Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2022; 28(27): 3435-3454
Published online Jul 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3435
Published online Jul 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3435
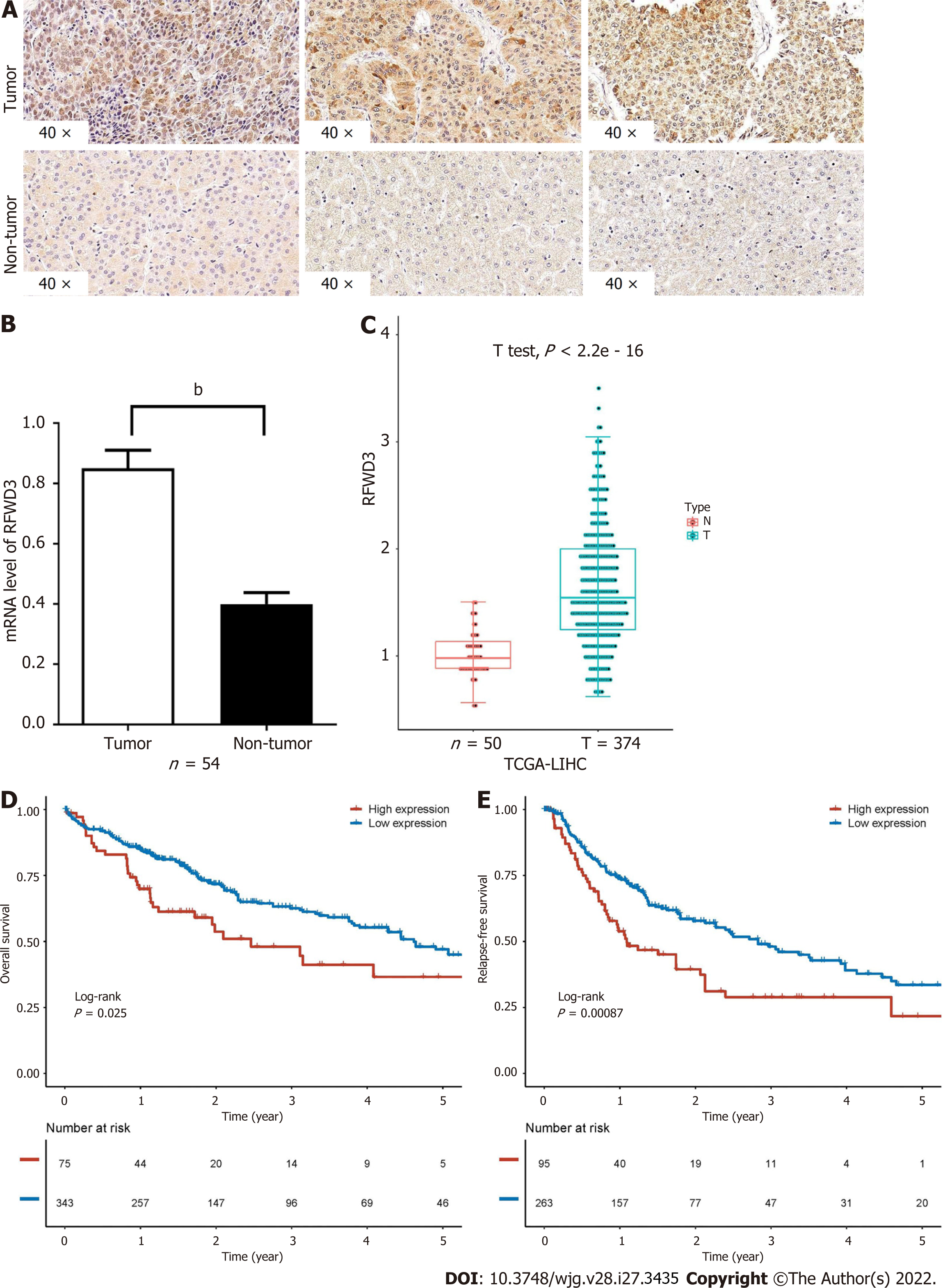
Figure 1 Expression of RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with a worse prognosis.
