Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2021; 27(21): 2895-2909
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2895
Published online Jun 7, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2895
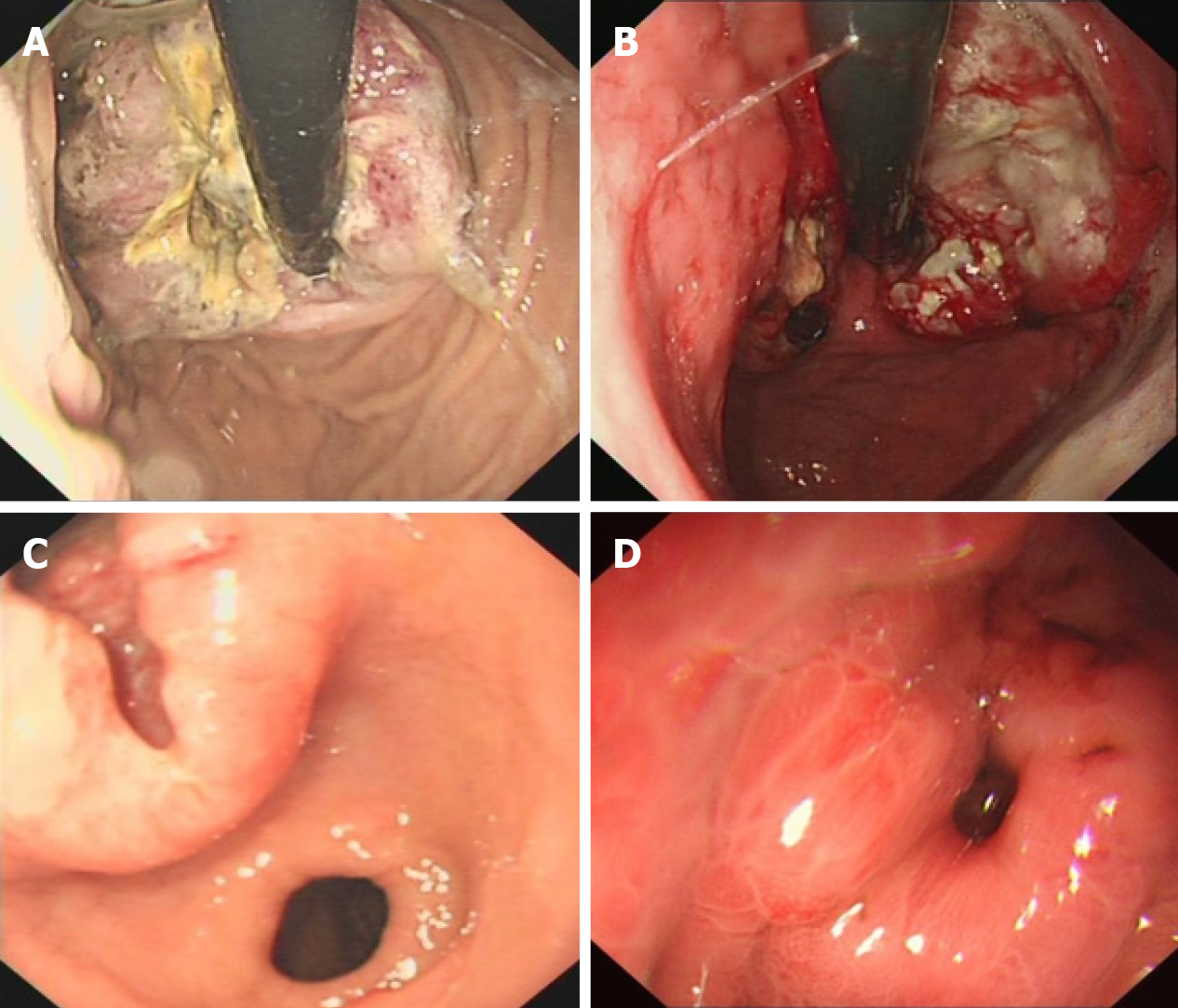
Figure 1 Endoscopic detection of poorly differentiated gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms.
