Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2022; 28(40): 5827-5844
Published online Oct 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5827
Published online Oct 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5827
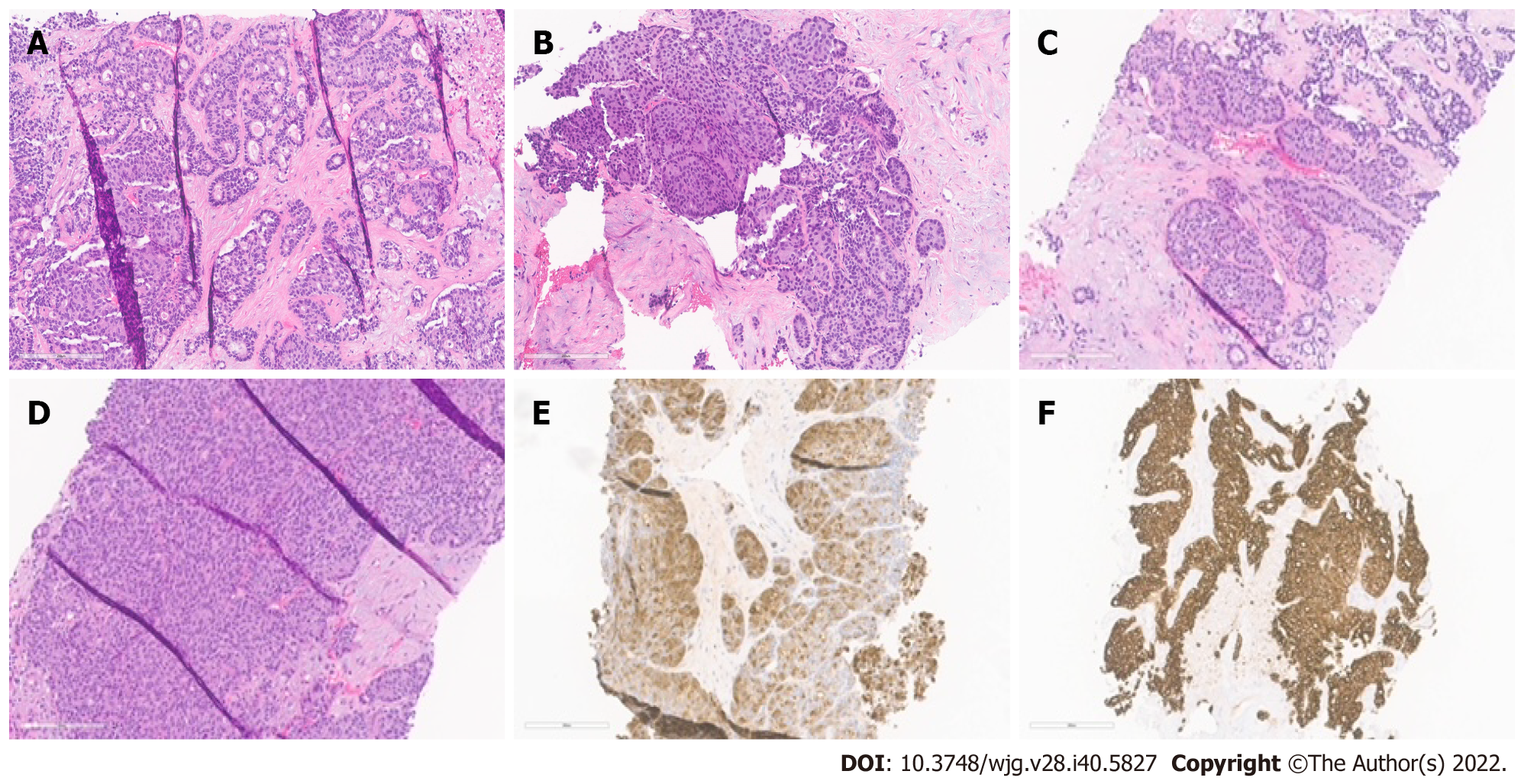
Figure 1 Histopathological patterns.