A: RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3) expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor and non-tumor tissues detected using immunohistochemical staining; B: Expression analysis of RFWD3 in 54 tissue sample pairs (some invalid samples were removed) using quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (bP < 0.01); C: Comparison of RFWD3 expression between tumor and non-tumor tissues in HCC patients (T = 374, n = 50, the data source is the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) (TCGA) database); D and E: Kaplan-Meier survival curves of HCC patients with high and low expression of RFWD3 (n = 91, the data source is the TCGA database).
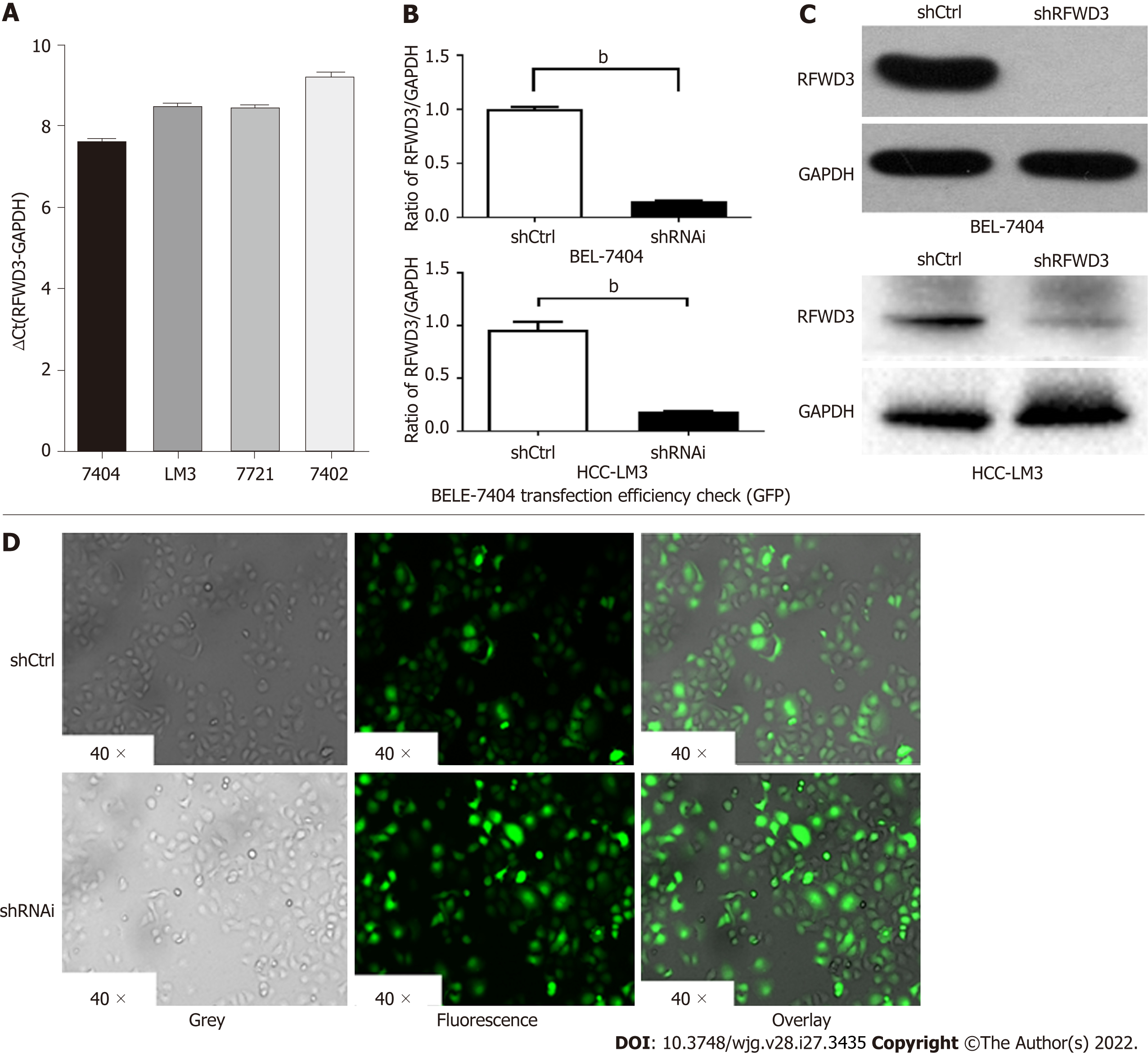
Figure 2 Validation of lentivirus knockdown efficiency in cell lines.
