Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2022; 28(27): 3346-3358
Published online Jul 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3346
Published online Jul 21, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3346
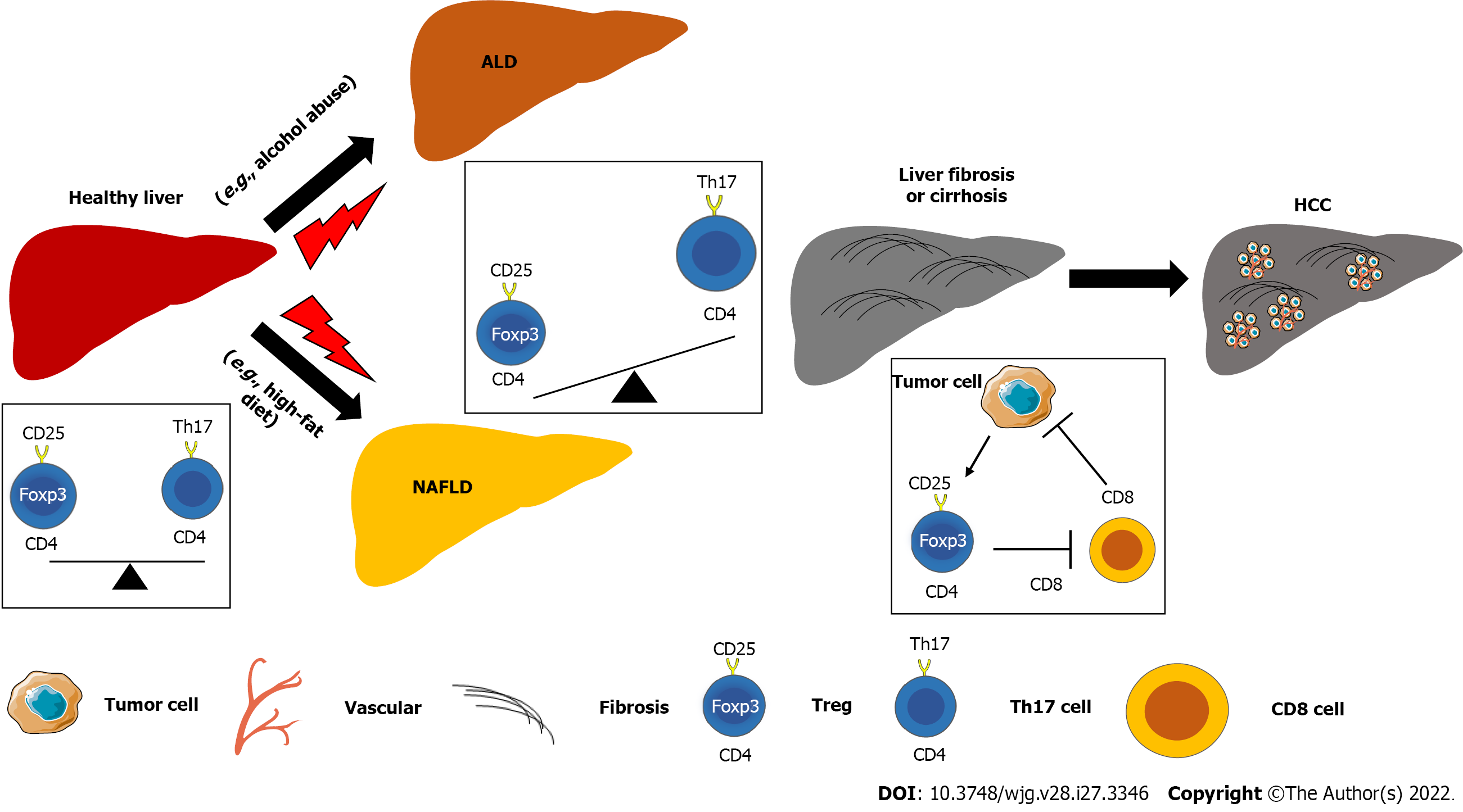
Figure 1 The imbalance of regulatory T cells and effector T cells promotes the progression of chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Chronic liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by factors such as alcohol abuse and high-fat diet, respectively, can induce liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma. The imbalance of regulatory T cells with T helper 17 cells or CD8 T cells is involved in the pathogenesis of liver inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer progression. ALD: Alcoholic liver disease; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Treg: Regulatory T cells; Th: T helper.