A: Acinar cell carcinoma with the predominant acinar pattern. The acinar pattern is characterized by structures resembling normal acini, with small lumina and cells arranged in a monolayer with basally located nuclei; B: Acinar cell carcinoma with the predominant glandular pattern. Acinar structures with dilated lumina characterize the glandular pattern; C: Acinar cell carcinoma with the predominant trabecular pattern. The trabecular pattern is characterized by ribbons of cells resembling those of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors; D: Acinar cell carcinoma with a predominant solid pattern. Large sheets of cells characterize the solid pattern without lumina; E: Acinar cell carcinoma, immunohistochemical staining for trypsin; F: Acinar cell carcinoma, immunohistochemical staining for cytokeratin 7.
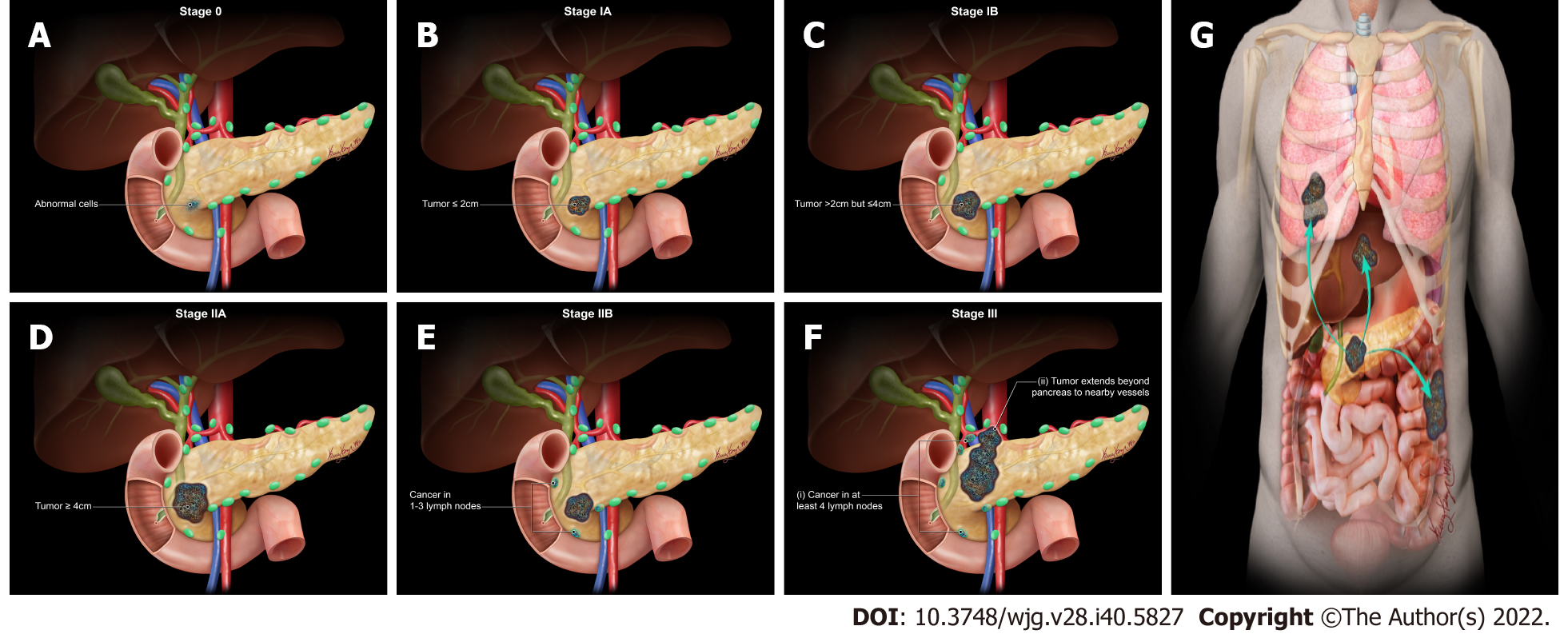
Figure 2 American Joint Committee on Cancer 8th Edition cancer staging for exocrine pancreatic tumor such as pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma.