A: Circumferential raised lesions on the cardia with uneven surfaces; B: Irregular bumps on the side of the minor curvature of the cardia, accompanied by erosions, ulcers, and unclear boundaries that bled easily when contacted; C: A raised ulcer with a diameter of 4 cm was observed in the small curvature of the antrum; D: A deep ulcer with a diameter of approximately 0.5 cm on the posterior wall of the gastric fundus was observed, and the base was not clear.
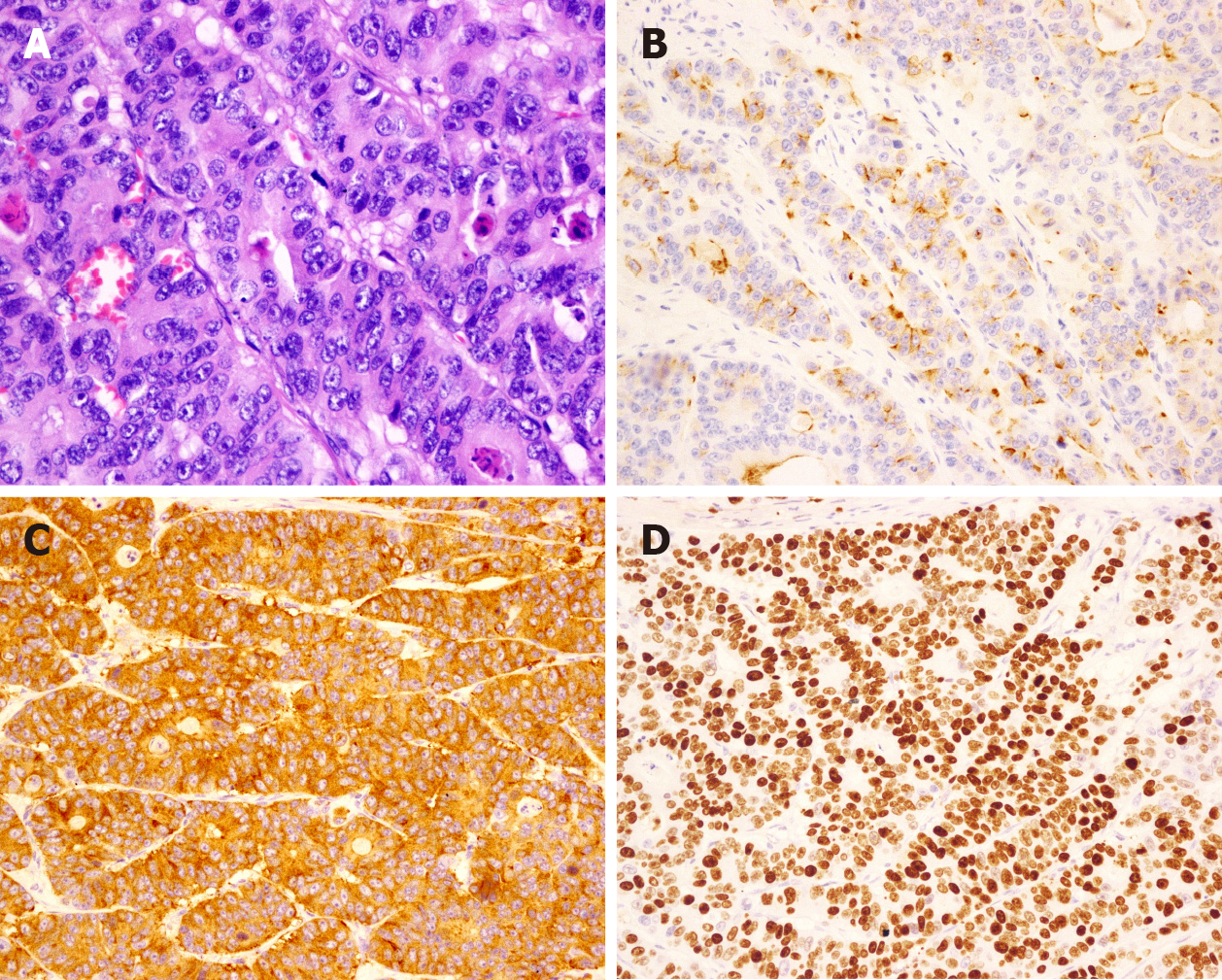
Figure 2 Morphology and immunohistochemical staining of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma in the cardia.
