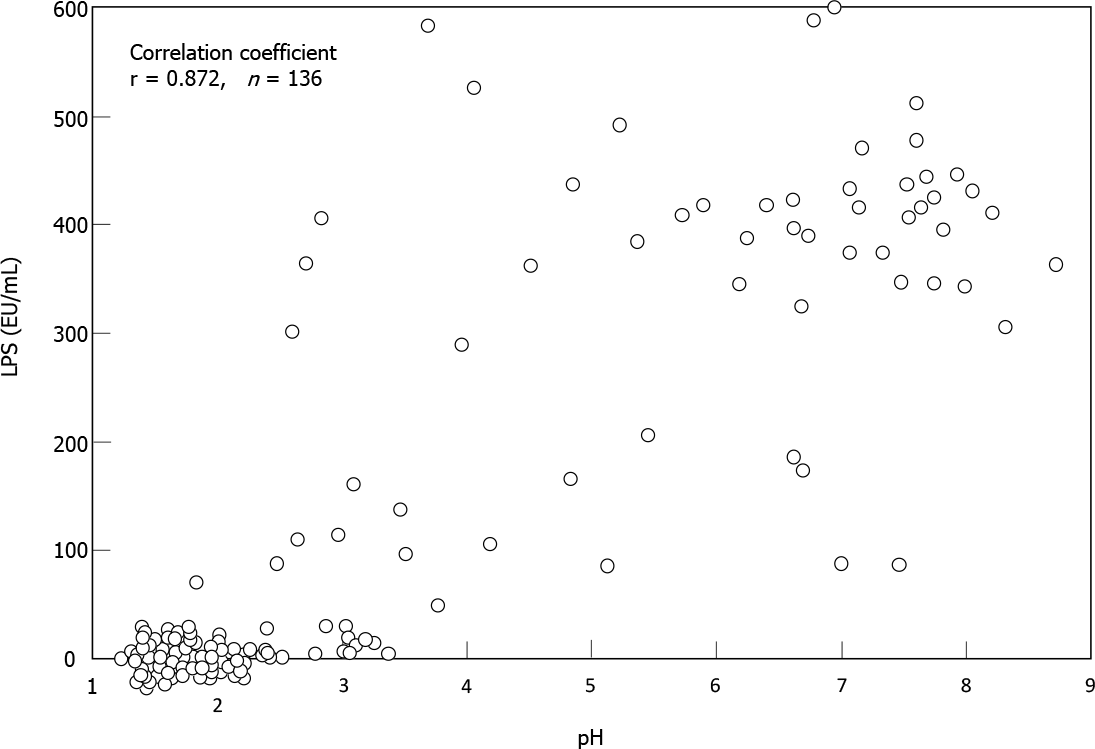
Figure 3 Correlation between pH and lipopolysaccharide activity in gastric fluid.
