Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2022; 28(34): 4943-4958
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.4943
Published online Sep 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.4943
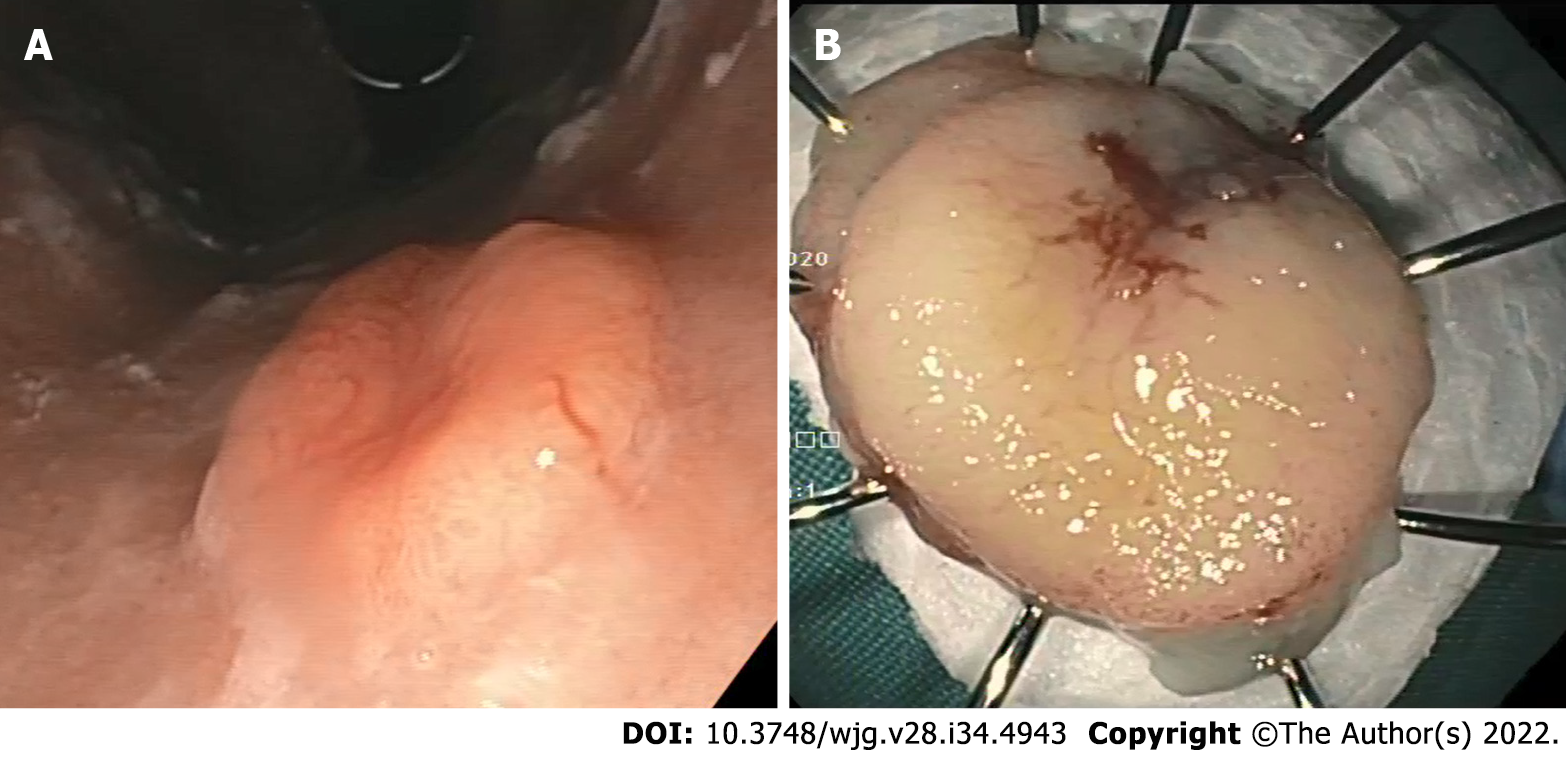
Figure 1 Gastric neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Endoscopic image demonstrates a flat lesion in the stomach fundus with depressed center; B: Endoscopic en bloc resection was achieved.
