Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2021; 27(31): 5152-5170
Published online Aug 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i31.5152
Published online Aug 21, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i31.5152
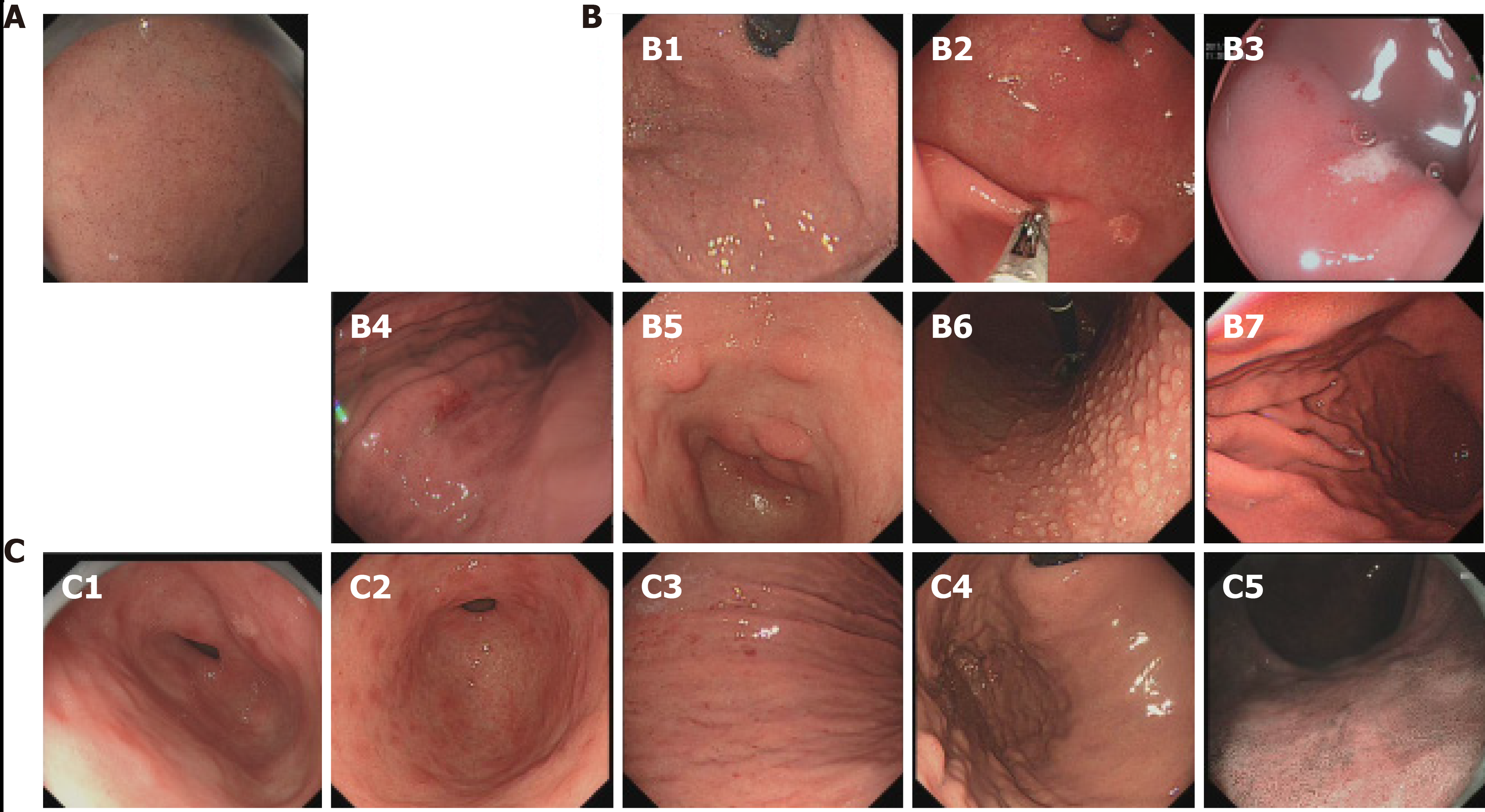
Figure 1 Endoscopic features for Helicobacterpylori infection.
A: Normal gastric mucosa. Regular arrangement of collecting venules is seen; B: Infected gastric mucosa. B1: Spotty redness; B2: Gastric xanthoma; B3: Erosion; B4: Multiple redness and erosion; B5: Hyperplastic polyp; B6: Nodular gastritis; B7: Intestinal metaplasia; C: Gastric mucosa after eradication. C1: Patchy redness; C2: Map-like redness; C3: Redness; C4: Atrophy; C5: Intestinal metaplasia.