A: Stage 0 (TNM: Tis, N0, M0). Tis = Carcinoma in situ. N0 = No regional lymph node metastases. M0 = No distant metastasis; B: Stage IA (TNM: T1, N0, M0). T1 = Tumor ≤ 2 cm in greatest dimension. N0 = No regional lymph node metastases. M0 = No distant metastasis; C: Stage IB (TNM: T2, N0, M0). T2 = Tumor > 2 cm and ≤ 4 cm in greatest dimension. N0 = No regional lymph node metastases. M0 = No distant metastasis; D: Stage IIA (TNM: T3, N0, M0). T3 = Tumor > 4 cm in greatest dimension. N0 = No regional lymph node metastases. M0 = No distant metastasis; E: Stage IIB (TNM: T 1/2/3, N1, M0). T 1/2/3 = Tumor ≤ 2 cm > 4 cm in greatest dimension. N1 = Metastasis in one to three regional lymph nodes. M0 = No distant metastasis; F: Stage III (TNM: T 1/2/3, N2, M0 or T4, Any N, M0). T 1/2/3 = Tumor ≤ 2 cm > 4 cm in greatest dimension. N2 = Metastasis in four or more regional lymph nodes. T4 = Tumor involves celiac axis, superior mesenteric artery, and common hepatic artery, regardless of size; G: Stage IV (TNM: Any T, Any N, M1). M1 = Distant metastasis. T = Primary tumor; N = Regional lymph node; M = Distant metastasis.
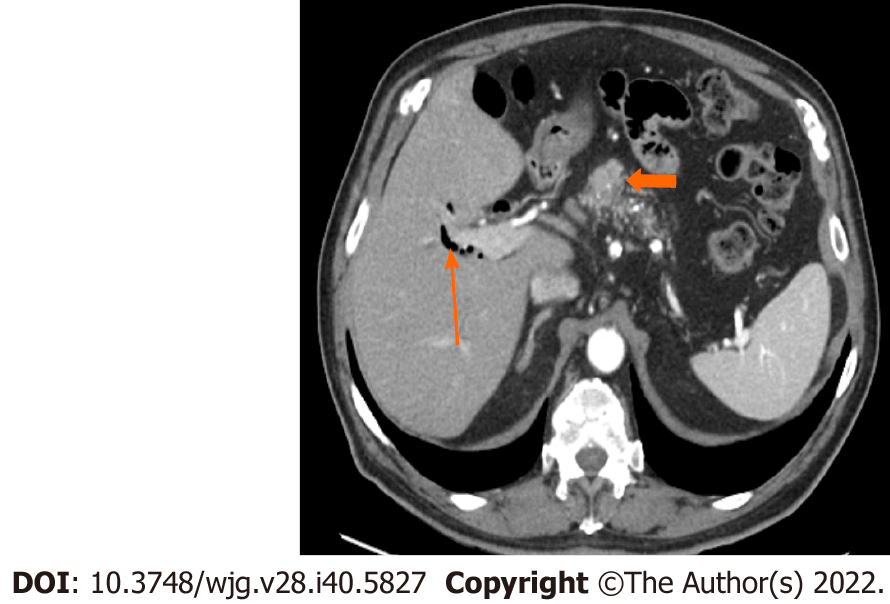
Figure 3 Stage IA (T1, N0, M0).
A 77-year-old male patient with acinar cell carcinoma. Axial post-contrast portal-venous phase computed tomography image shows a solid mass (short arrows) measuring 1.8 cm × 1.6 cm and involving the region of the pancreatic head/body. Incidental findings are calcifications seen throughout the pancreas (likely related to changes in chronic pancreatitis) and mild dilatation of the biliary tree with pneumobilia (long arrow).
Figure 4 Stage IB (T2, N0, M0).
An 89-year-old male patient with acinar cell carcinoma. Axial post-contrast computed tomography arterial phase image shows a large mass in the body of the pancreas (arrow) measuring 3.3 cm × 3 cm. No regional adenopathy is identified.
