Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2022; 28(30): 4120-4132
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4120
Published online Aug 14, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4120
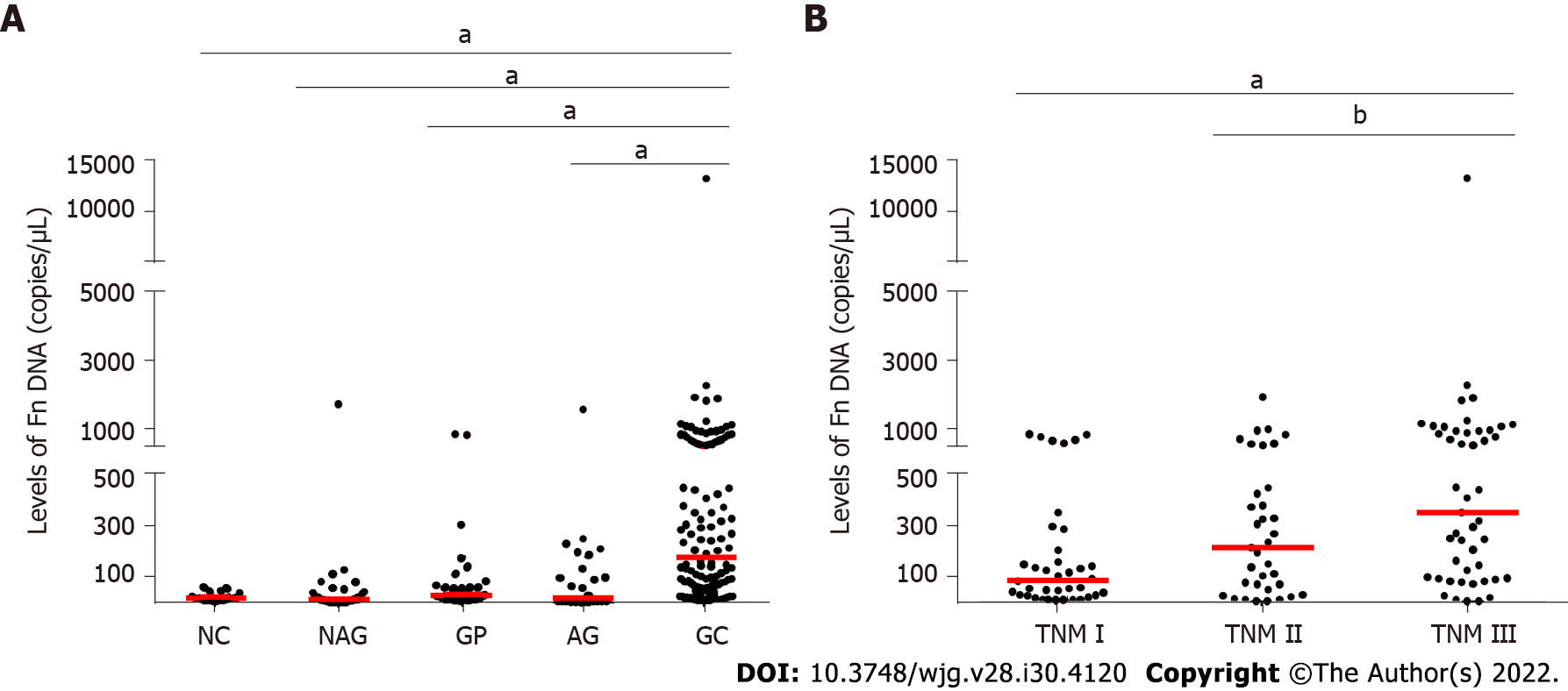
Figure 1 Fusobacterium nucleatum levels in different groups.
A: Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) levels in normal control, atrophic gastritis (AG), non-AG, gastric polyps, and gastric cancer (GC) groups; B: Fn levels in different TNM stages of GC patients. Red lines represent the median. aP < 0.001, bP < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test). NC: Normal controls; NAG: Non-atrophic gastritis; GP: Gastric polyps; AG: Atrophic gastritis; GC: Gastric cancer; Fn: Fusobacterium nucleatum.