A: Morphology (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 400); B: Chromogranin A-positive staining [immunohistochemical (IHC), × 200]; C: Synaptophysin-positive staining (IHC, × 200); D: Ki-67 index: 90% (IHC, × 200).
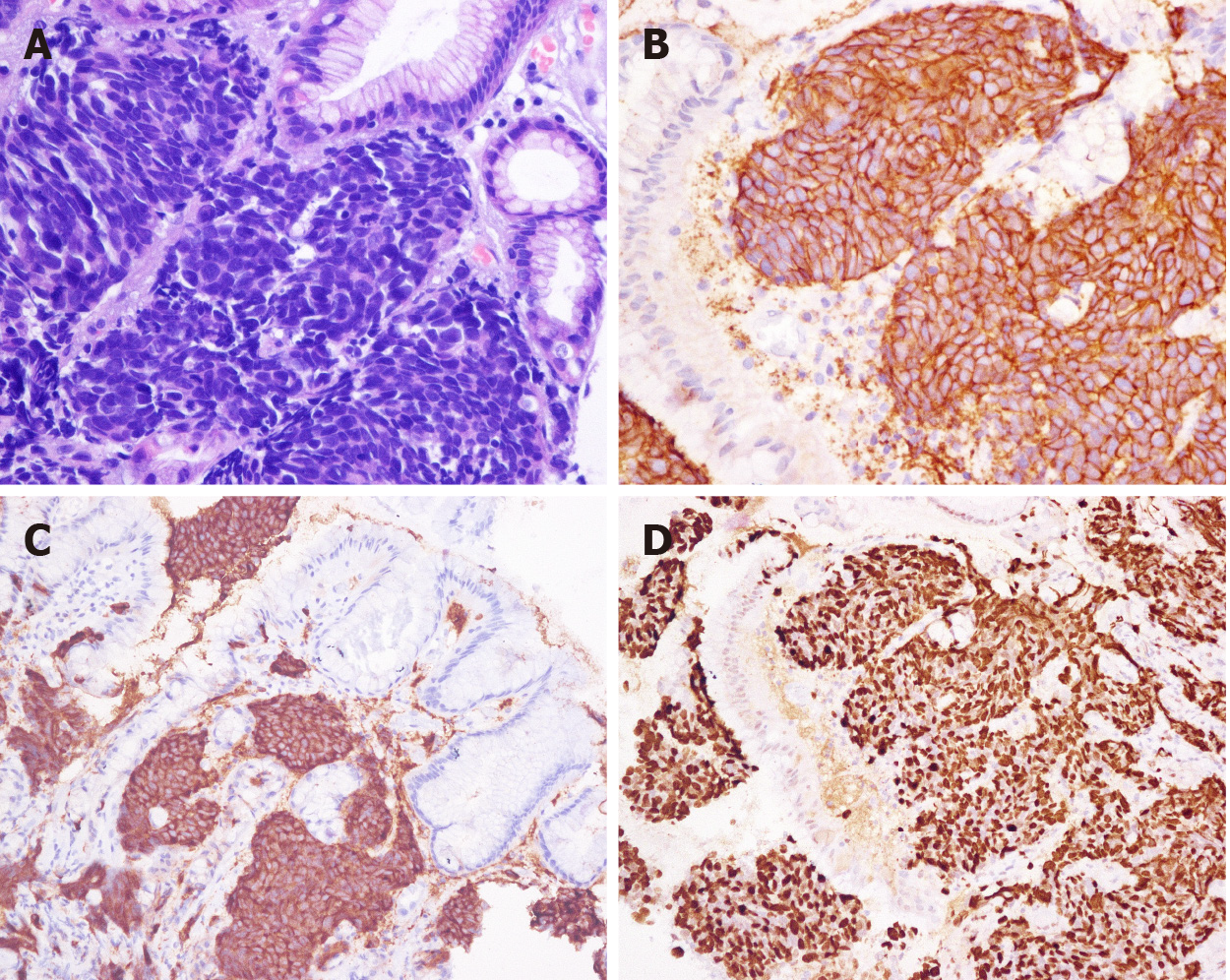
Figure 3 Morphology and immunohistochemical staining of gastric small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
A: Morphology (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 400); B: CD56-positive staining [immunohistochemical (IHC), × 400]; C: Synaptophysin-positive staining (IHC, × 200); D: Ki-67 index: 90% (IHC, × 200).