The pH values and lipopolysaccharide activity of gastric fluid samples from 136 subjects were examined using a recombinant factor C assay kit. The correlation coefficients of the both parameters by Spearman test (r) is shown on the upper left. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide. Citation: Sano M, Uchida T, Igarashi M, Matsuoka T, Kimura M, Koike J, Fujisawa M, Mizukami H, Monma M, Teramura E, Yoshihara S, Sato H, Morimachi M, Ito A, Ueda T, Shiraishi K, Matsushima M, Suzuki T, Koga Y. Increase in the Lipopolysaccharide Activity and Accumulation of Gram-Negative Bacteria in the Stomach With Low Acidity. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2020; 11: e00190. Copyright ©Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. 2020. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
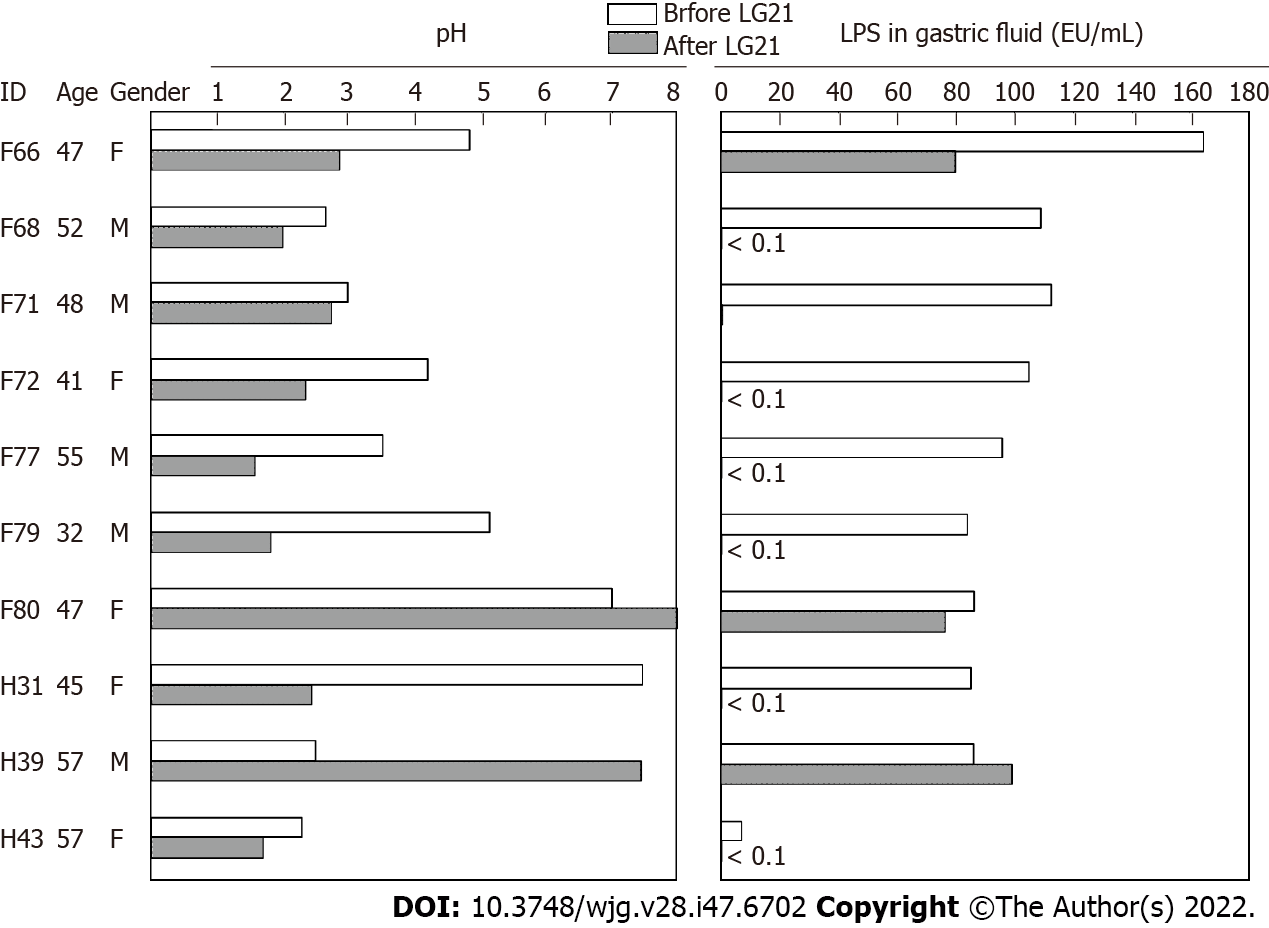
Figure 4 Effect of LG21 administration on the pH and lipopolysaccharide activity in the gastric fluid.