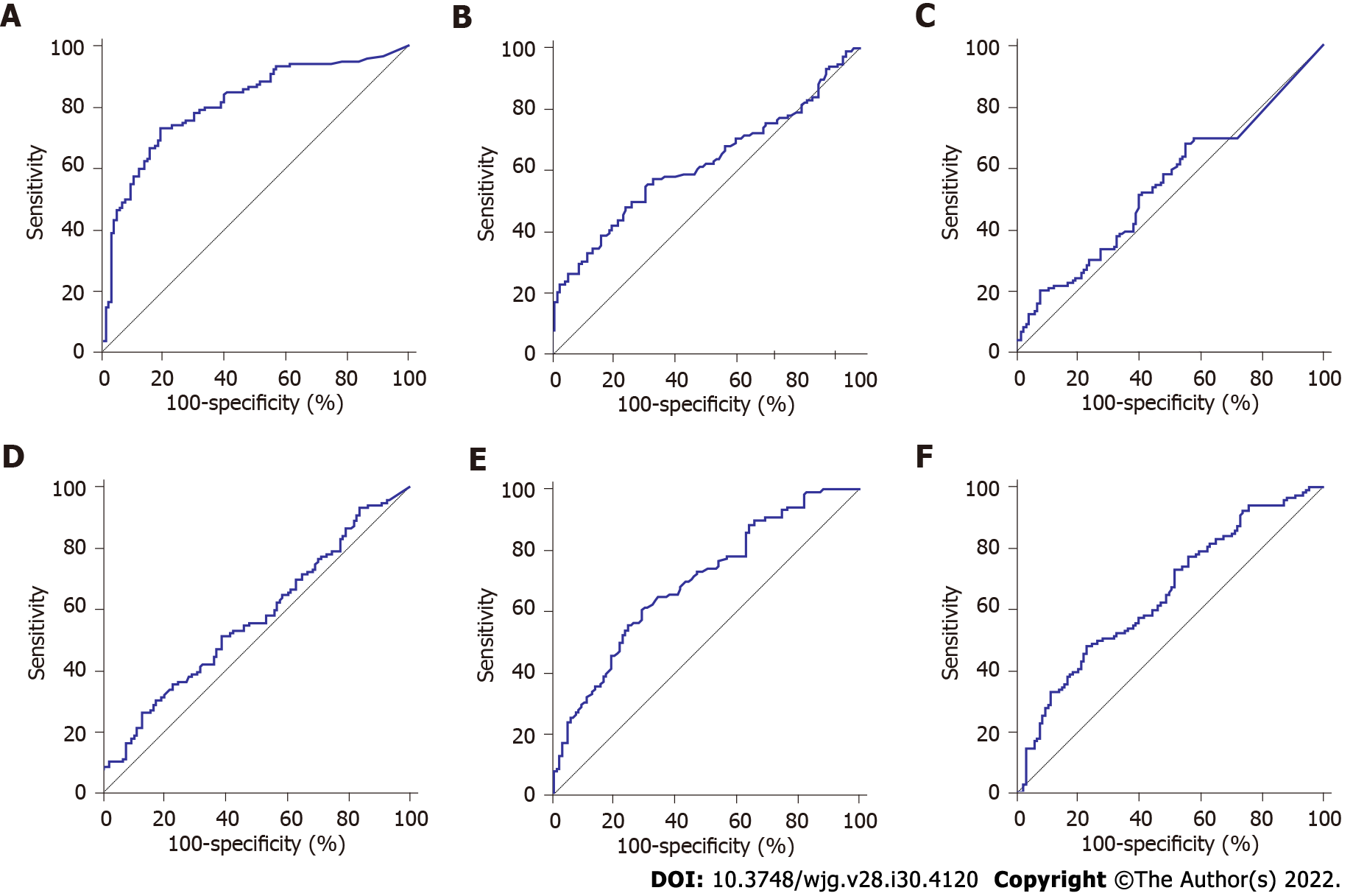
Figure 2 Diagnostic significance analysis of Fusobacterium nucleatum and traditional serum markers.
Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for the detection of gastric cancer. A: Fusobacterium nucleatum; B: Carcinoembryonic antigen; C: Carbohydrate antigen 72-4; D: Carbohydrate antigen 19-9; E: Ferritin; F: Sialic acid.