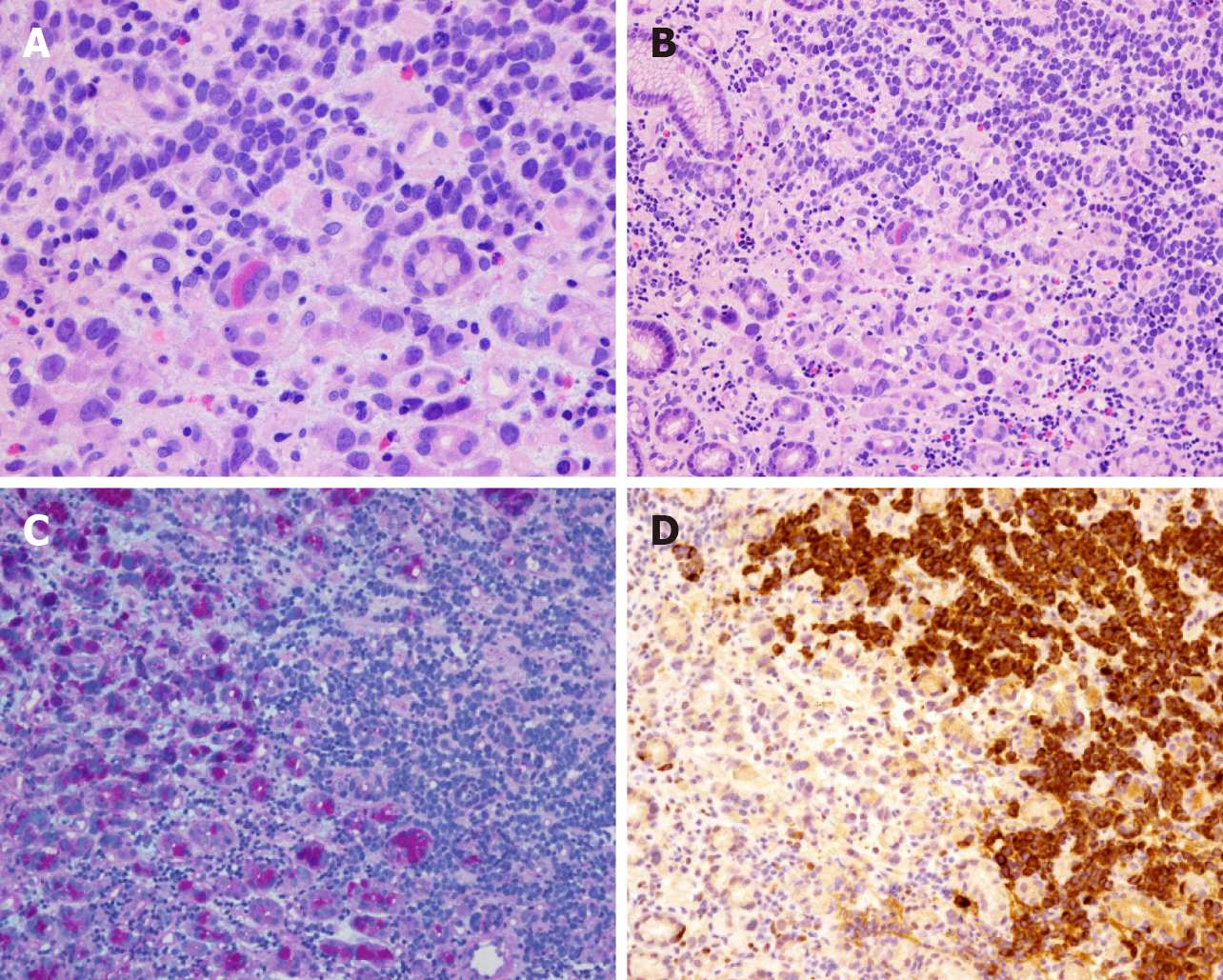
Figure 4 Morphology and immunohistochemical staining of mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma.
