Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2022; 28(24): 2654-2666
Published online Jun 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2654
Published online Jun 28, 2022. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2654
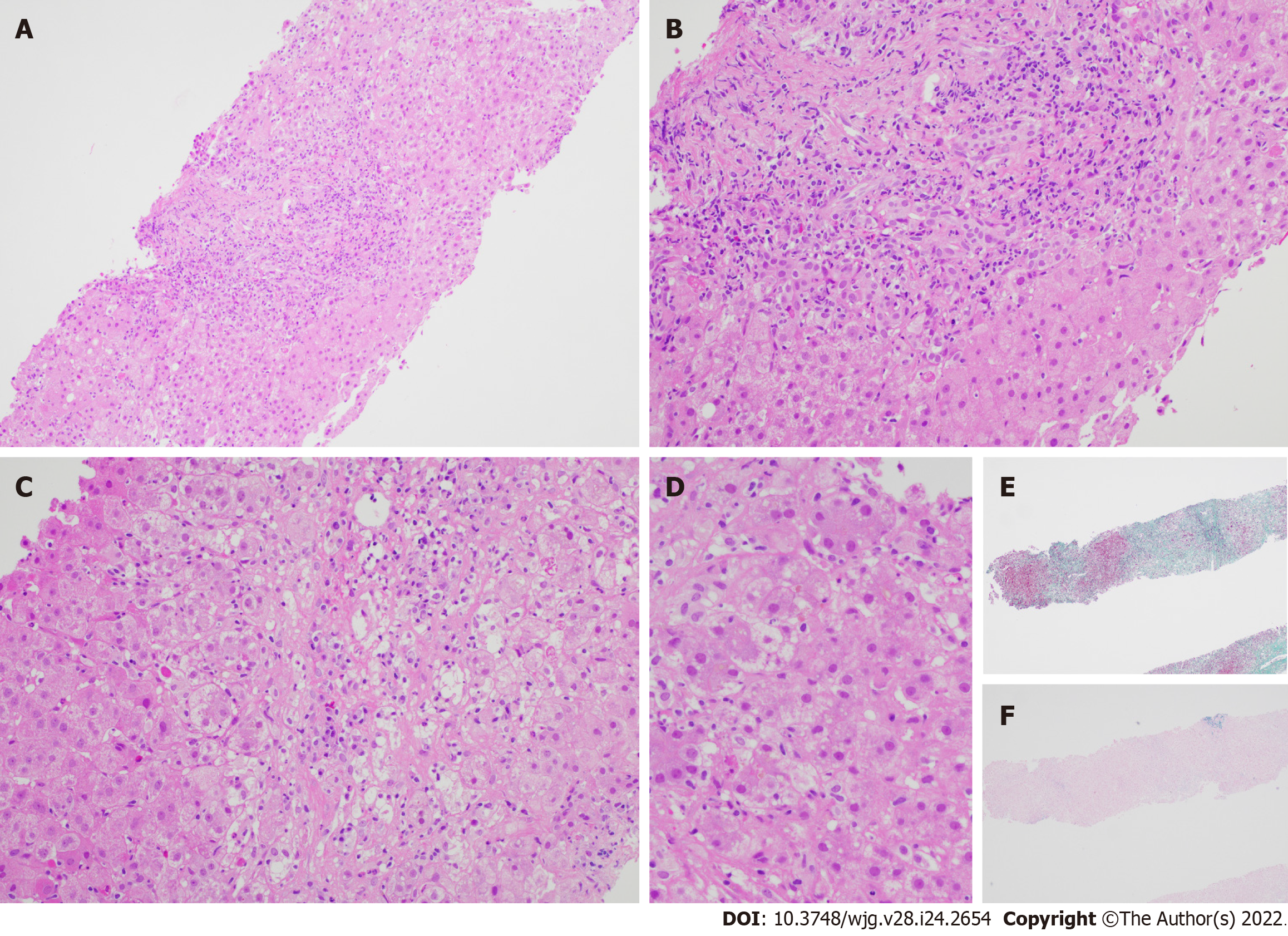
Figure 1 Liver biopsy specimen for patient A.
A: Low power view [hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) 100 ×] displays conspicuous portal and lobular inflammation with lobular disarray. Mild steatosis is also noted; B: Higher magnification of the portal tract (H&E 200 ×), zone 1, shows moderate chronic inflammation, lymphoplasmacytic predominantly, and rare eosinophils, with interface damage; C: At similar magnification (H&E 200 ×), the lobule including the perivenular region, e.g., zones 2 and 3, exhibits lobulitis characterized by aggregates of plasma cells, swollen hepatocytes with rosetting, Councilman bodies, and hepatocyte drop-out; D: High power view (H&E 400 ×) demonstrates rosetting of hepatocytes with droplets of orange-brown bile pigment; E and F: Histochemical stains Masson trichrome (E, 40 ×) showing collapse with mild early young fibrosis and Victoria blue (F, 40 ×) revealing paucity of elastic fibers, thus in keeping with subacute injury. Overall, the appearances are supportive of subacute drug-induced liver injury in association with autoimmune hepatitis histological pattern.