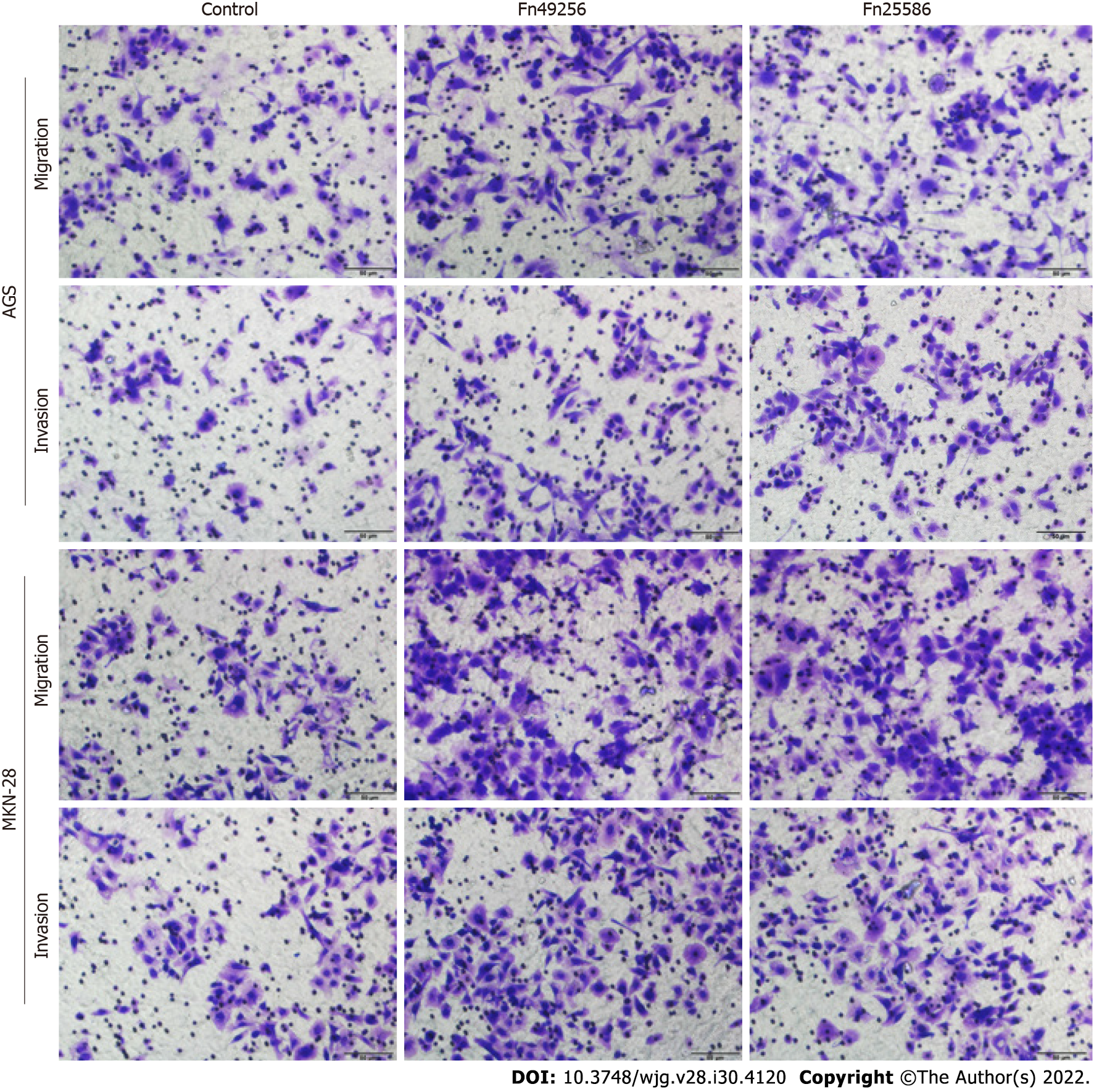
Figure 3 Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes the invasion of gastric cancer cells.
Transwell assay of AGS and MKN-28 cells was performed 48 h after coculture with Fusobacterium nucleatum. The cells in the control group were treated with phosphate buffer solution. Fn: Fusobacterium nucleatum.
