Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2021; 27(20): 2615-2629
Published online May 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2615
Published online May 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2615
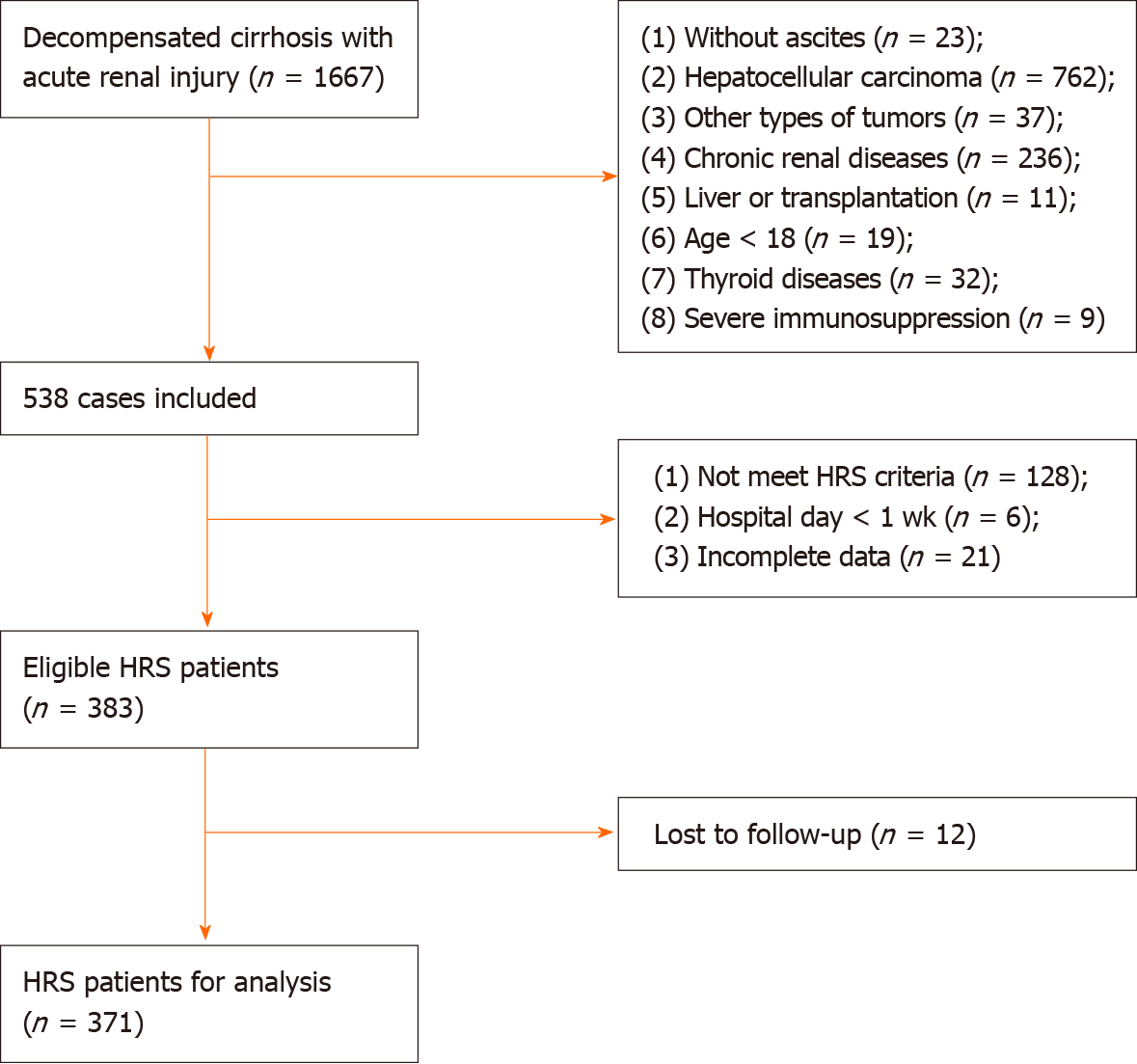
Figure 1 Workflow.
The eligible cohort selection process after applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria from four hospitals. HRS: Hepatorenal syndrome.