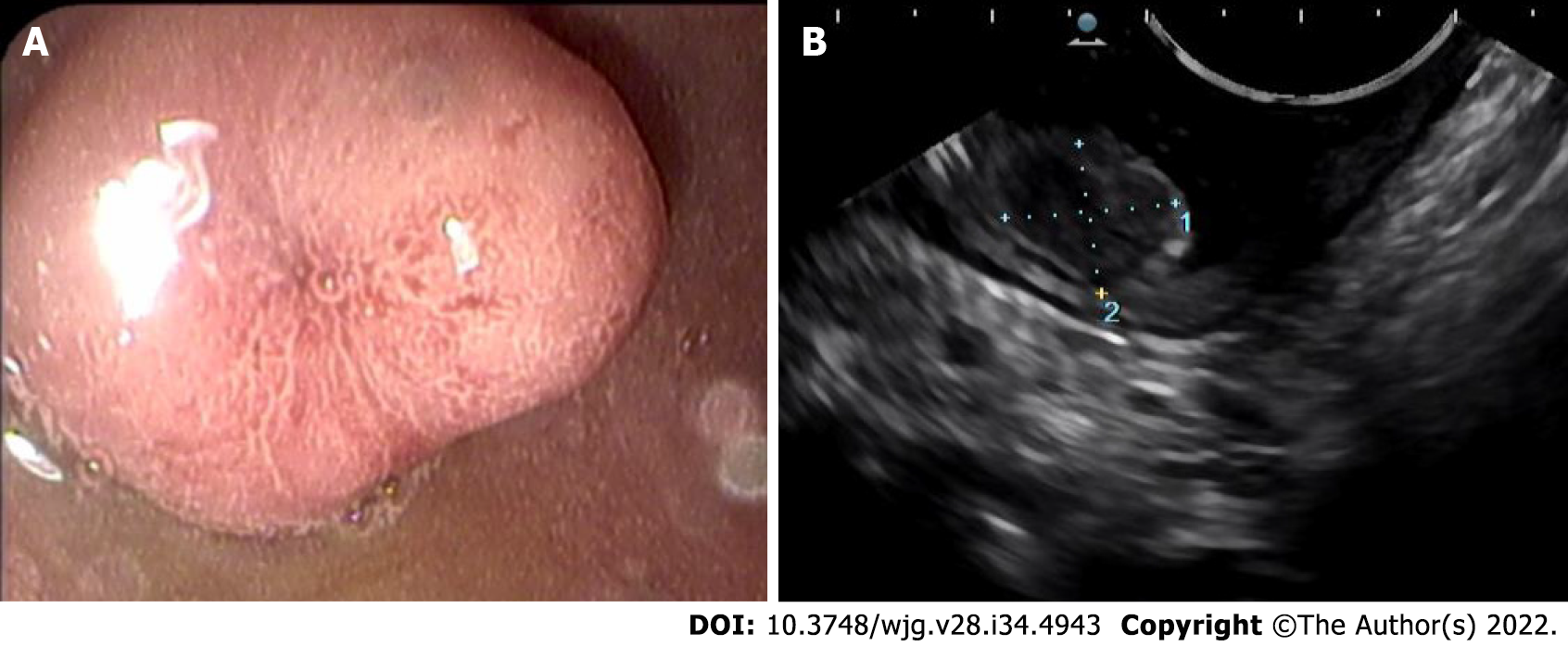
Figure 2 Duodenal neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Endoscopic image demonstrates a sessile polyp with central depression; B: Endoscopic ultrasound demonstrates a hypoechoic intramural structure in the submucosal layer of the duodenal wall.
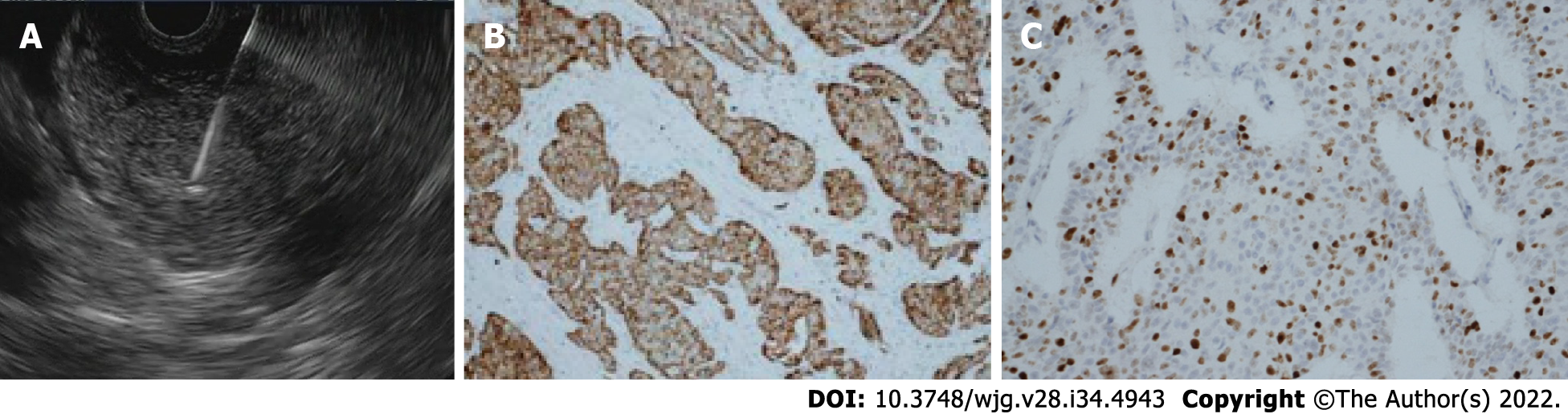
Figure 3 Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm.
