Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2021; 27(20): 2458-2473
Published online May 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2458
Published online May 28, 2021. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2458
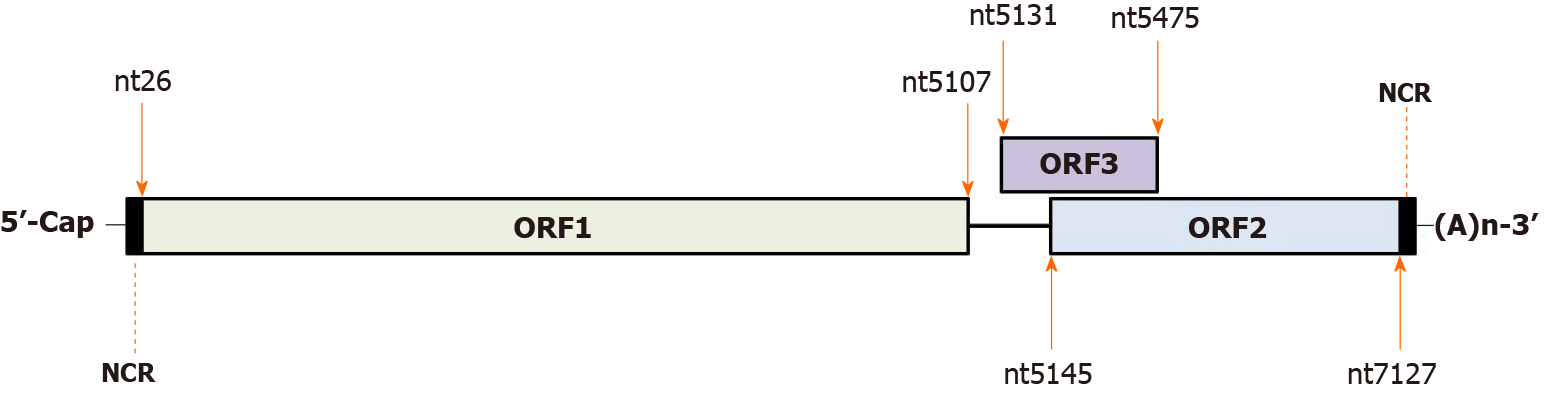
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of hepatitis E virus genome and three well-defined open reading frames.
The numbers above or below the RNA boxes indicate nucleotide numbers based on hepatitis E virus-1 prototype Sar55 strain (GenBank accession number AF444002). NCR: Non-coding region; ORF: Open reading frame.
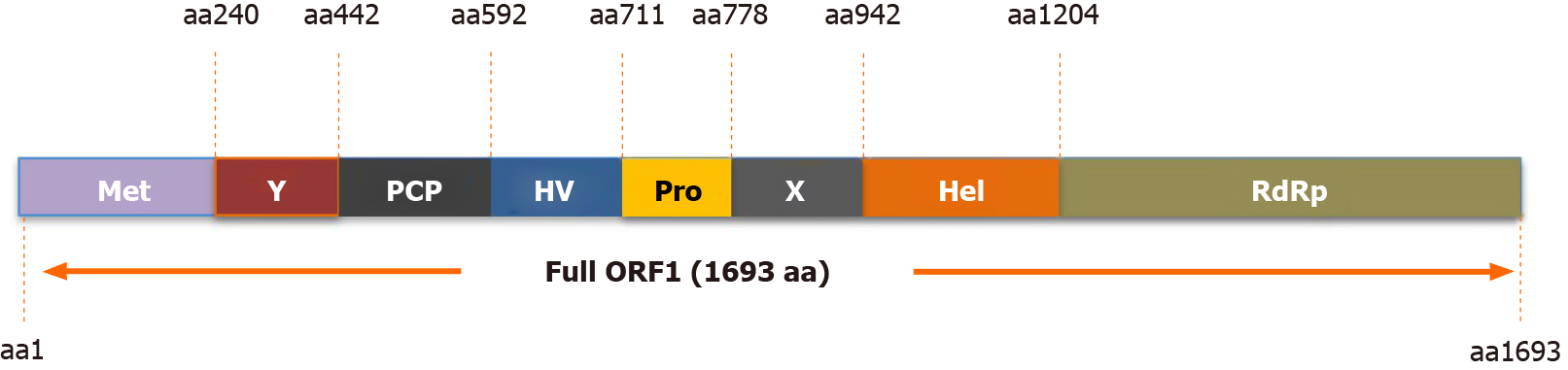
Figure 2 Function domains of hepatitis E virus-open reading frame 1 polyprotein.