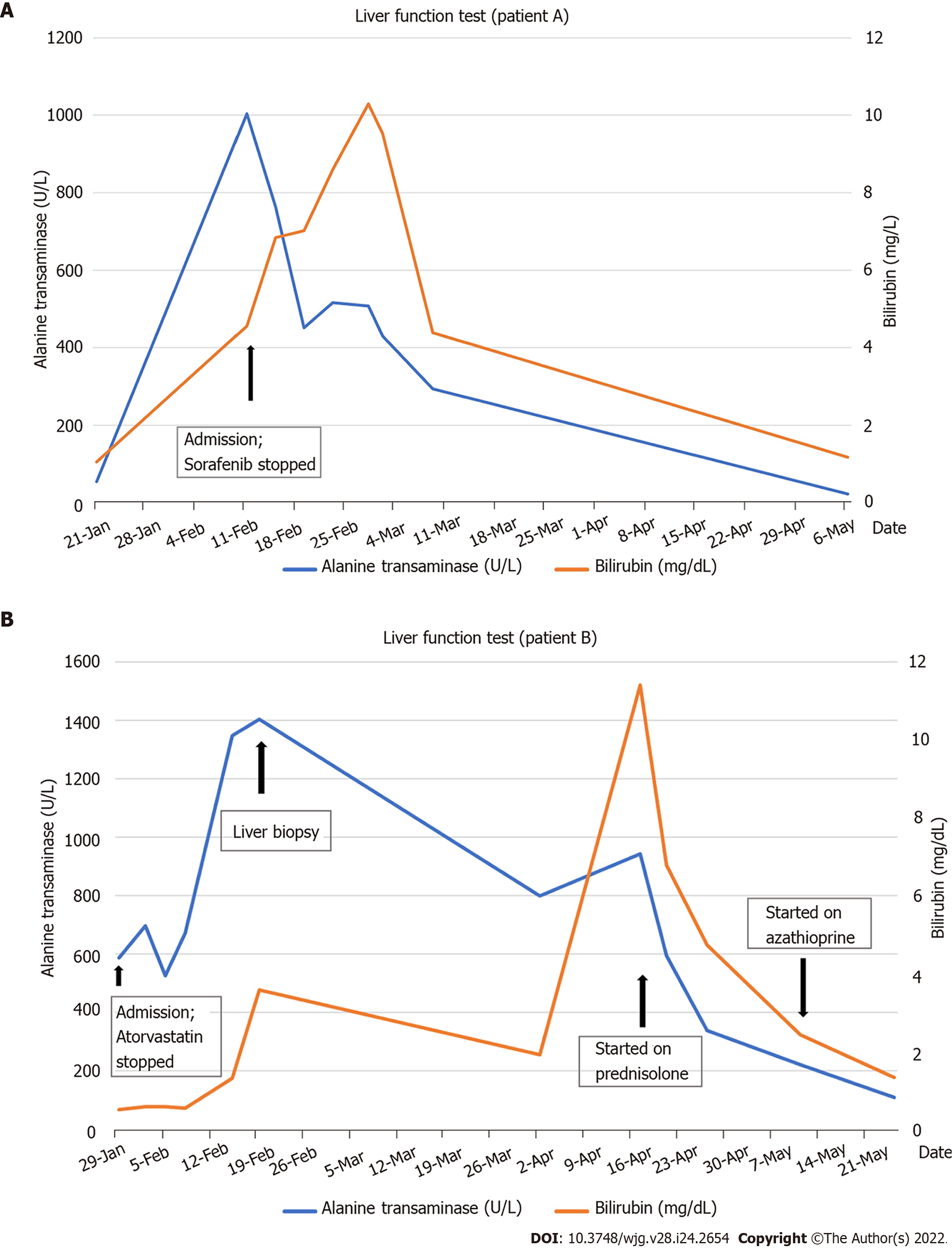
Figure 2 Bilirubin and alanine transaminase trend for patients A and B.
A: Patient A; B: Patient B.