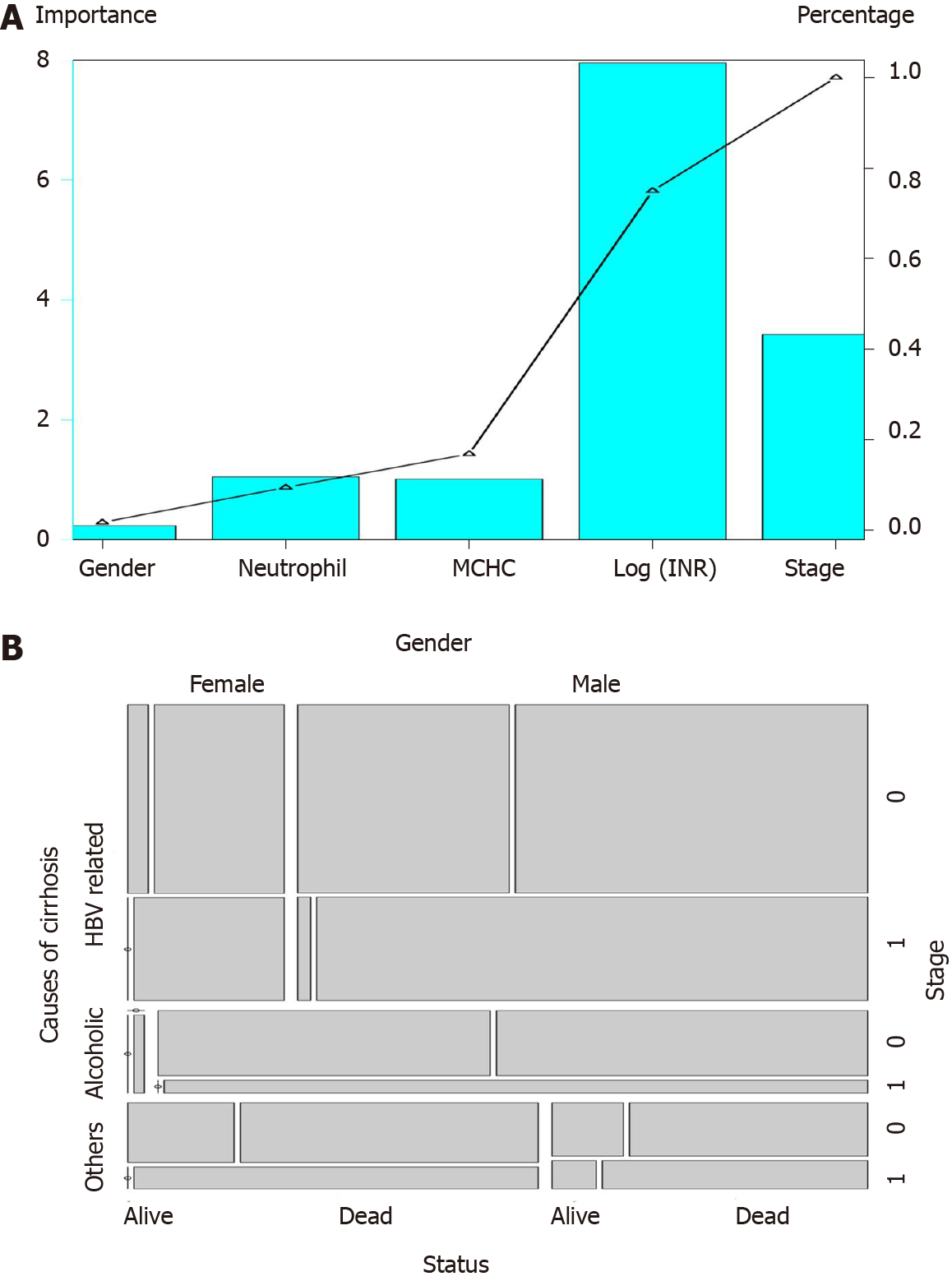
Figure 2 Characteristics associated with survival.
A: Importance of each characteristic of GIMNS; B: Mosaic plot. Survival status of patients with different causes of cirrhosis, gender, and stage. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; INR: International normalized ratio; MCHC: Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration.