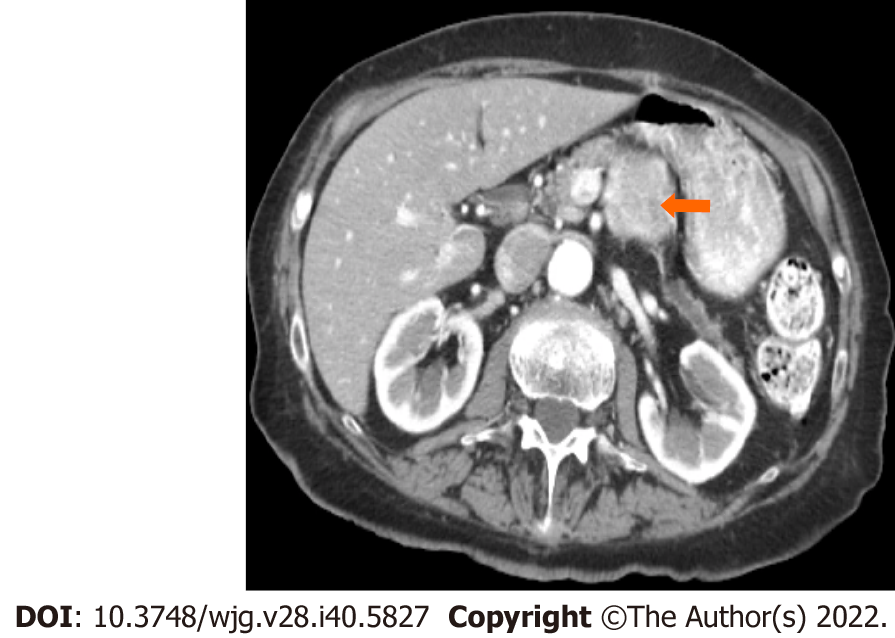
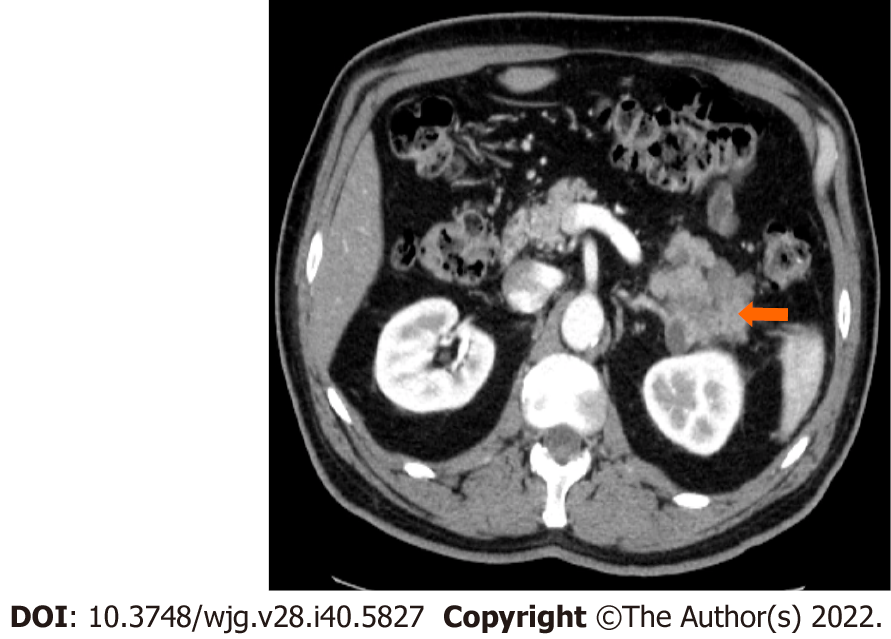
Figure 5 Stage IIA (T3, N0, M0).
A 66-year-old patient with acinar cell carcinoma. Axial post-contrast computed tomography image in the arterial phase shows a solid lobulated mass measuring 6.5 cm × 5.4 cm arising from the tail of the pancreas (arrow). The mass is heterogeneous in density with areas of low-density and solid-enhancing areas. No regional or distant lymphadenopathy was detected.