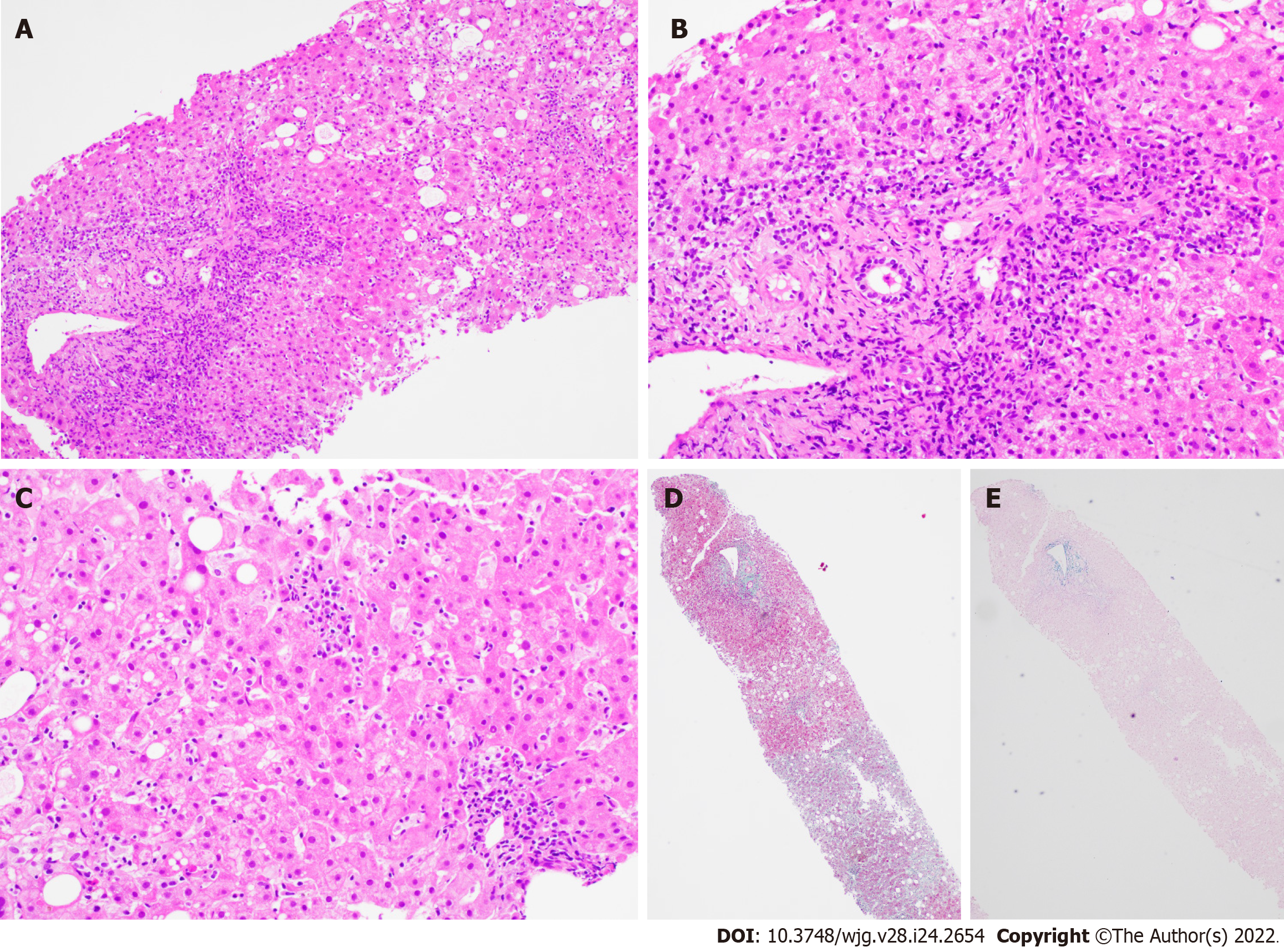
Figure 3 Liver biopsy findings for patient B.
A: Low power view [hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) 100 ×] shows portal and lobular inflammation with lobular disarray and mild steatosis; B: Higher magnification of the portal tract (H&E 200 ×) demonstrates moderate plasma cell-rich chronic inflammation with continuous interface damage; C: Lobulitis with aggregates of plasma cells and rosetting of hepatocytes is present in the lobule (H&E 200 ×); D and E: Masson trichrome (D, 40 ×) and Victoria blue (E, 40 ×) display mild early young fibrosis and paucity of elastic fibers, respectively. The absence of old mature type fibrosis suggested not a chronic injury. The autoimmune hepatitis histological pattern observed was therefore interpreted to be drug related, atorvastatin-induced.
- Citation: Tan CK, Ho D, Wang LM, Kumar R. Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: A minireview. World J Gastroenterol 2022; 28(24): 2654-2666
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v28/i24/2654.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2654