Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2021; 27(21): 2910-2920
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2910
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2910
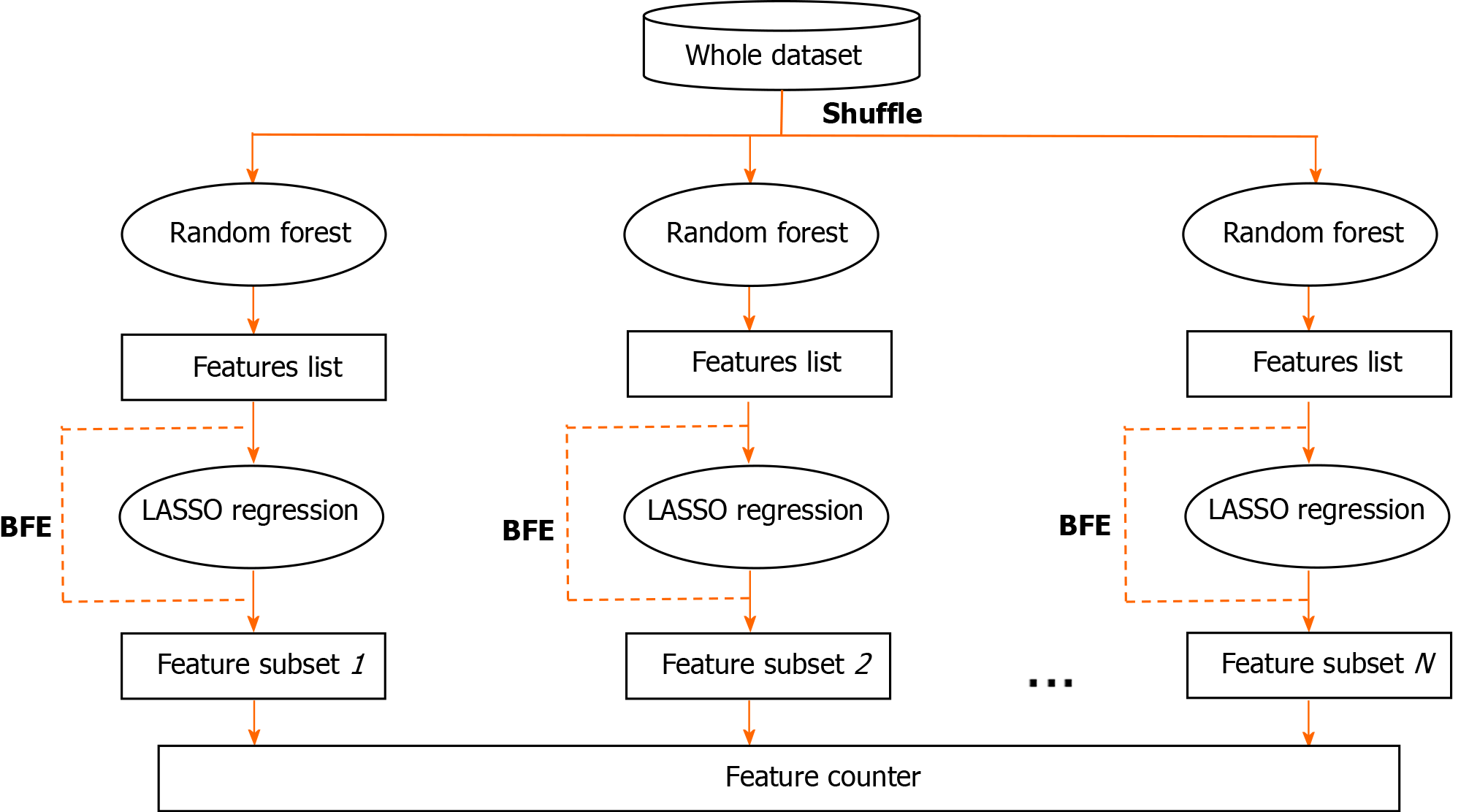
Figure 1 The main procedure of the random forest-backward feature elimination algorithm.
BFE: Backward feature elimination; LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator.