A: RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3) expression in BEL-7404 and Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-LM3 cells obtained using quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis; B and C: The shRNAi group shows obvious knockdown of RFWD3 [BEL-7404: qRT-PCR: bP < 0.01, western blot (WB): bP < 0.01; HCC-LM3: qRT-PCR: bP < 0.01, WB: bP < 0.01]; D: Confirmation of the lentivirus transduction efficiency using GFP fluorescence imaging.
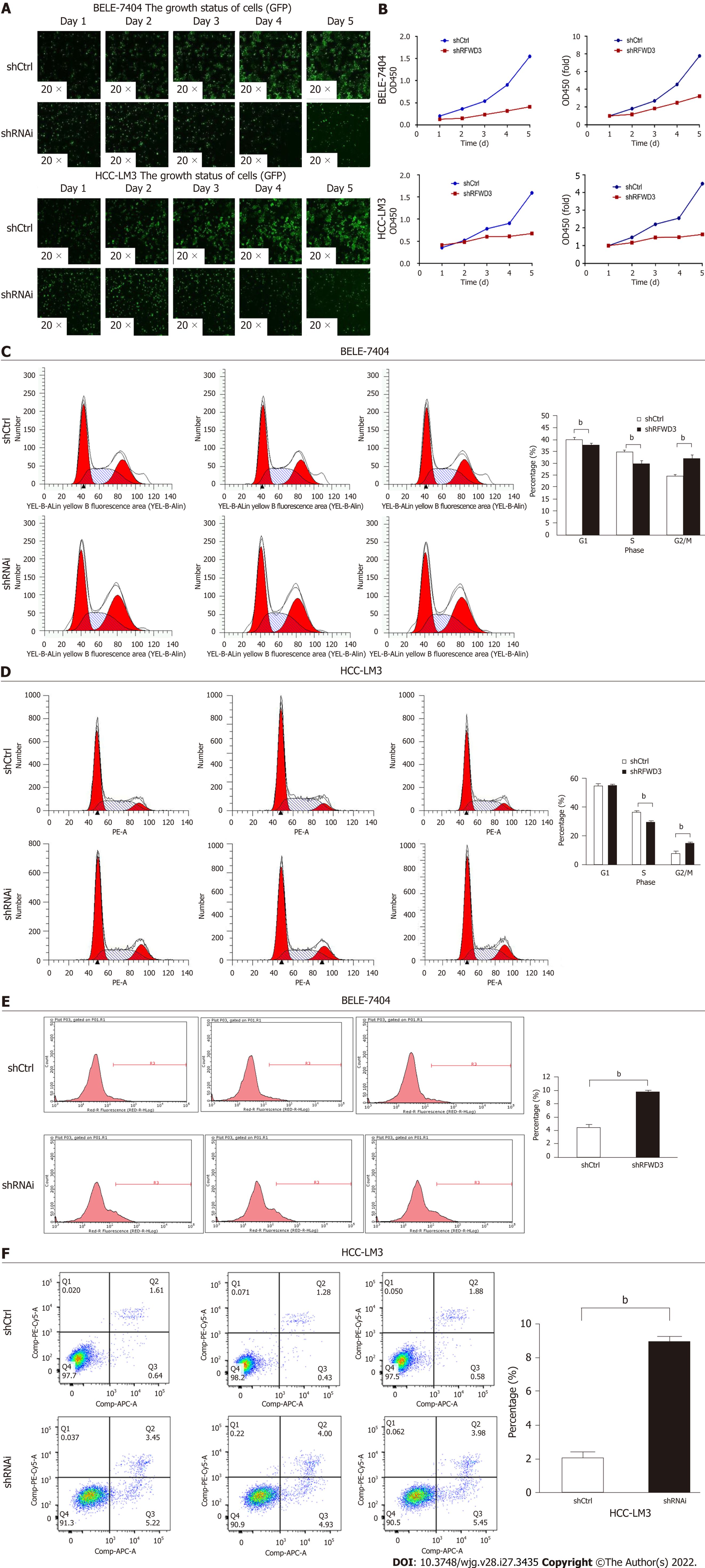
Figure 3 RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 knockdown inhibits cell growth and proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
A: Cell growth and proliferation of BEL-7404, Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-LM3 shRNAi, and shCtrl cells continuously monitored using a Celigo instrument for five days; B: MTT assay demonstrating that RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 siRNA significantly reduced the proliferation of HCC cells; C and D: The cell cycle progression evaluated by flow cytometry (FCM) with propidium iodide (PI) and RNase A (bP < 0.01); E and F: FCM to assess the apoptosis in shRNAi and shCtrl groups of cells using Annexin V-APC/PI Apoptosis Detection Kit (bP < 0.01).
