Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2022; 28(29): 3814-3824
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3814
Published online Aug 7, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3814
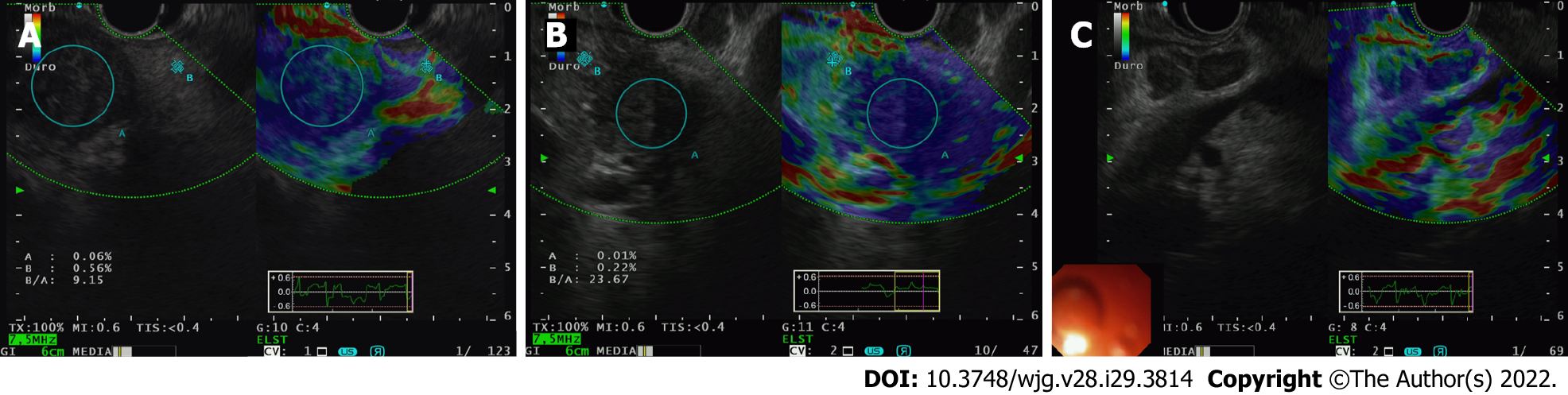
Figure 1 Endoscopic ultrasound-elastography.
A and B: Endoscopic ultrasound-elastography (EUS-E) use in demonstrating stiffness of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissue (encircled A) against normal pancreatic parenchyma (encircled B); C: EUS-E use in demonstrating stiffness of metastatic lymph nodes in patient from B. The nodes in B-mode when seen with elastography are blue, indicating that it’s hard and potentially malignant.
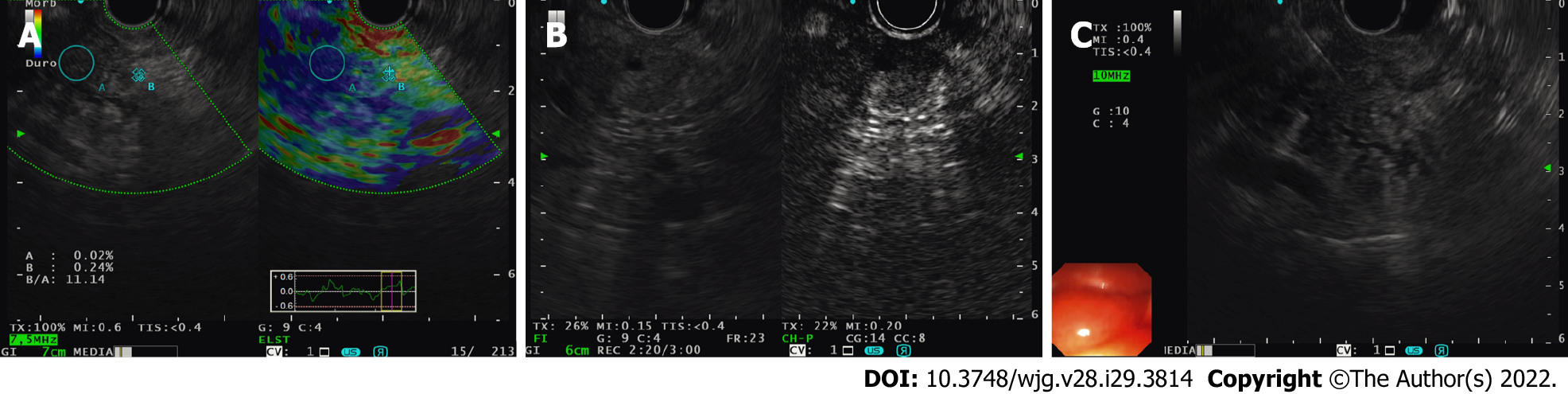
Figure 2 The clinical application of endoscopic ultrasound-elastography (with contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound) to target fine needle biopsy sampling in a patient with a degenerated intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm under our surveillance.