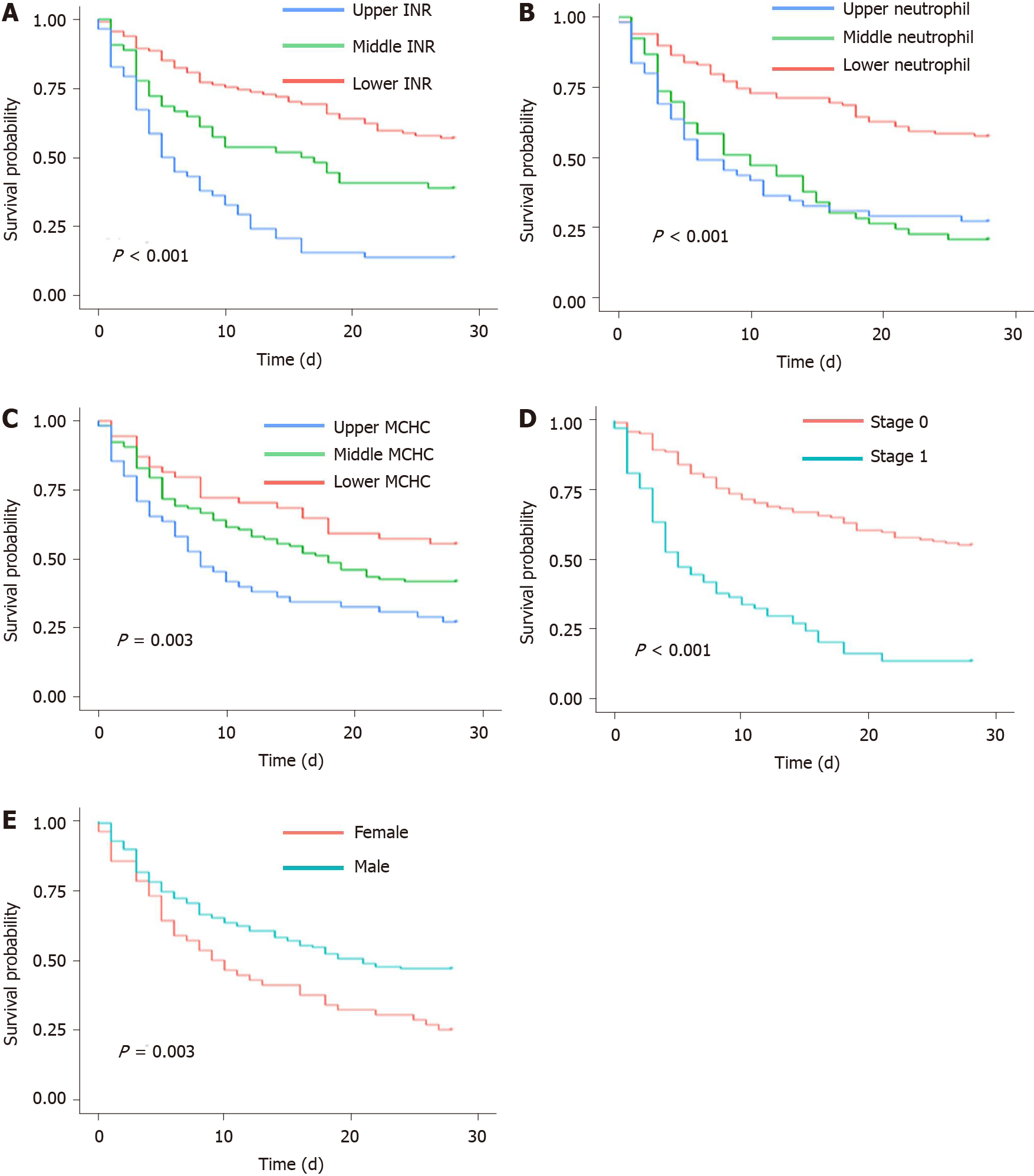
Figure 3 Kaplan–Meier curves of variables of GIMNS.
A: Stratified international normalized ratio; B: Stratified neutrophil percentage; C: Stratified mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; D: Stage; E. Gender. INR: International normalized ratio; MCHC: Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration.