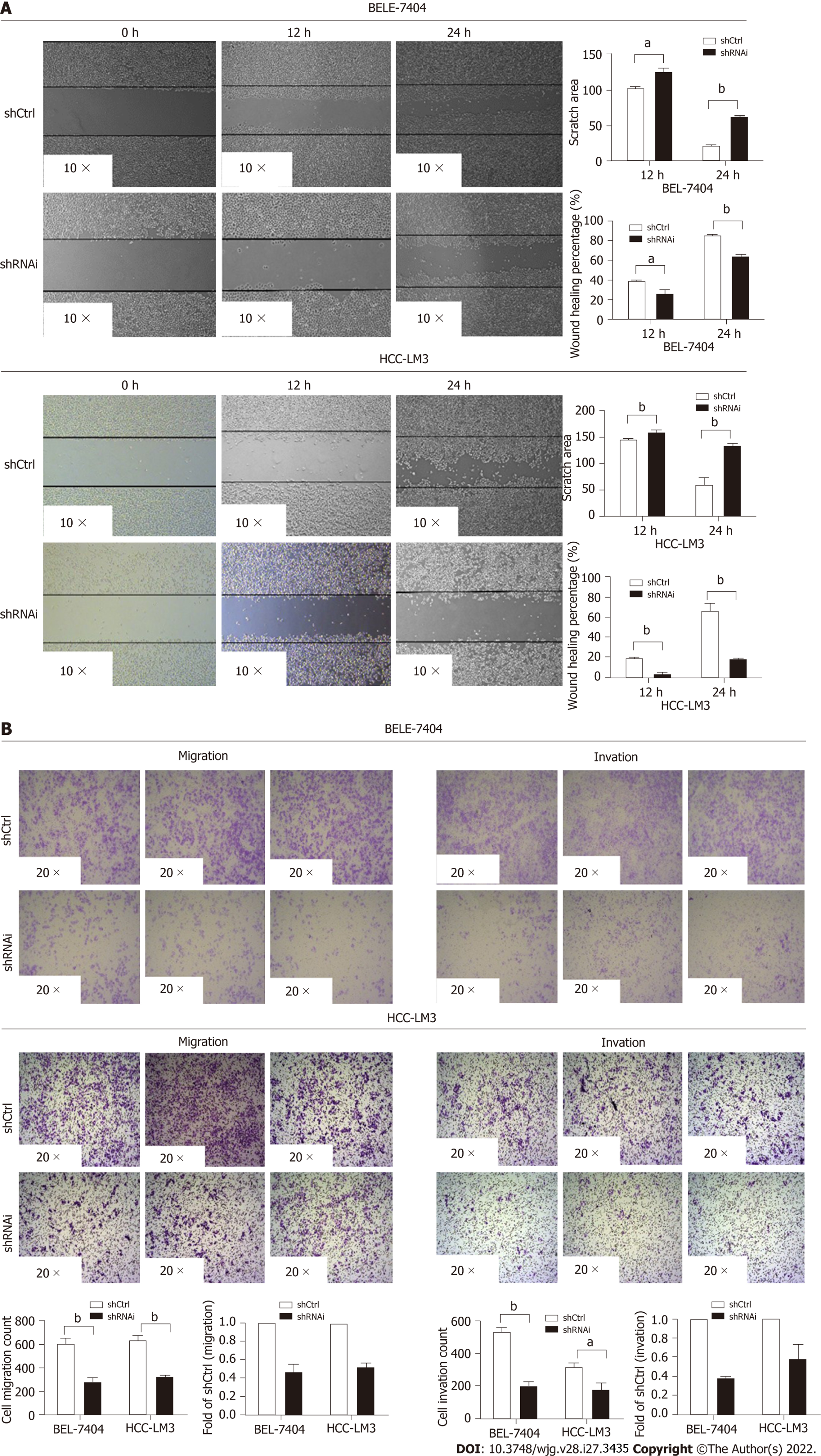
Figure 4 RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 knockdown reduces hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and migration.