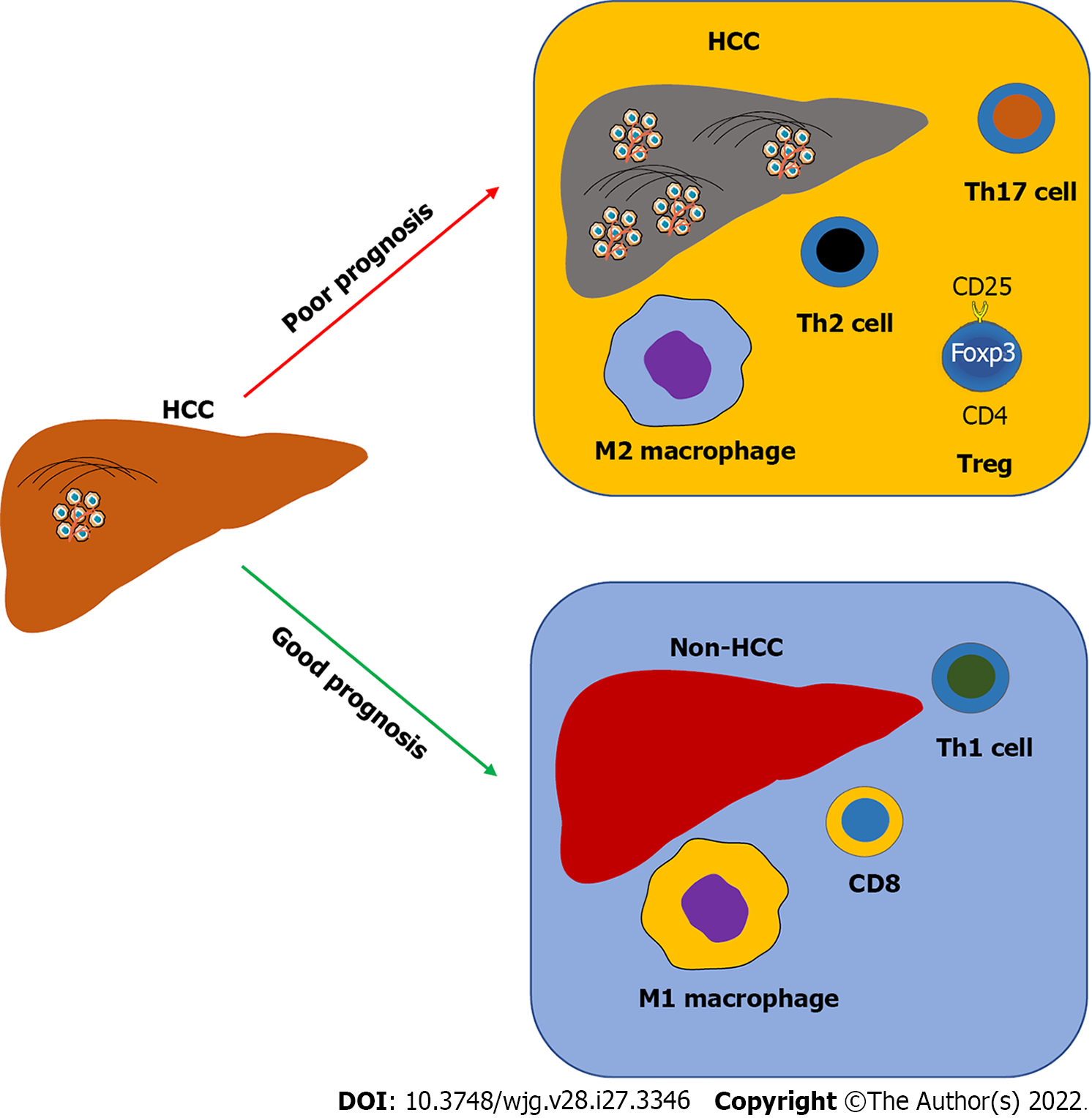
Figure 2 The alteration of intrahepatic immunity predicts the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
Usually, an increase of regulatory T cells, T helper (Th) 2 cells, and Th17 cells, as well as M2 macrophages is positively associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression in patients, whereas an abundance of CD8 T cells, Th1 T cells, and M1 macrophages is associated with HCC therapy and good prognosis for HCC patients. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Treg: Regulatory T cells; Th: T helper.