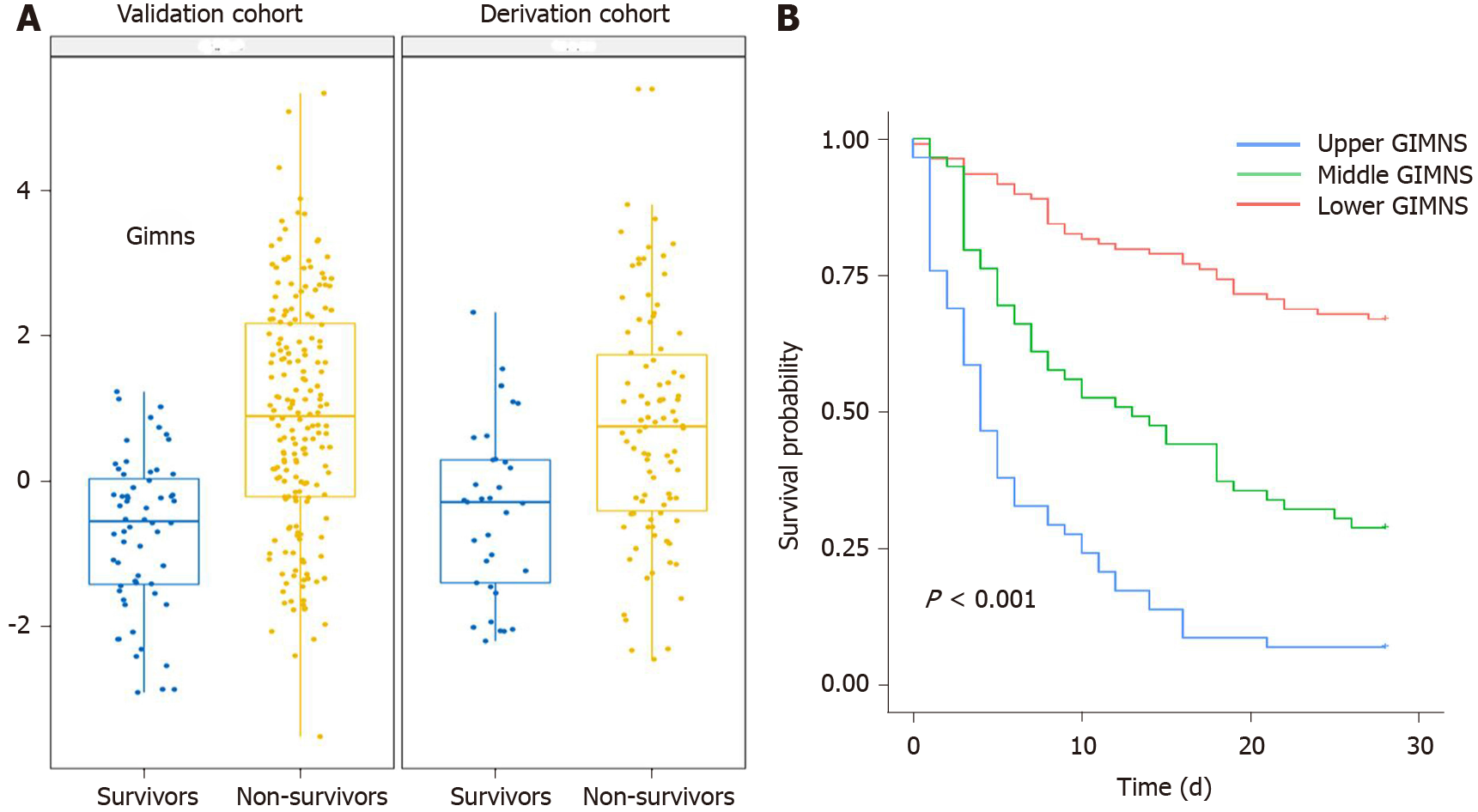
Figure 4 Distributions of the GIMNS score.
A: The GIMNS score distribution between survivors and non-survivors in the derivation and validation cohorts; B: Kaplan–Meier curves of GIMNS.