Ten subjects who had gastric fluid (GF) with low acidity and high lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activity consumed yogurt containing 109 CFU of LG21 every day for 3 mo. The pH value and LPS activity in the GF were measured before and after LG21 treatment. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
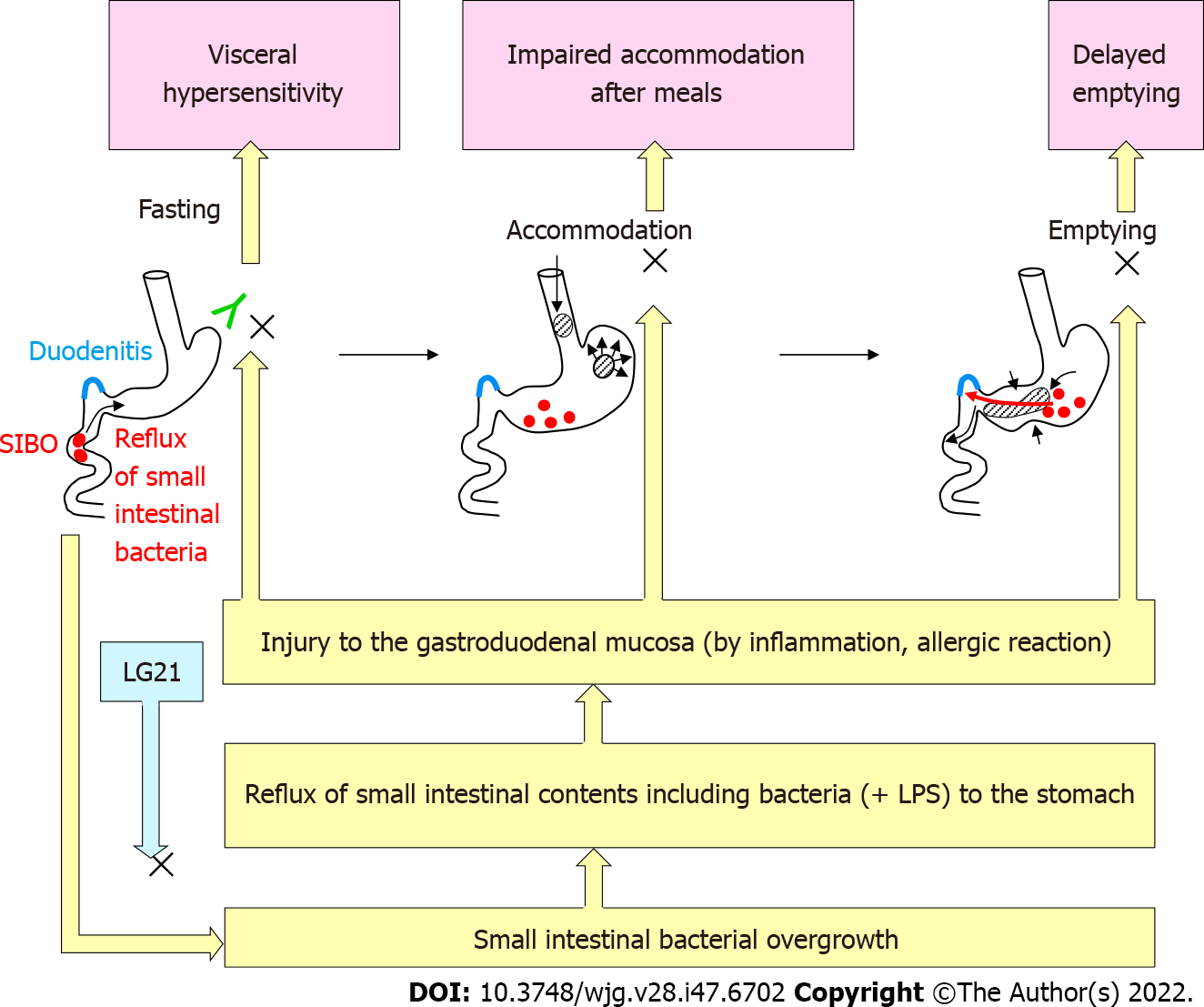
Figure 5 Pathophysiology of functional dyspepsia and possible mechanisms of the effects of LG21 treatment.
SIBO: Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Koga Y. Microbiota in the stomach and application of probiotics to gastroduodenal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(47): 6702-6715
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i47/6702.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6702