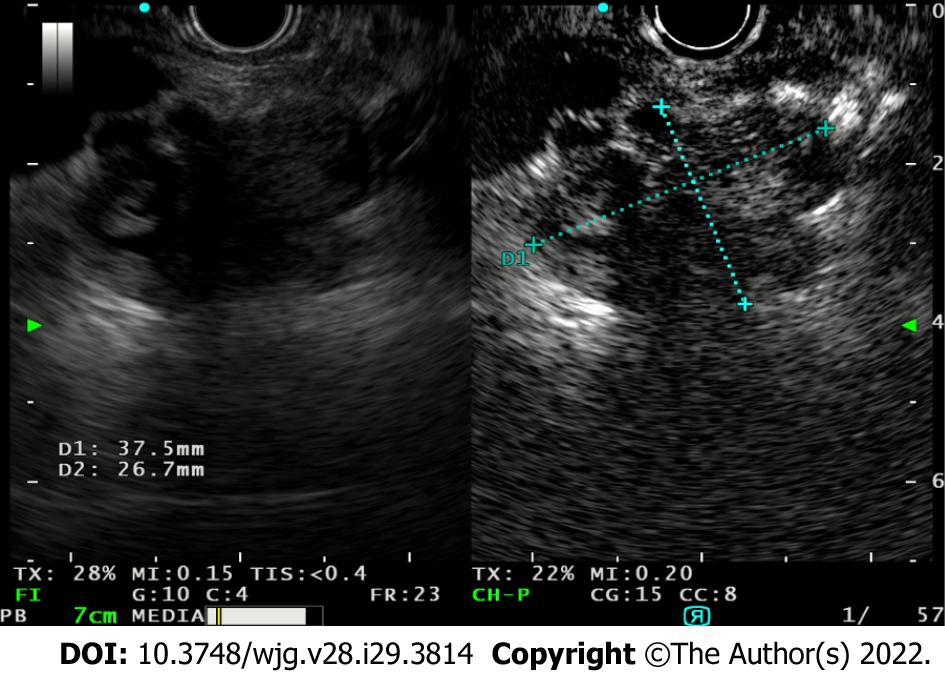
A: Case demonstration of a degenerated intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and combination use of endoscopic ultrasound-elastography (EUS-E) to direct fine needle biopsy (FNB) sampling. Pre-EUS-E, the area of concern was iso-echoic, resembling normal parenchyma; however, under EUS-E, the area is stiff (blue); B: Contrast use post-FNB showing hypo-enhancement of the area of concern, confirming the area previously highlighted by EUS-E; C: Post-EUS-E and contrast-enhanced EUS guided FNB sampling in the same patient, allowing targeted sampling of the hard area.