Putative functional domains of hepatitis E virus (HEV)-open reading frame 1 polyprotein based on HEV-1 prototype Sar55 strain are listed as follows: Methyltransferase domain; Y domain; papain-like cysteine protease; hypervariable region; proline-rich domain; X-domain; Hhelicase; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Met: Methyltransferase domain; Y: Y domain; PCP: Papain-like cysteine protease; HV: Hypervariable region; Pro: Proline-rich domain; X: X-domain; Hel: Helicase; RdRp: RNA polymerase; ORF: Open reading frame.
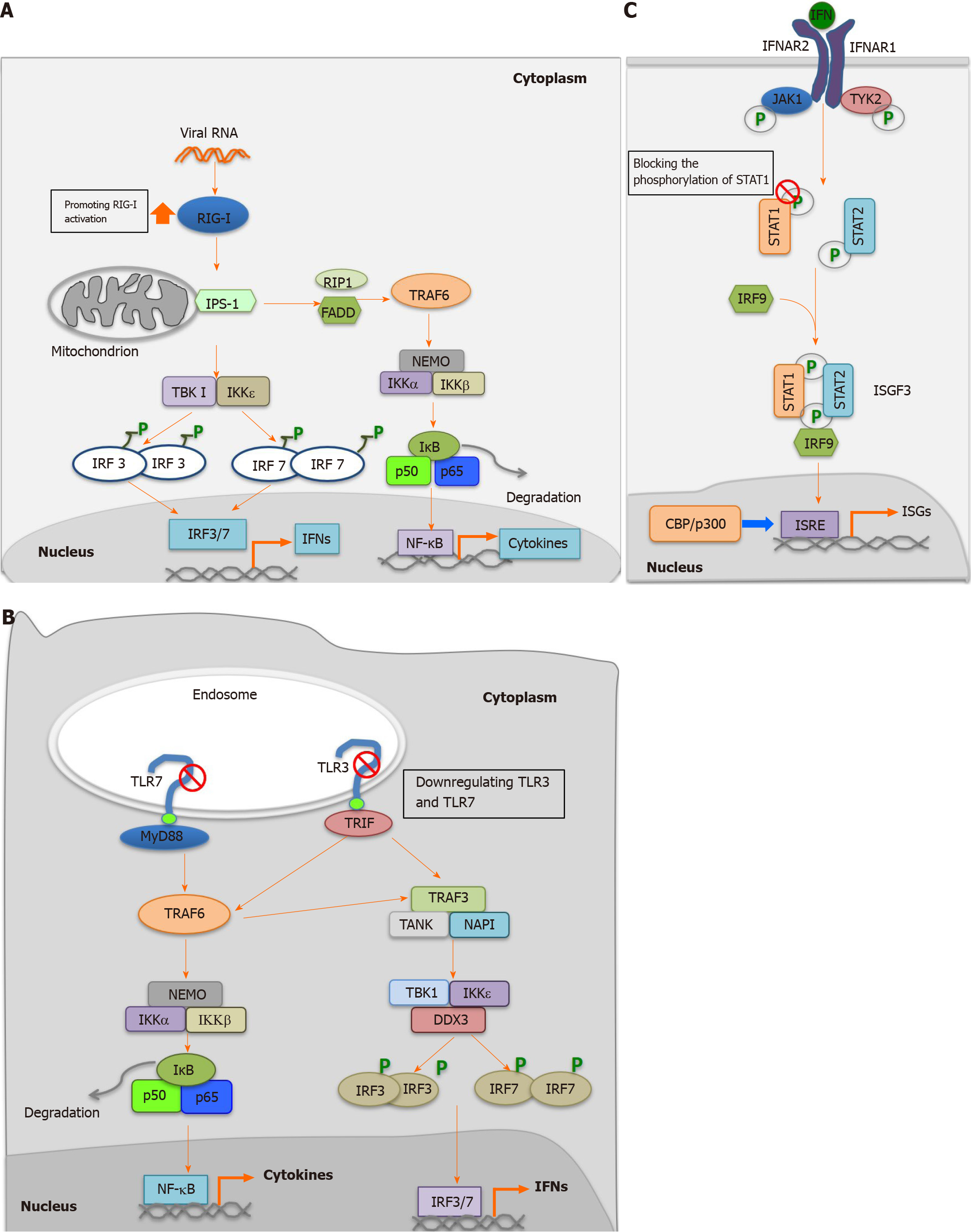
Figure 3 Regulation of host innate immune response by hepatitis E virus-open reading frame 3 proteins.