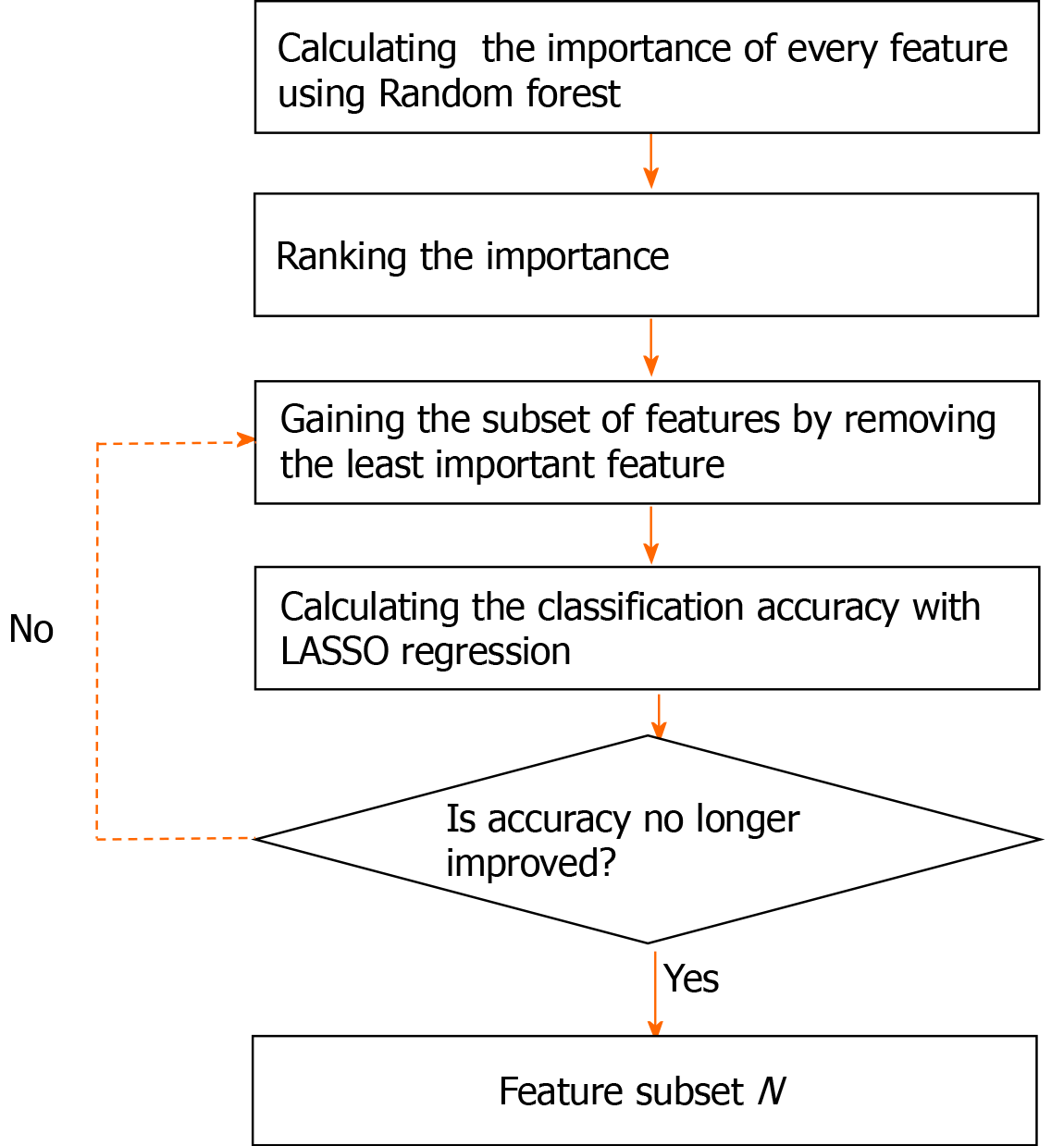
Figure 2 Feature selection scheme in an iteration.
LASSO: Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator.