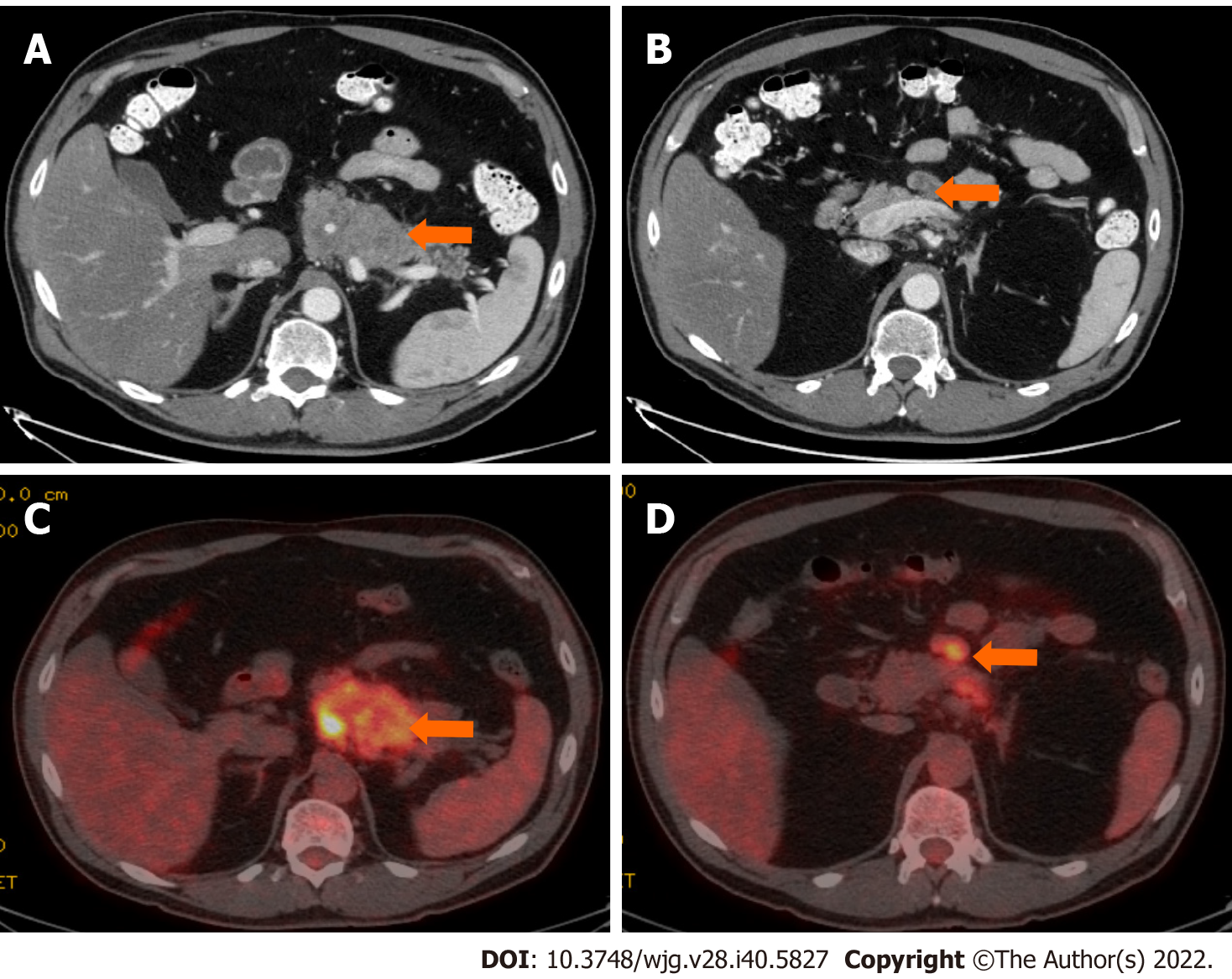
Figure 6 Stage IIB (T3, N1, M0).
A 61-year-old patient with acinar cell carcinoma. A: Axial post-contrast computed tomography (CT) image in the portovenous phase shows an infiltrative mass arising from the pancreatic body and tail (arrow); B: axial post-contrast CT images in the portovenous phase shows an enlarged mesenteric lymph node (arrow) measuring 2.6 cm × 1.2 cm; C: Axial positron emission tomography/CT image in the portovenous phase shows hypermetabolic pancreatic body and tail mass (arrow); D: Axial post-contrast CT images in the portovenous phase shows hypermetabolic enlarged mesenteric lymph node (arrow). Pathology of the mass revealed Acinar cell carcinoma with a metastatic mesenteric lymph node.