A: Endoscopic ultrasound revealed a 15 mm hypoechoic lesion of the pancreas; B: Stained immun
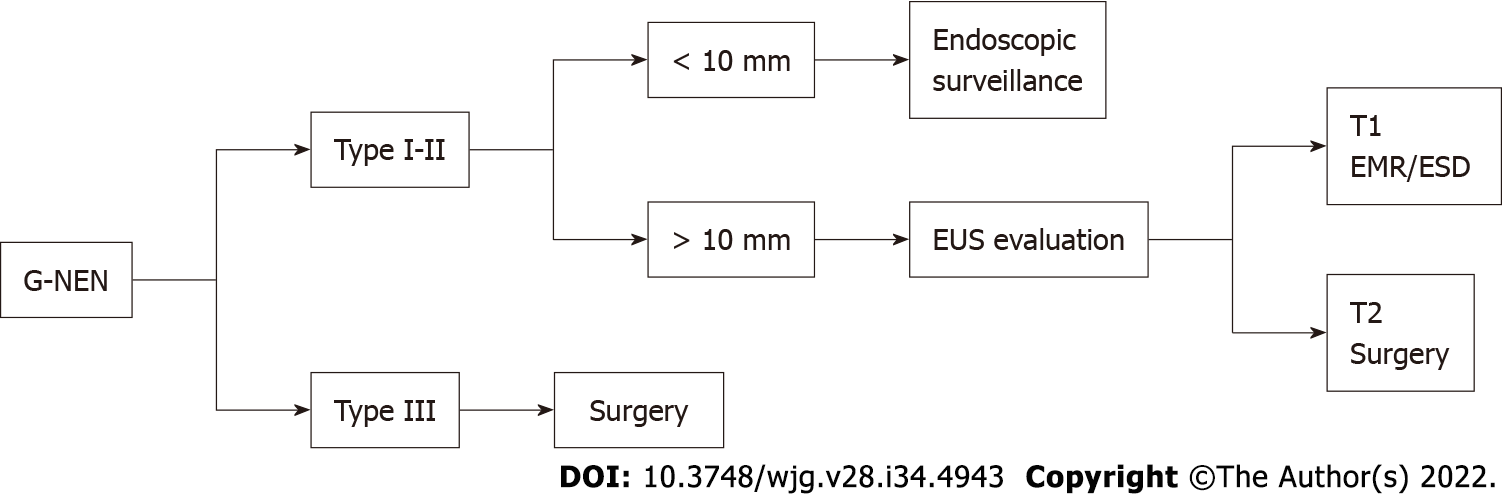
Figure 4 Algorithm for gastric neuroendocrine neoplasm management.
EMR: Endoscopic mucosal resection; ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasonography; G-NEN: Gastric neuroendocrine neoplasm.