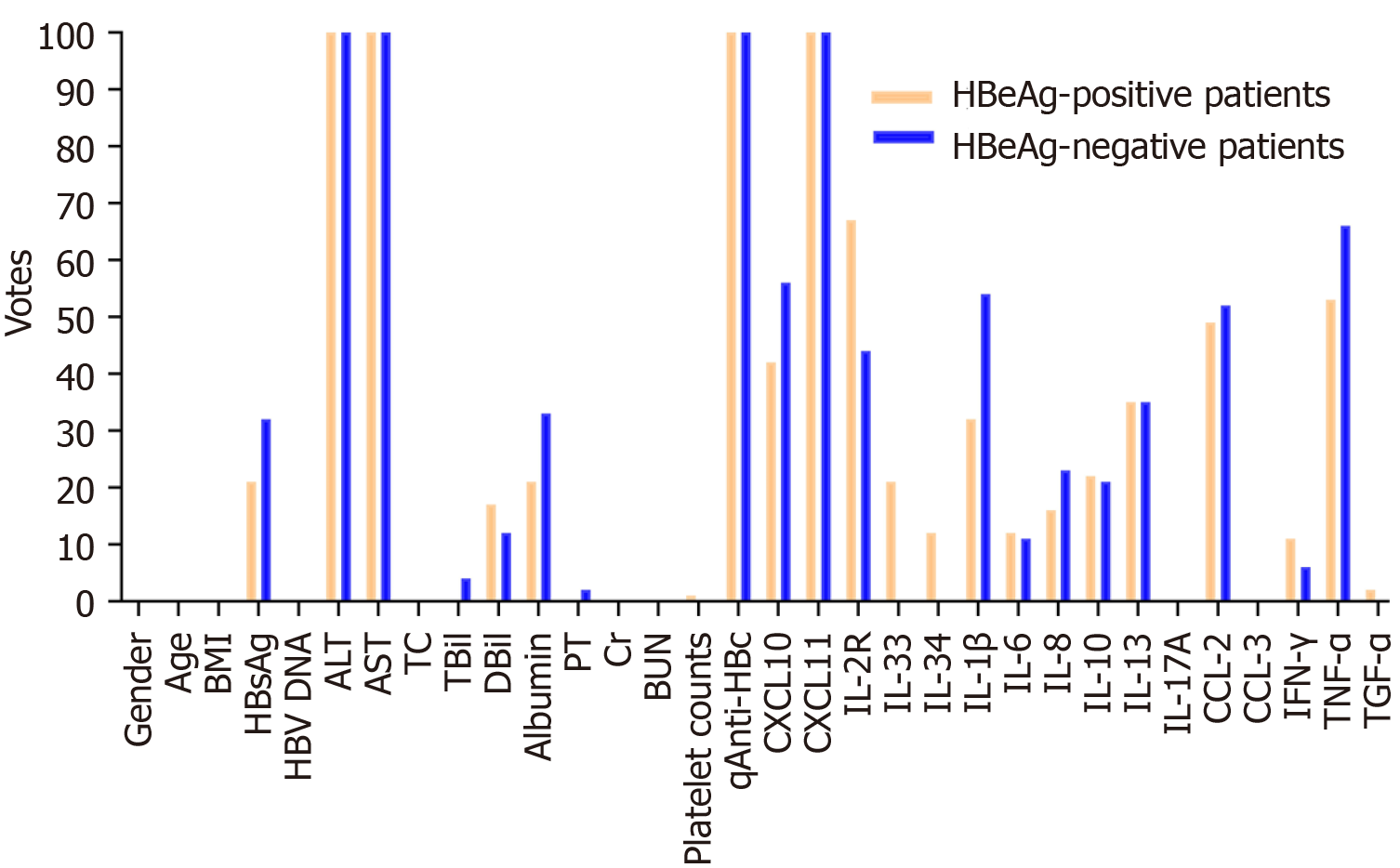
Figure 3 istogram of the votes in the feature counter.