A: Wound-healing assay in the shCtrl and shRNAi groups (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01); B: The migration ability of both BEL-7404 and hepatocellular carcinoma-LM3 shRNAi cells. Invasion assays demonstrating similar results (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01).
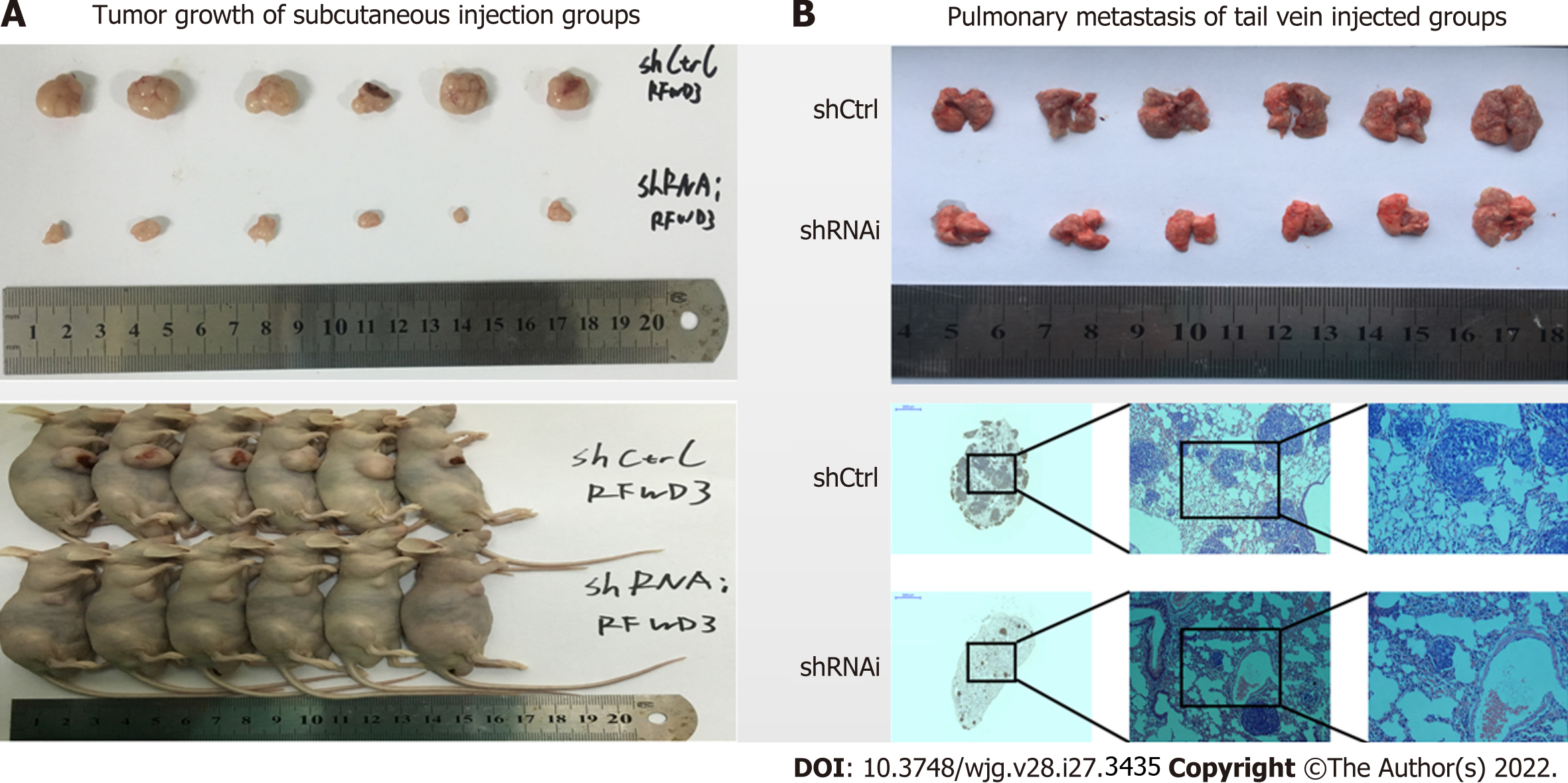
Figure 5 RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 knockdown reduces hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vivo.