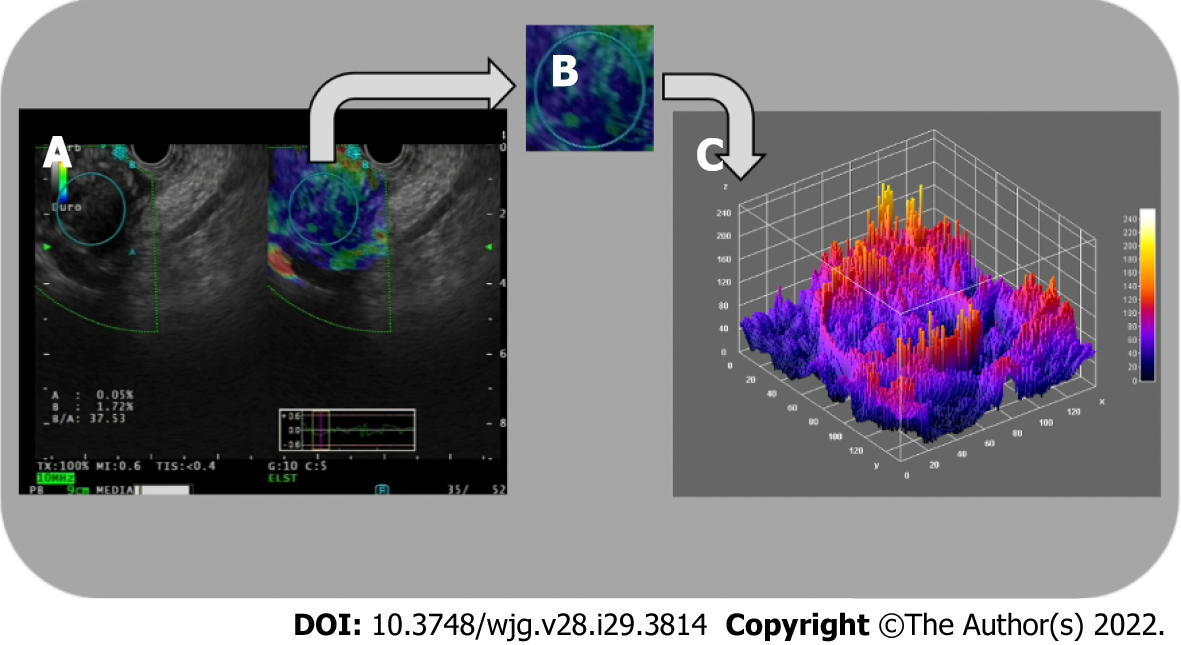
Figure 3 Three-dimensional surface fractal dimension estimate.
A and B: Endoscopic ultrasound-elastography images (A) are used to highlight representative parenchymal regions (B) of solid pancreatic lesions; C: A computer-aided image analysis system generates an irregularly-shaped three-dimensional surface as a “shape matrix” of points with the column and row numbers proportional to the x and y coordinates and with the depth information z (x, y) stored as a matrix element. The three-dimensional fractal dimension, which is an index of the “surface roughness”, is automatically determined using the box-counting algorithm. The fractal dimension of a surface is expressed by a real number greater than 2 (the Euclidean dimension of a two-dimensional surface) and less than 3 (the Euclidean dimension of a solid). A surface with a higher surface fractal dimension is wrinkled than one with a lower dimension.
Figure 4 Use of contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound to study the evolution of a degenerated intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and the vegetations within, allowing differentiate between mucus and vegetations as only tumor vegetations will show inhomogeneous enhancement.
Figure 5 Graphical representation of existing diagnostic applications to endoscopic ultrasound imaging in the form of a fractal tree, fractal analysis with artificial intelligence being the possible future of enhanced endoscopic ultrasound imaging.
AI: Artificial intelligence; CH-EUS: Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound; FNB: Fine needle biopsy.
- Citation: Spadaccini M, Koleth G, Emmanuel J, Khalaf K, Facciorusso A, Grizzi F, Hassan C, Colombo M, Mangiavillano B, Fugazza A, Anderloni A, Carrara S, Repici A. Enhanced endoscopic ultrasound imaging for pancreatic lesions: The road to artificial intelligence. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(29): 3814-3824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i29/3814.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i29.3814