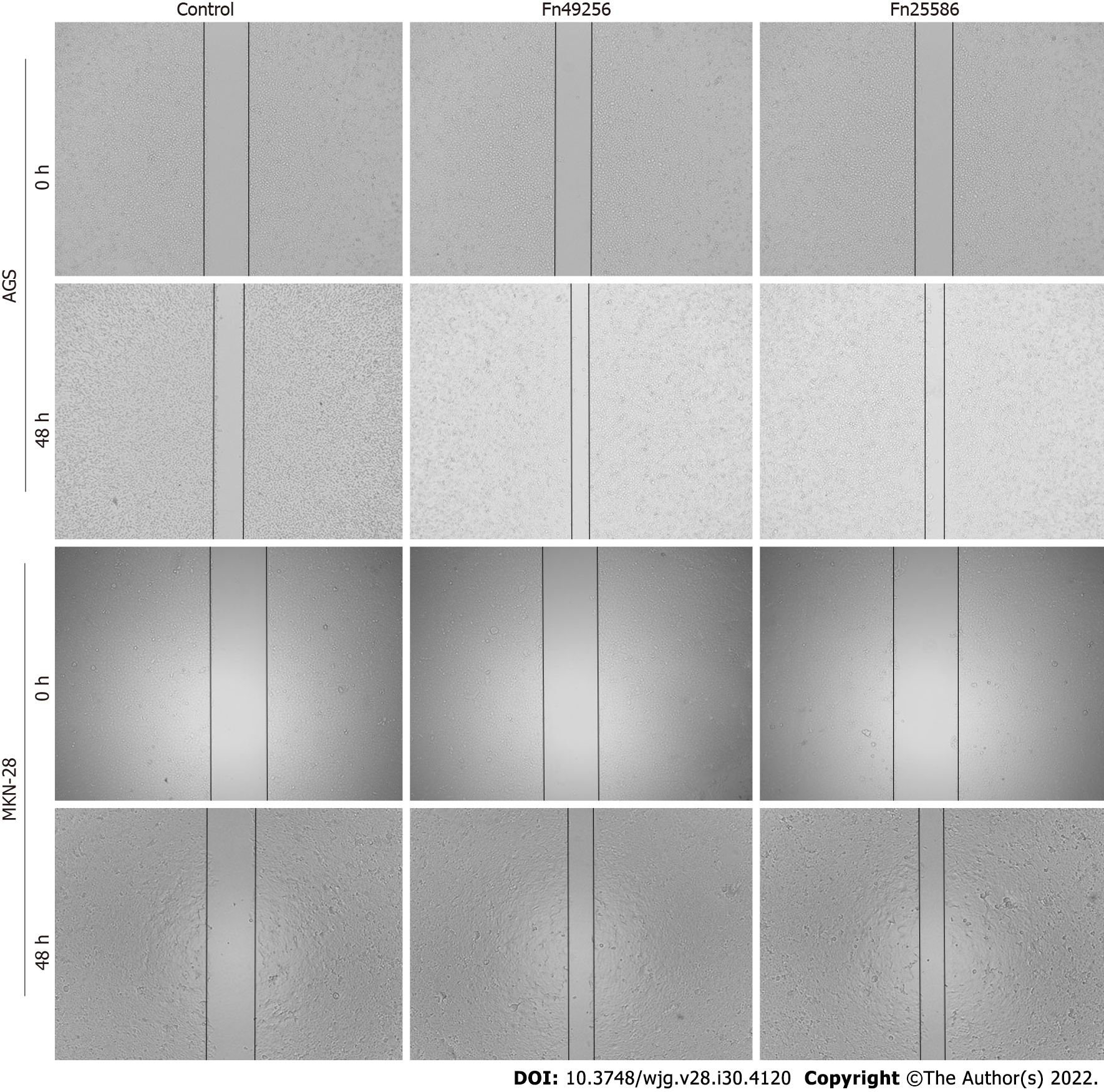
Figure 4 Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes the migration of gastric cancer cells.
Wound-healing assay of AGS and MKN-28 cells was performed 48 h after coculture with Fusobacterium nucleatum. The cells in the control group were treated with phosphate buffer solution. Fn: Fusobacterium nucleatum.