A: Promotion of retinoic acid-inducible gene I mediated activation by hepatitis E virus (HEV)-open reading frame (ORF) 3; B: Inhibition of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3 and TLR7 by HEV-ORF3; C: Blocking of the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 to inhibit Janus kinase/STAT signaling. RIG-I: Retinoic acid-inducible gene I; RIP-I: Ribosome-inactivating proteins type I; FADD: Fas-associated protein with death domain; IKK: IkappaB kinase; TBK: Tank-Binding-Kinase; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kB; IFN: Interferon; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TRIF: Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain-containing adapter inducing interferon-beta; NAPI: Net anthropogenic phosphorus input; IFNAR: Inflammation-the type I interferon receptor; JAK: Janus kinase; TYK: Targeting tyrosine kinase; STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; ISGF: Interferon-stimulated gene factor; ISRE: Interferon-stimulated response element; ISGs: Interferon-stimulated genes; CBP: CREB-binding protein.
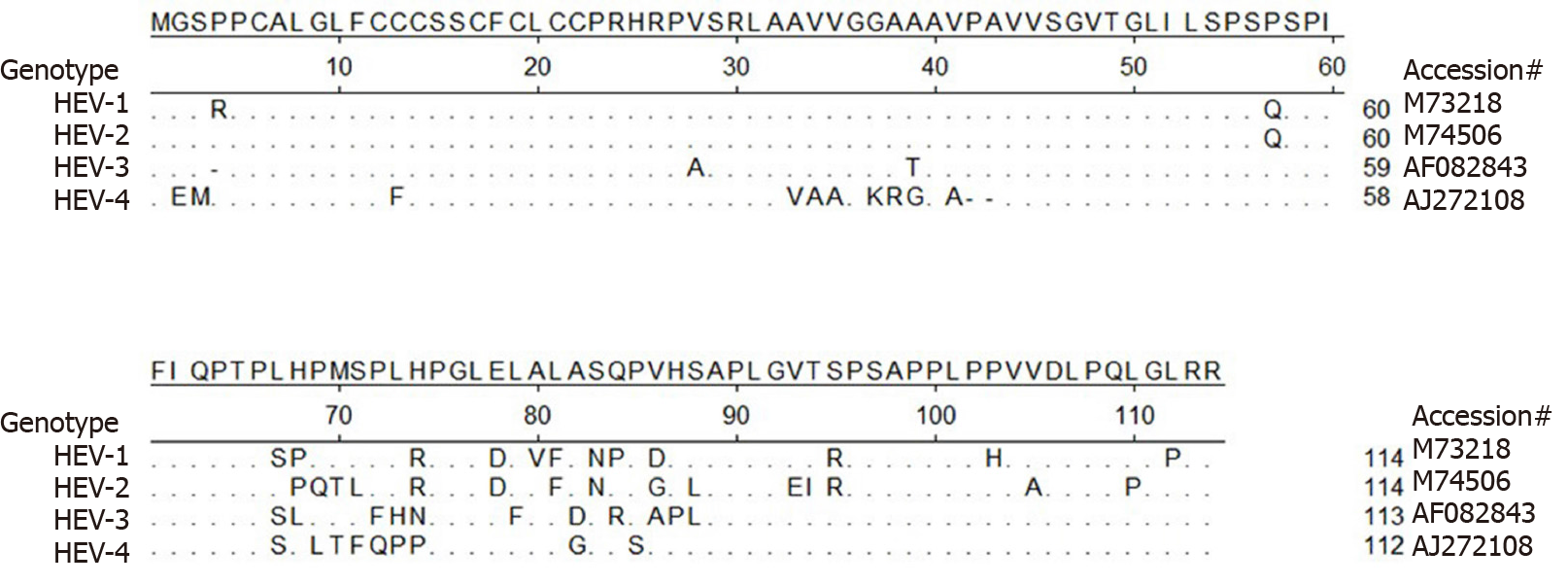
Figure 4 Alignment of amino acid sequence of hepatitis E virus-open reading frame 3 from 4 genotypes in Orthohepevirus A virus.