A and B: Morphology of gastric small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma mixed with adenocarcinoma (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 400); C: Gastric small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma mixed with adenocarcinoma (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 200). Alcian blue/periodic acid–Schiff (AB-PAS) staining (× 200): The left side of the picture shows adenocarcinoma (AB-PAS positive); D: Chromogranin A-positive staining (× 200). The right side of the picture shows small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
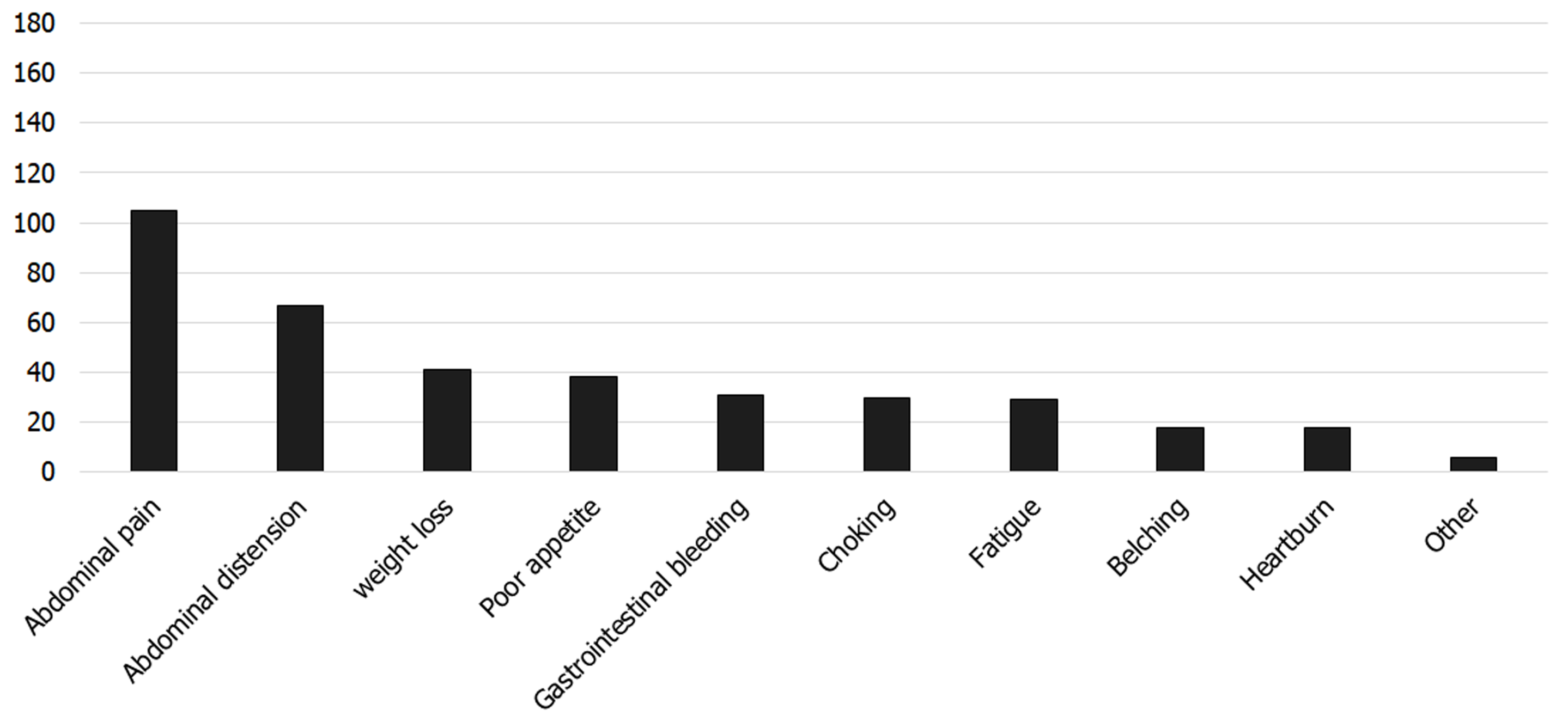
Figure 5
Distribution of nonspecific clinical symptoms in 190 patients with poorly differentiated gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms.