A: Imaging analysis of the tumor and lung tissues of mice injected with shRNAi and shCtrl cells; B: Imaging analysis of pulmonary metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in mice injected with shRNAi and shCtrl cells.
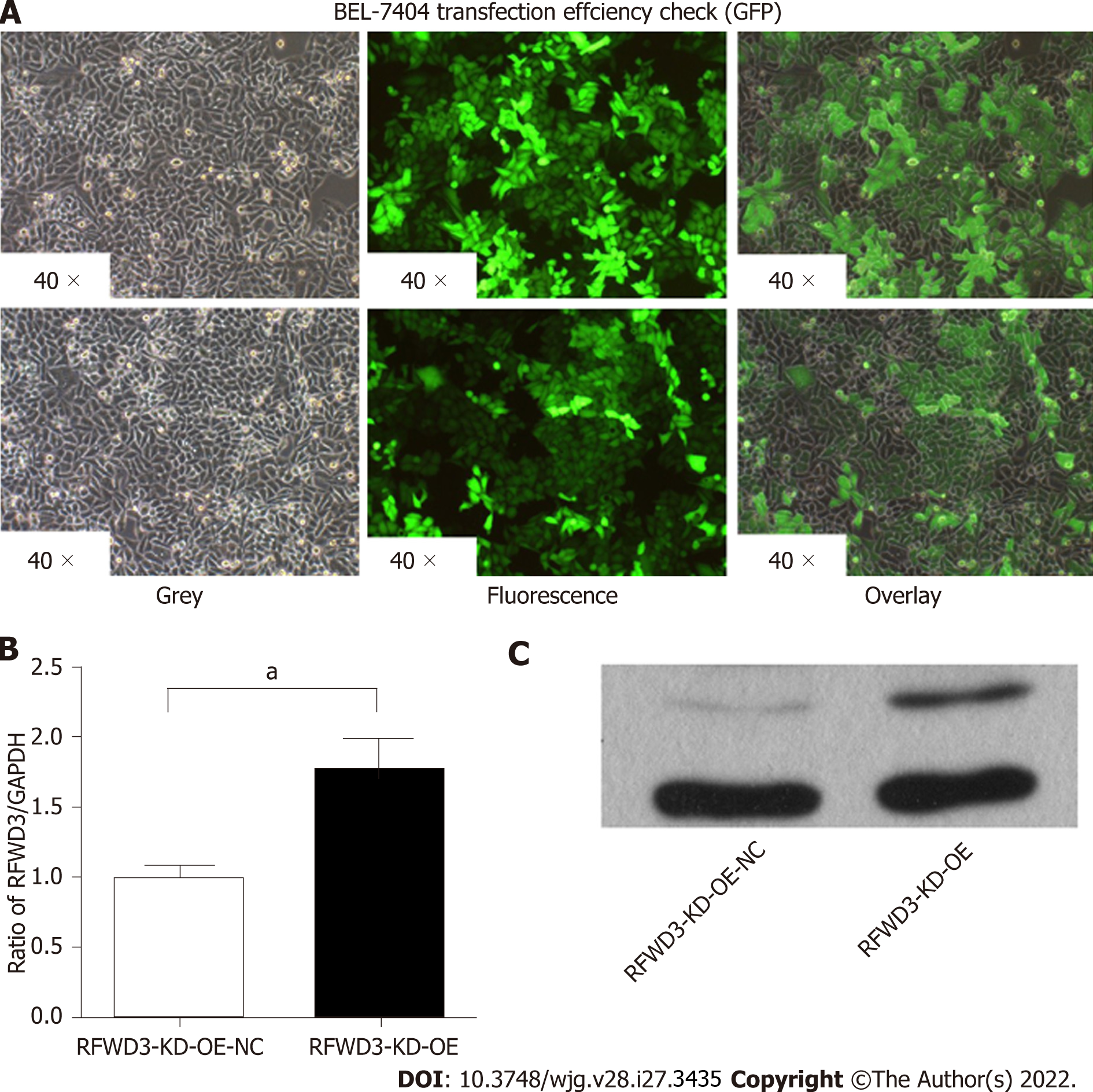
Figure 6 Validation of lentiviral-mediated rescue RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 shRNAi efficiency in cell lines.