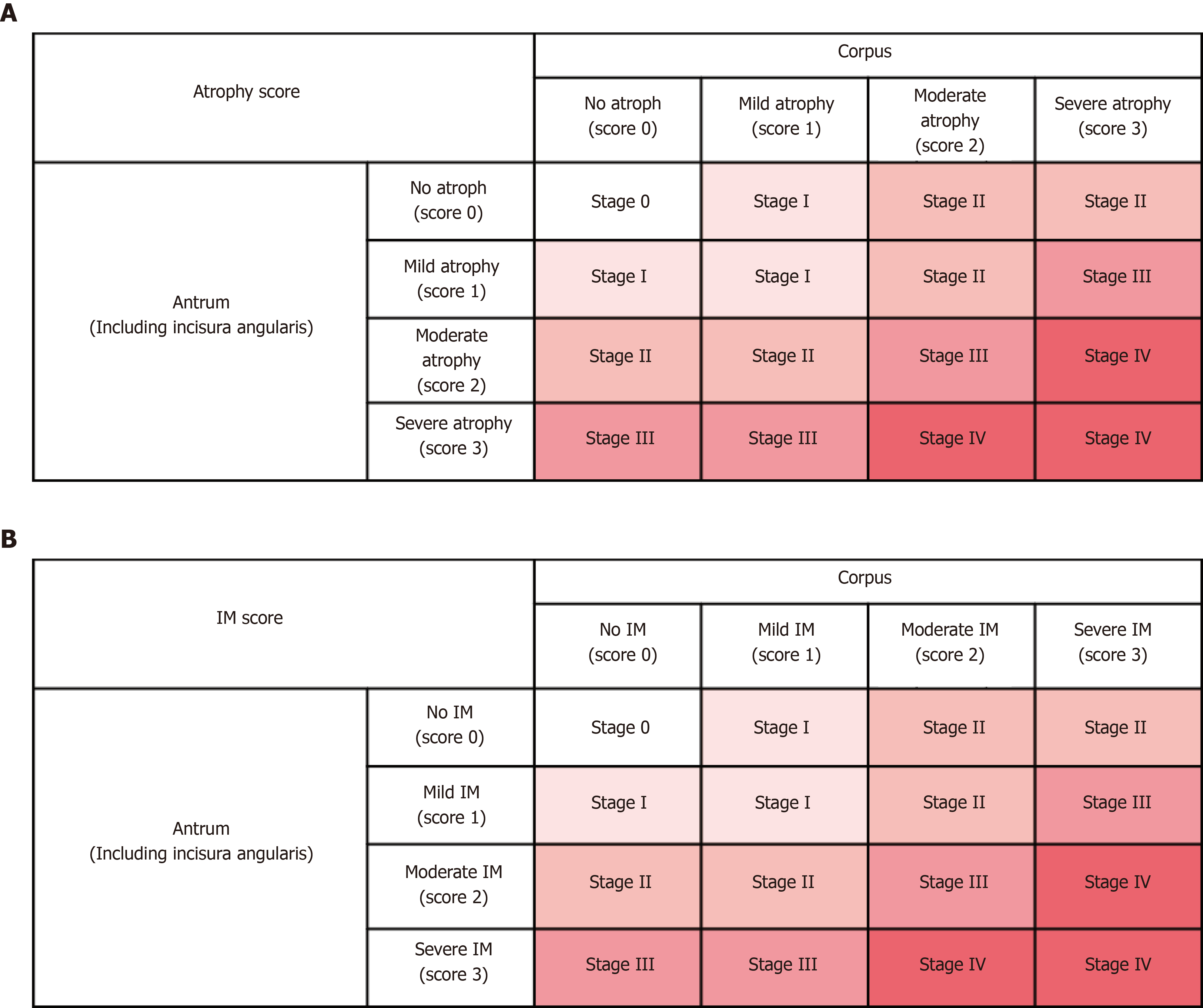
Figure 2 Operative link on gastritis assessment staging system (A) and operative link on gastric intestinal metaplasia assessment (B) staging system.
IM: Intestinal metaplasia; OLGA: Operative link on gastritis assessment staging system; OLGIM: Operative link on gastric intestinal metaplasia assessment.
- Citation: Weng CY, Xu JL, Sun SP, Wang KJ, Lv B. Helicobacter pylori eradication: Exploring its impacts on the gastric mucosa. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(31): 5152-5170
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i31/5152.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i31.5152