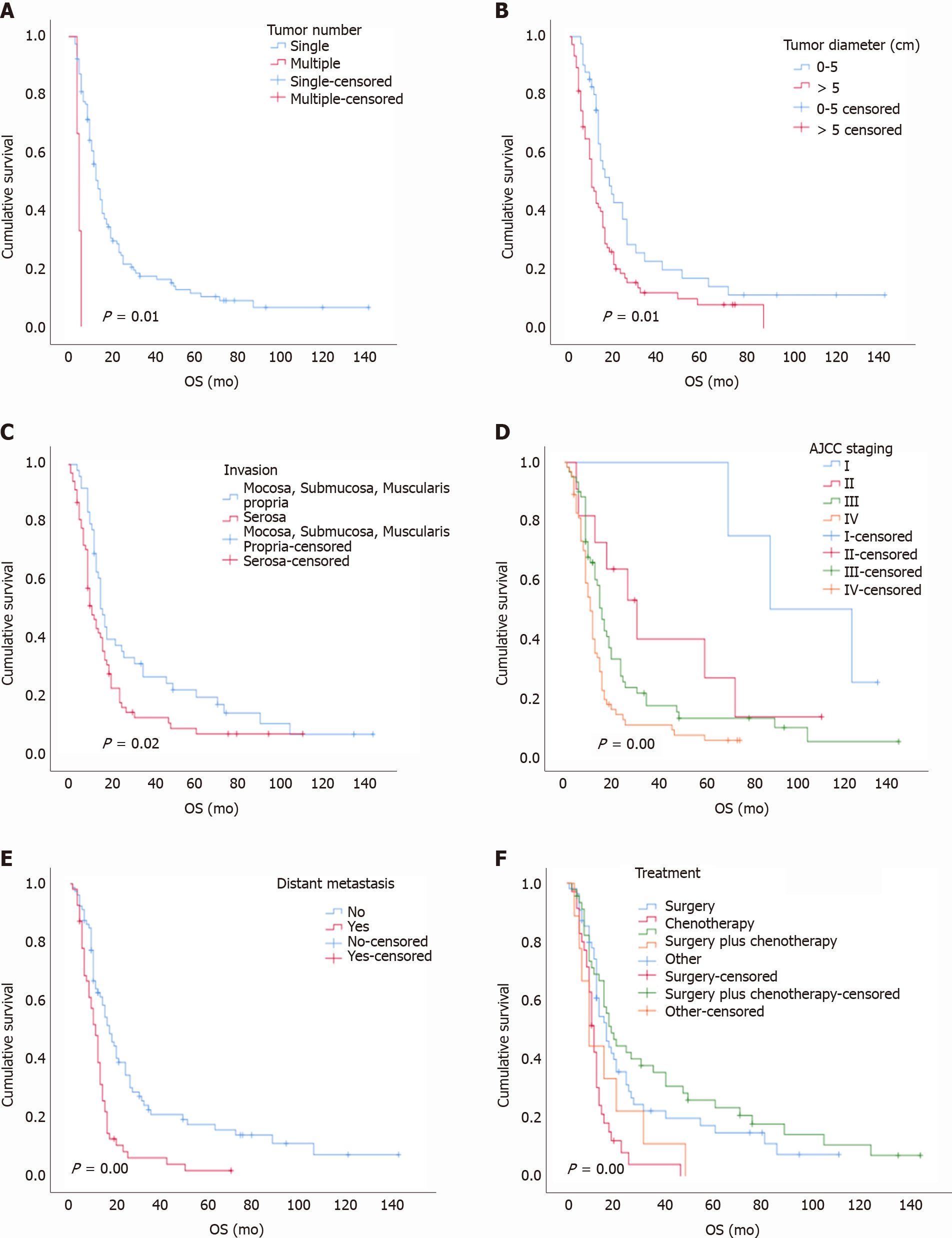
Figure 6 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (P < 0.
05). A: Tumor number (P = 0.01); B: Tumor diameter (P = 0.01); C: Invasion (P = 0.02); D: American Joint Committee on Cancer stage (P < 0.001); E: Distant metastasis (P < 0.001); F: Treatment for patients without distant metastases (P < 0.001). AJCC: American Joint Committee on Cancer; OS: Overall survival.
- Citation: Han D, Li YL, Zhou ZW, Yin F, Chen J, Liu F, Shi YF, Wang W, Zhang Y, Yu XJ, Xu JM, Yang RX, Tian C, Luo J, Tan HY. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of 232 patients with poorly differentiated gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(21): 2895-2909
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i21/2895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i21.2895