Alignment of amino acid sequence of open reading frame 3 from all seven genotypes classified as Orthohepevirus A virus. Hepatitis E virus (HEV)-1 (reference sequence GenBank accession #M73218), HEV-2 (reference sequence GenBank accession #M74506), HEV-3 (reference sequence GenBank accession #AF082843), and HEV-4 (reference sequence GenBank accession #AJ272108) are shown. Those residues that are the same as consensus sequence are shown as “.”. HEV: Hepatitis E virus.
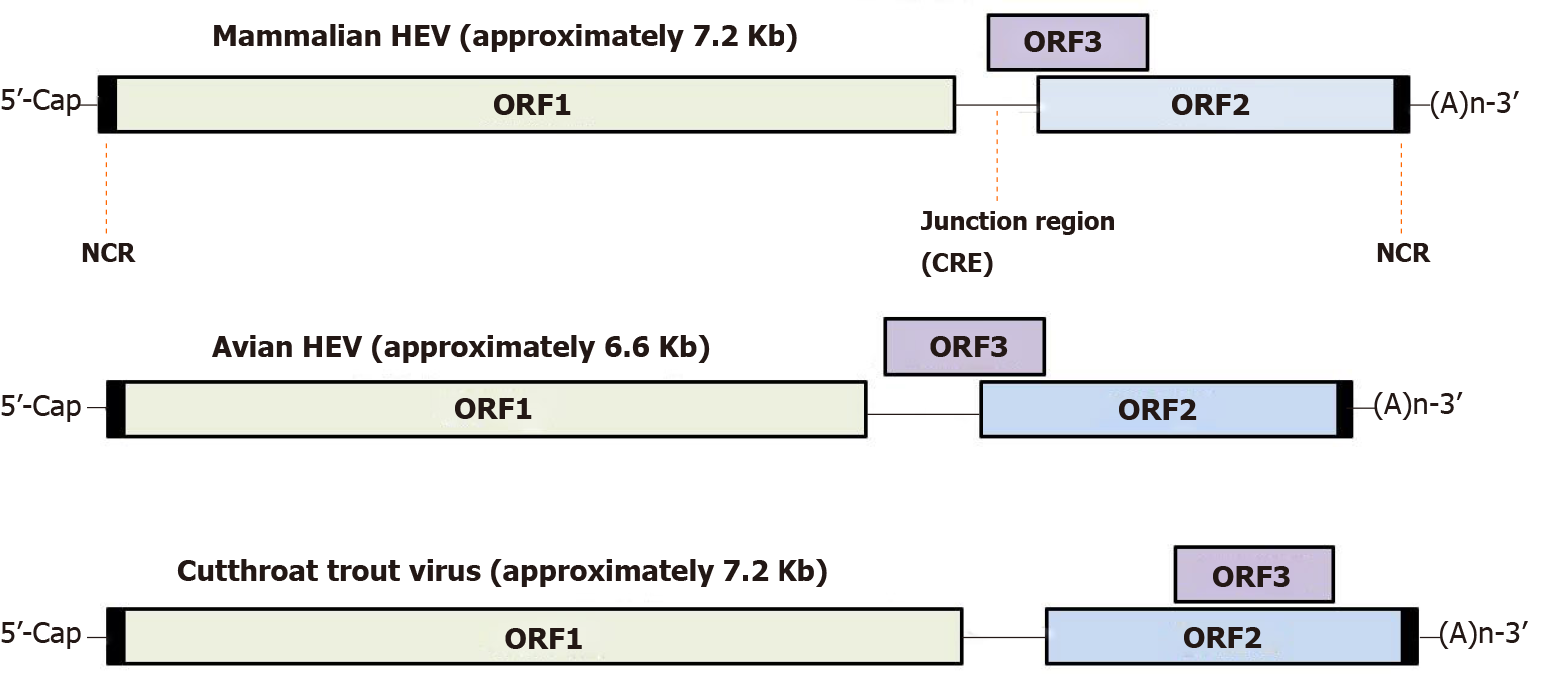
Figure 5 Hepatitis E virus genome organization.
Genome location of open reading frame 3 among different hepeviruses. HEV: Hepatitis E virus; NCR: Non-coding region; CRE: Cis-reactive element; ORF: Open reading frame.
- Citation: Yang YL, Nan YC. Open reading frame 3 protein of hepatitis E virus: Multi-function protein with endless potential. World J Gastroenterol 2021; 27(20): 2458-2473
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v27/i20/2458.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2458