A: GFP fluorescence imaging confirms the lentivirus transduction efficiency; B: Compared with the RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3)-KD-OE-NC group, the RFWD3-KD-OE group shows upregulated RFWD3 in the quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis (aP < 0.05); C: Western blot analysis confirms the same upshot.
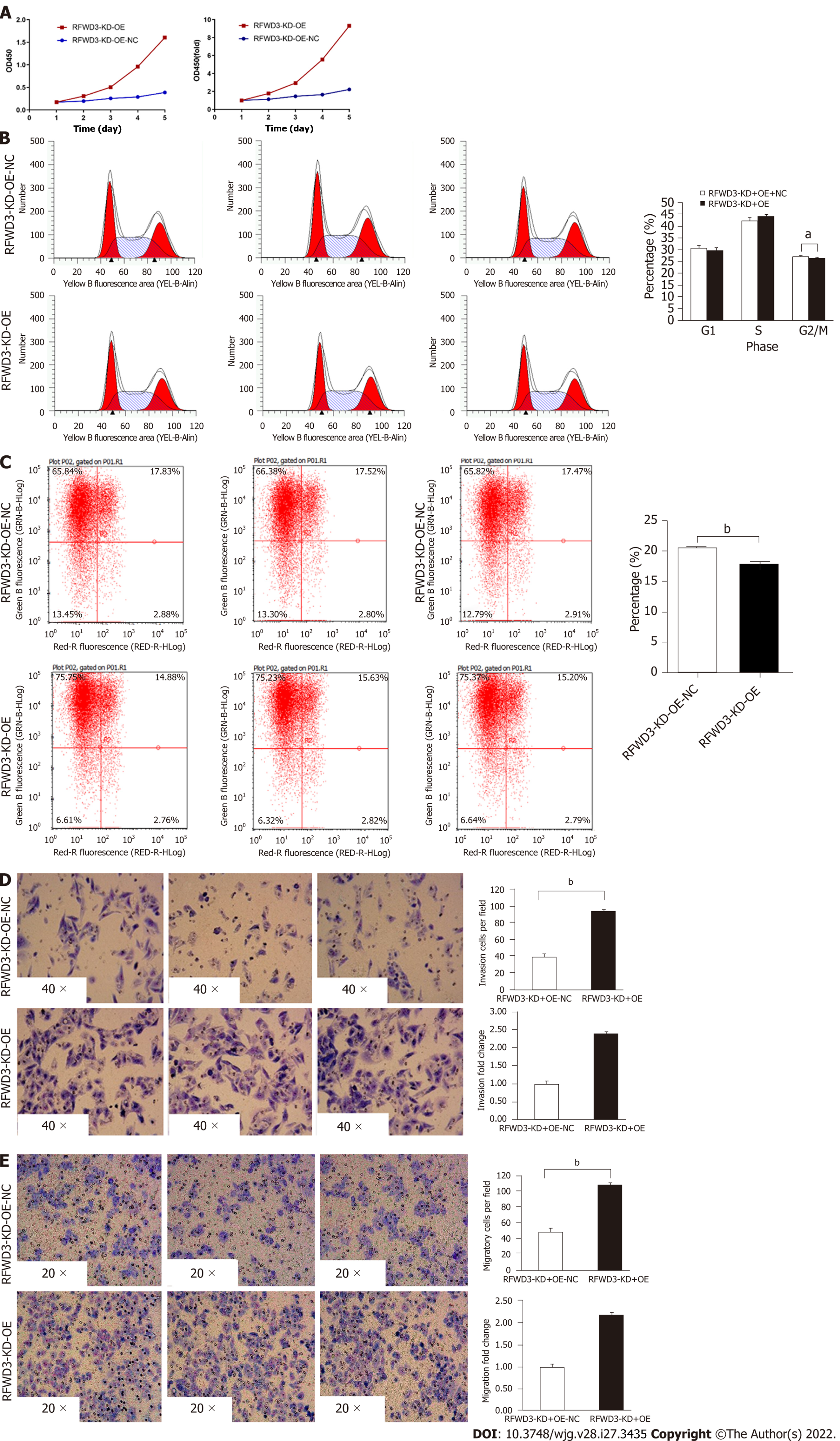
Figure 7 RING finger and WD repeat domain 3-KD-OE reverses the cell phenotype of shRNAi BEL-7404 cells.