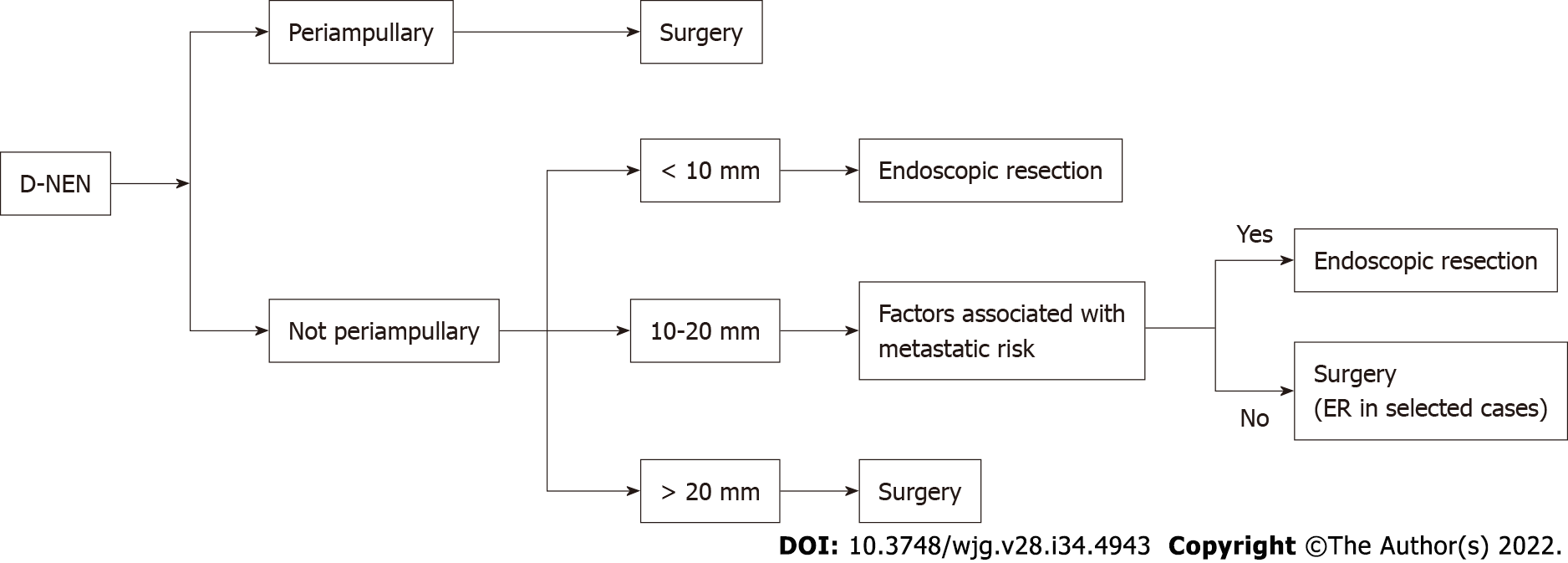
Figure 5 Algorithm for duodenal neuroendocrine neoplasms management.
D-NEN: Duodenal neuroendocrine neoplasm; ER: Endoscopic resection.
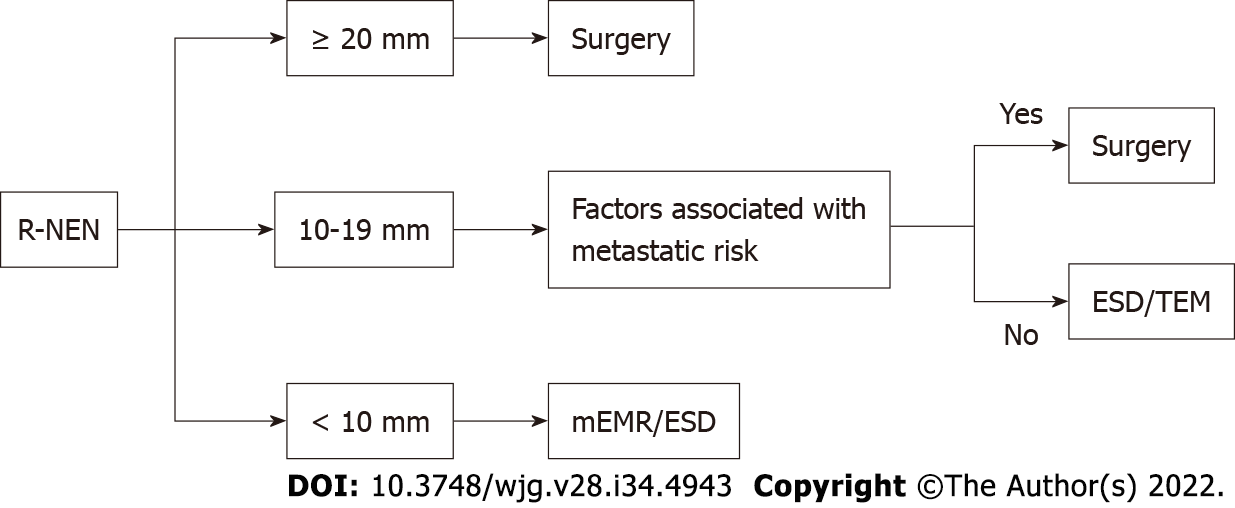
Figure 6 Algorithm for rectal neuroendocrine neoplasms management.
ESD: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; mEMR: Modified endoscopic mucosal resection; R-NEN: Rectal neuroendocrine neoplasm; TEM: Transanal endoscopic microsurgery.
- Citation: Iabichino G, Di Leo M, Arena M, Rubis Passoni GG, Morandi E, Turpini F, Viaggi P, Luigiano C, De Luca L. Diagnosis, treatment, and current concepts in the endoscopic management of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(34): 4943-4958
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i34/4943.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i34.4943