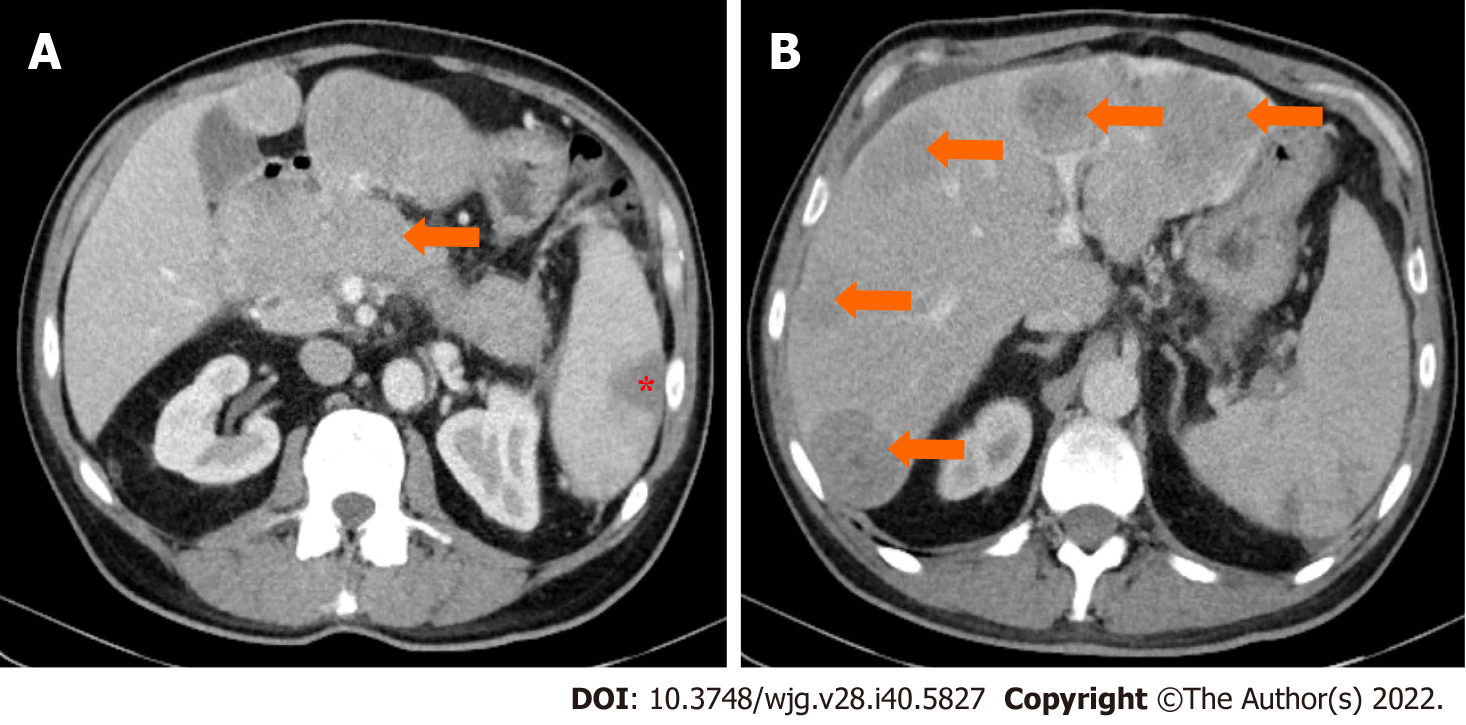
Figure 7 Stage IV.
A 64-year-old patient with acinar cell carcinoma. A: Axial post-contrast image port venous phase shows a pancreatic head mass measuring about 3.2 cm × 2.8 cm (arrow); B: Axial post-contrast image port venous phase shows multiple bilobar variable-sized hepatic metastatic lesions (arrows). An incidental finding is an area of splenic infarction (asterisk in image A).
- Citation: Calimano-Ramirez LF, Daoud T, Gopireddy DR, Morani AC, Waters R, Gumus K, Klekers AR, Bhosale PR, Virarkar MK. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(40): 5827-5844
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i40/5827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5827