A: MTT assay; B: The cell cycle distribution in RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3)-KD-OE-NC and RFWD3-KD-OE cells (aP < 0.05); C: Rate of apoptosis in RFWD3-KD-OE-NC and RFWD3-KD-OE groups (bP < 0.01); D and E: RFWD3-KD-OE resumes BEL-7404 shRNAi cell invasion and migration ability in transwell (bP < 0.01) and invasion assays (bP < 0.01).
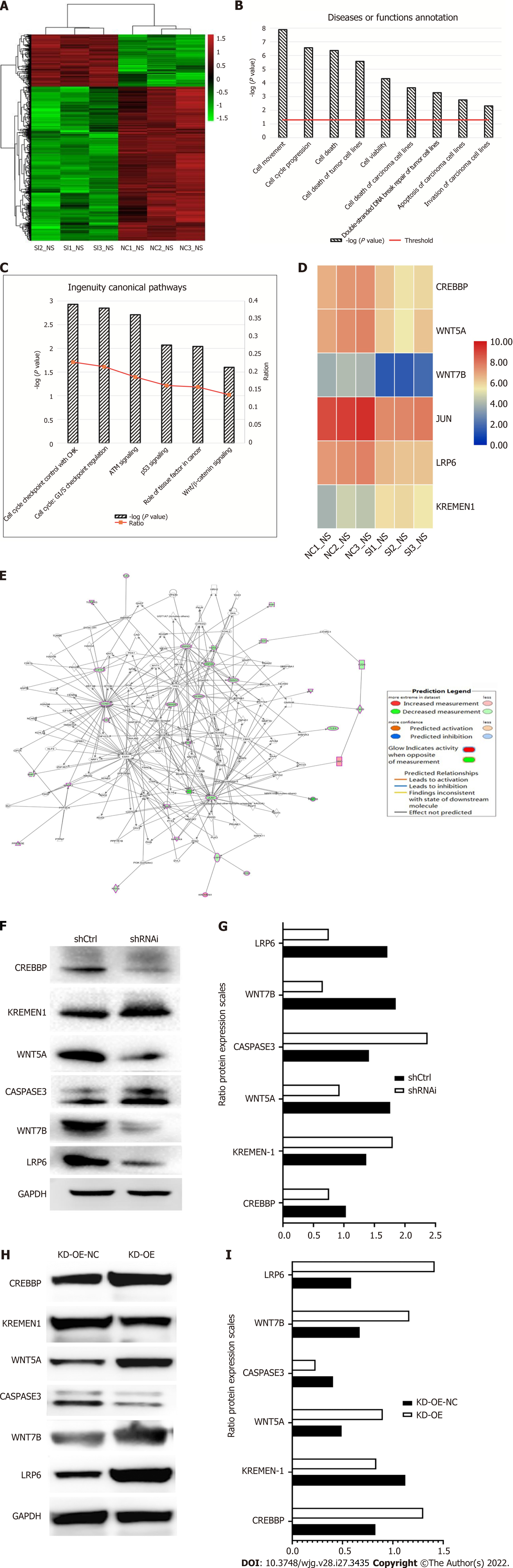
Figure 8 shRFWD3i influences the progress of hepatocellular carcinoma through the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway.
A: Heatmap analysis showing the gene expression changes after RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 (RFWD3) silencing (454 genes, above 2-fold); B: Disease and functional analysis to classify genes enriched after RFWD3 silencing; C: Classical pathway analysis indicates genes enriched after RFWD3 silencing; D: The microarray analysis reveals alteration in the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway following RFWD3 silencing; E: Knowledge-based interaction network of Wnt/β-catenin signalling targets (> 2-fold change, P < 0.05). The intensity of the node color indicates the degree of upregulation (red) or downregulation (green) following RFWD3 silencing in hepatocellular carcinoma cells; F-I: The expression of CREBBP, Wnt5A, JUN, Wnt7B and LRP6 were decreased, and the expression of KREMEN-1 was increased in the shRNAi group using western blot analysis, in rescue experiment, the results are reversed.
- Citation: Liang RP, Zhang XX, Zhao J, Lu QW, Zhu RT, Wang WJ, Li J, Bo K, Zhang CX, Sun YL. RING finger and WD repeat domain 3 regulates proliferation and metastasis through the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(27): 3435-3454
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i27/3435.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3435