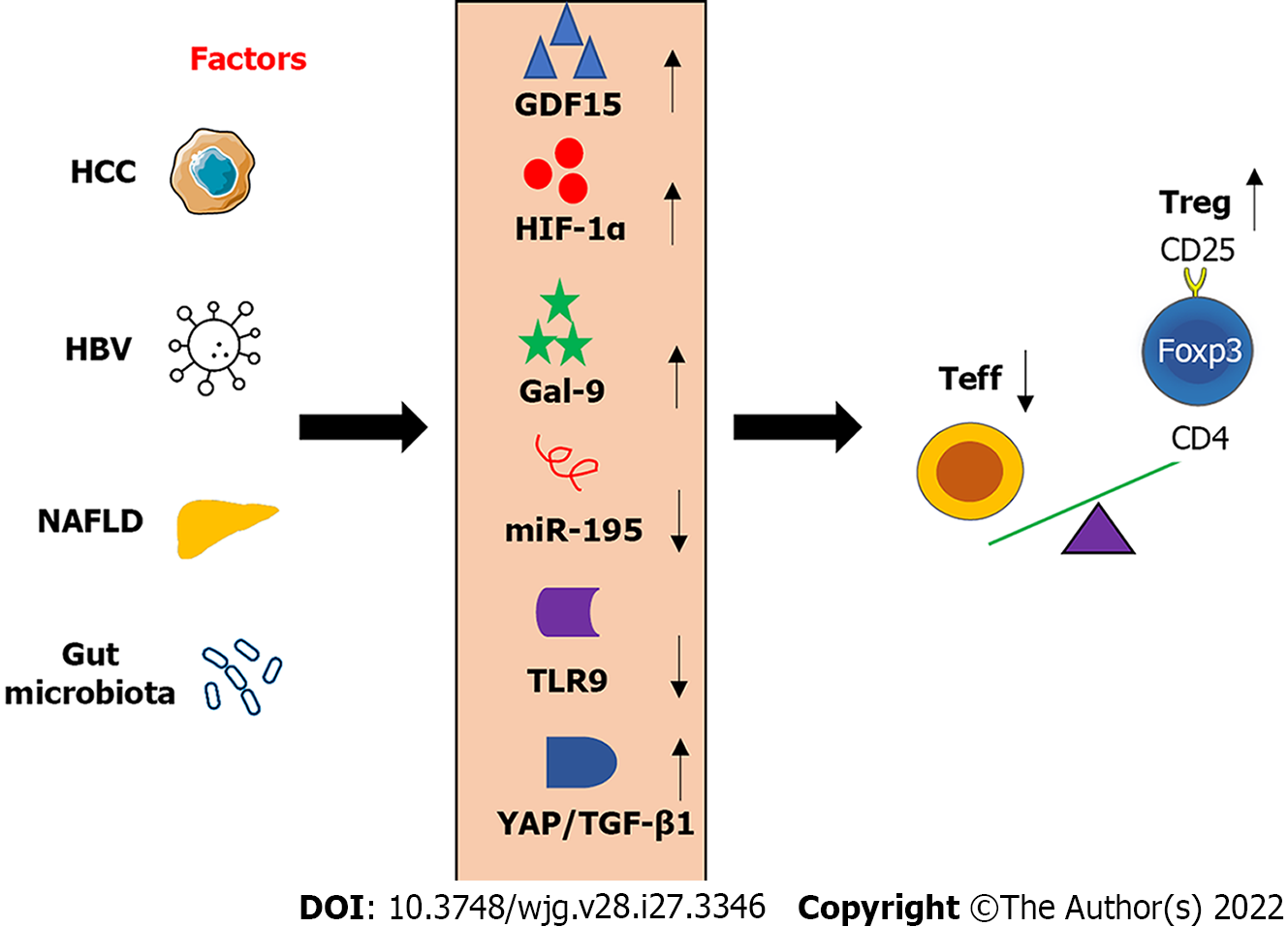
Figure 3 Factors mediated the imbalance of regulatory T cells/effector T cells.
Factor such as Hepatitis B virus, gut microbiota, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, as well as hepatocellular carcinoma tumor cells, can modulate several important molecules produced in the liver. Alteration of these molecules has been associated with the change of frequency and/or function of regulatory T cells in chronic liver disease, resulting in an imbalance of regulatory T cells/effector T cells. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Teff: Effector T cells; Treg: Regulatory T cells; GDF: Growth differentiation factor; HIF: Hypoxia-inducible transcription factors; Gal: Galectin; miR: micro ribonucleic acid; TLR: Toll-like receptor; YAP: Yes-associated protein; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta.
- Citation: Zhang CY, Liu S, Yang M. Regulatory T cells and their associated factors in hepatocellular carcinoma development and therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(27): 3346-3358
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i27/3346.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i27.3346