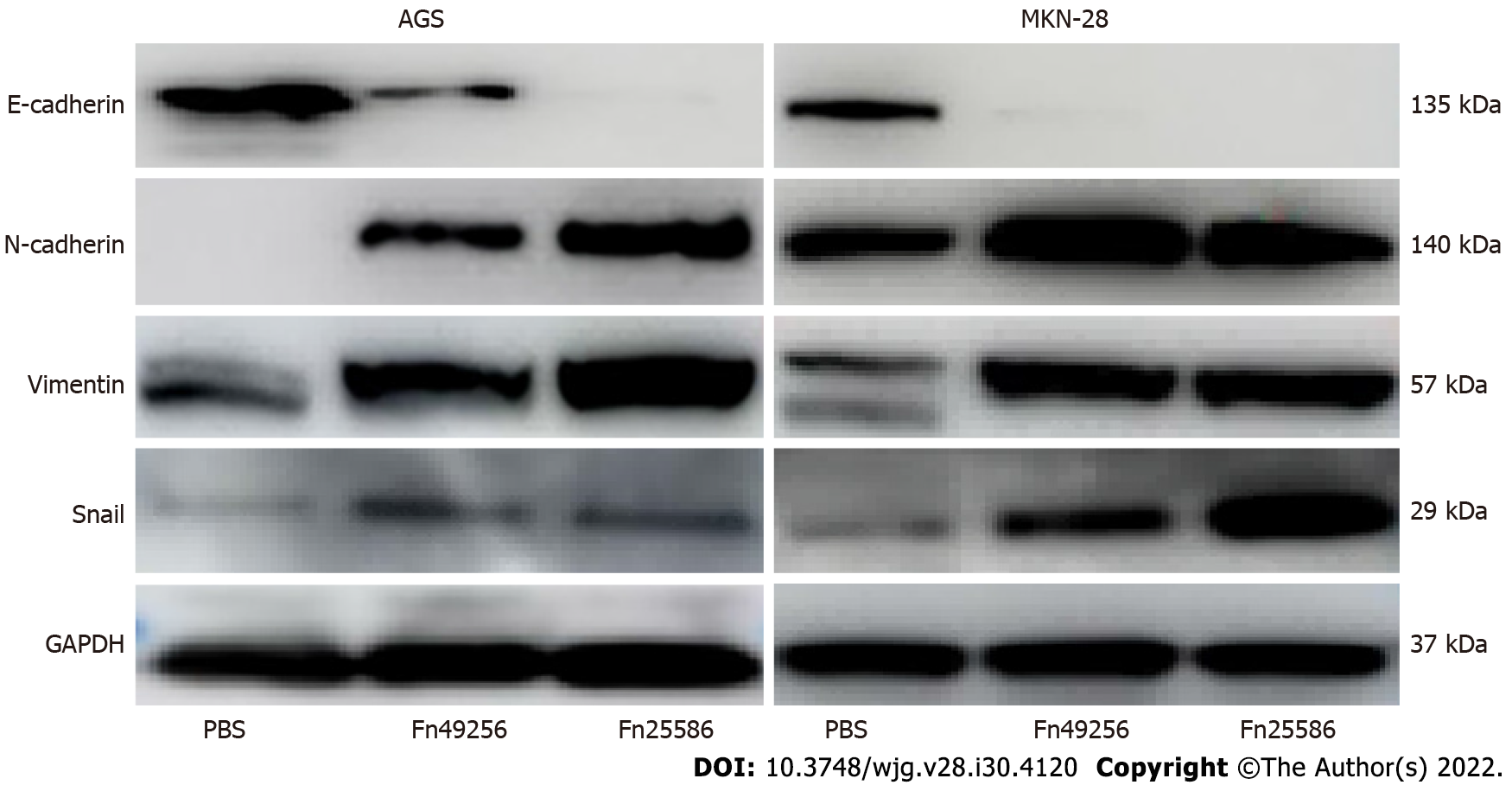
Figure 5 Fusobacterium nucleatum enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition of AGS and MKN-28 cells.
Fn: Fusobacterium nucleatum; PBS: Phosphate buffer solution; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Chen WD, Zhang X, Zhang MJ, Zhang YP, Shang ZQ, Xin YW, Zhang Y. Salivary Fusobacterium nucleatum serves as a potential diagnostic biomarker for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(30): 4120-4132
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i30/4120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i30.4120