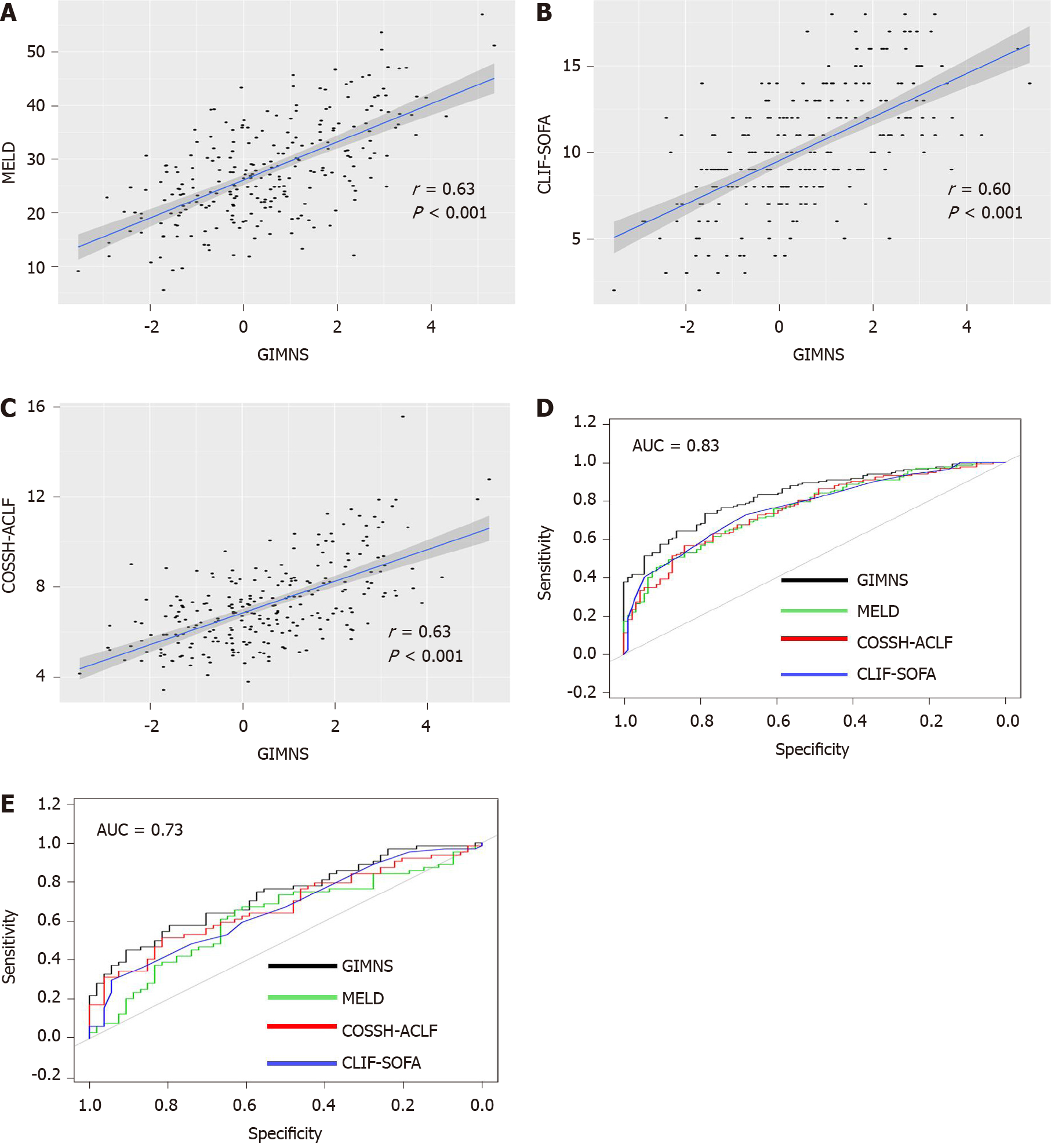
Figure 5 Relationship between GIMNS and other scoring systems and receiver operating characteristic curve curves.
A: GIMNS and Model for End-stage Liver Disease; B: GIMNS and Chronic Liver Failure-Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; C: GIMNS and Chinese Group on the Study of Severe Hepatitis B-Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure; D: Receiver operating characteristic curve curves in derivation cohort; E: Receiver operating characteristic curve in validation cohort. CLIF-SOFA: Chronic Liver Failure-Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; COSSH-ACLF: Chinese Group on the Study of Severe Hepatitis B-Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure; MELD: Model for End-stage Liver Disease; AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Sheng XY, Lin FY, Wu J, Cao HC. Development and validation of a prognostic model for patients with hepatorenal syndrome: A retrospective cohort study. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(20): 2615-2629
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i20/2615.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2615