BMI: Body mass index; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; TC: Total cholesterol; TBil: Total bilirubin; DBil: Direct bilirubin; PT: Prothrombin time; Cr: Creatinine; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; qAnti-HBc: Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody; IL: Interleukin, IFN: Interferon; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
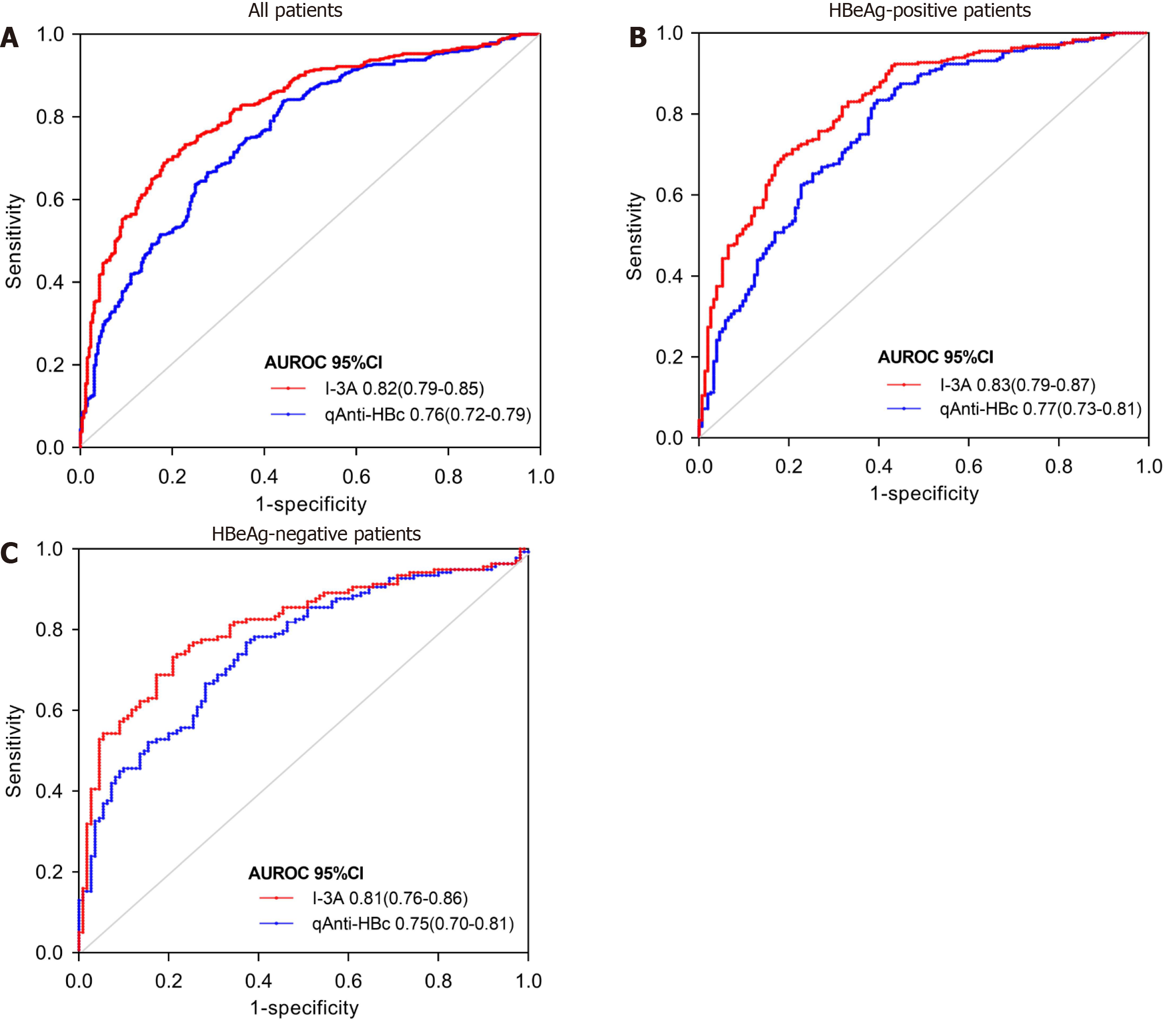
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for predicting moderate-to-severe inflammation in all patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection, HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection, and HBeAg-negative patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
A: All patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection; B: HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection; C: HBeAg-negative patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. AUROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristics curve; CI: Confidence interval; qAnti-HBc: Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody.
- Citation: Zhou JY, Song LW, Yuan R, Lu XP, Wang GQ. Prediction of hepatic inflammation in chronic hepatitis B patients with a random forest-backward feature elimination algorithm. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(21): 2910-2920
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i21/2910.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2910