Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2020; 26(45): 7263-7271
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7263
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7263
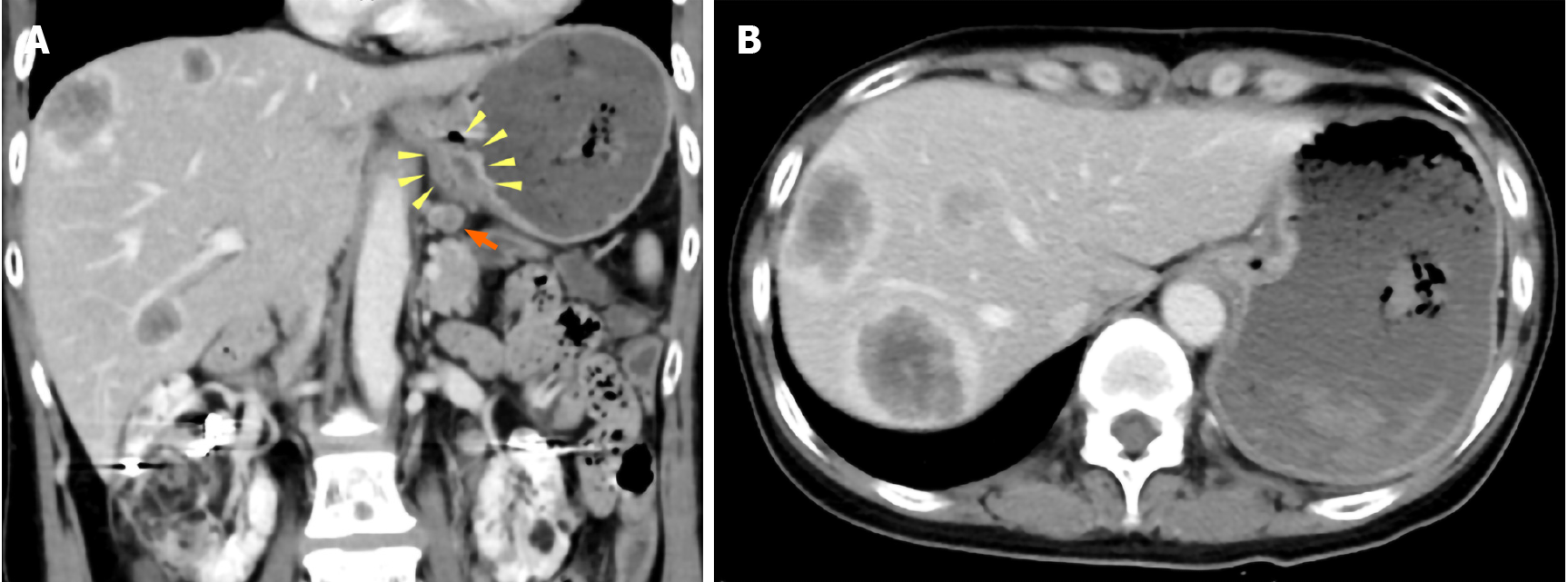
Figure 1 Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography images.
A: Wall thickness from the esophagogastric junction to the cardia (yellow arrowhead) and enlarged lymph nodes near the lesser curvature of the stomach (orange arrow); B: Multiple ring-enhanced tumors are observed in the liver.
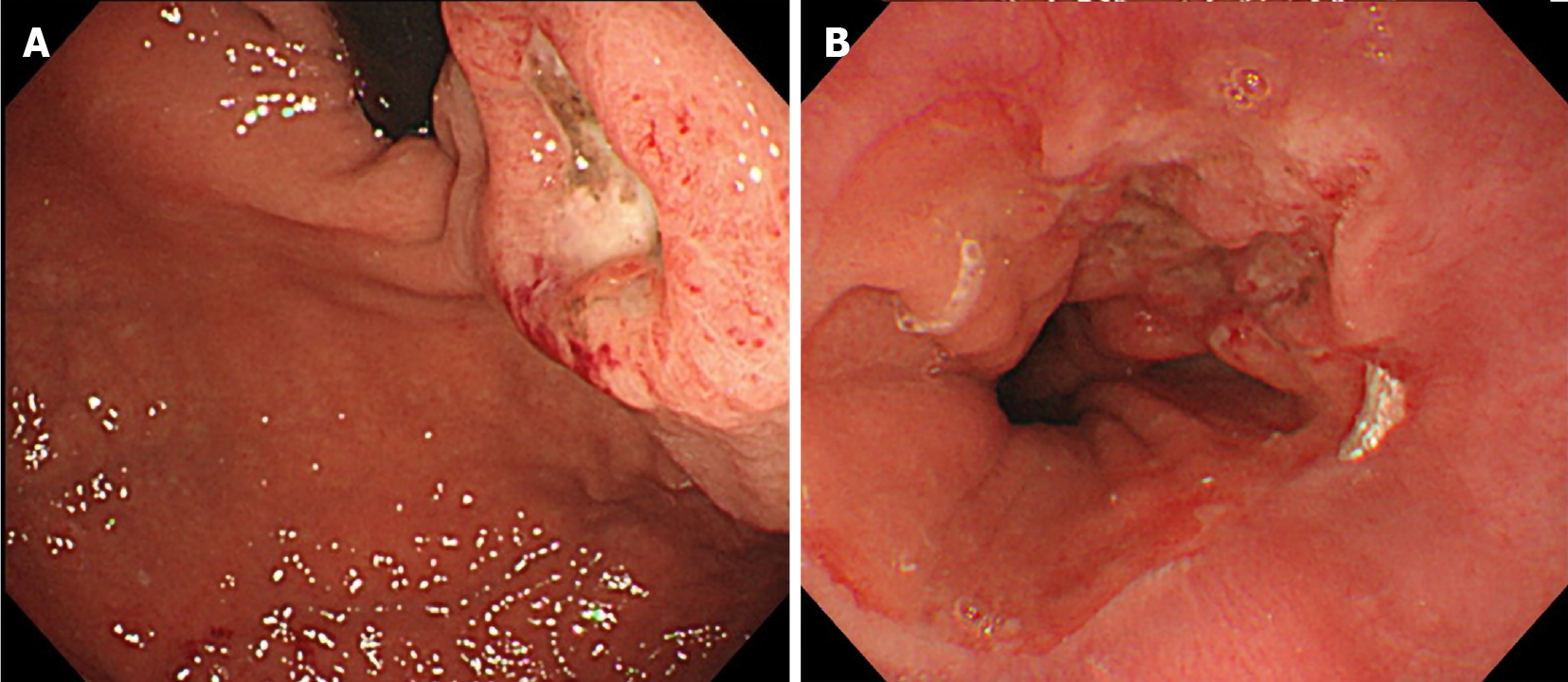
Figure 2 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy revealed type 3 tumor located from the esophagogastric junction to the cardia.
A: Image from endoscopic examination of esophagus; B: Image from endoscopic examination of stomach.
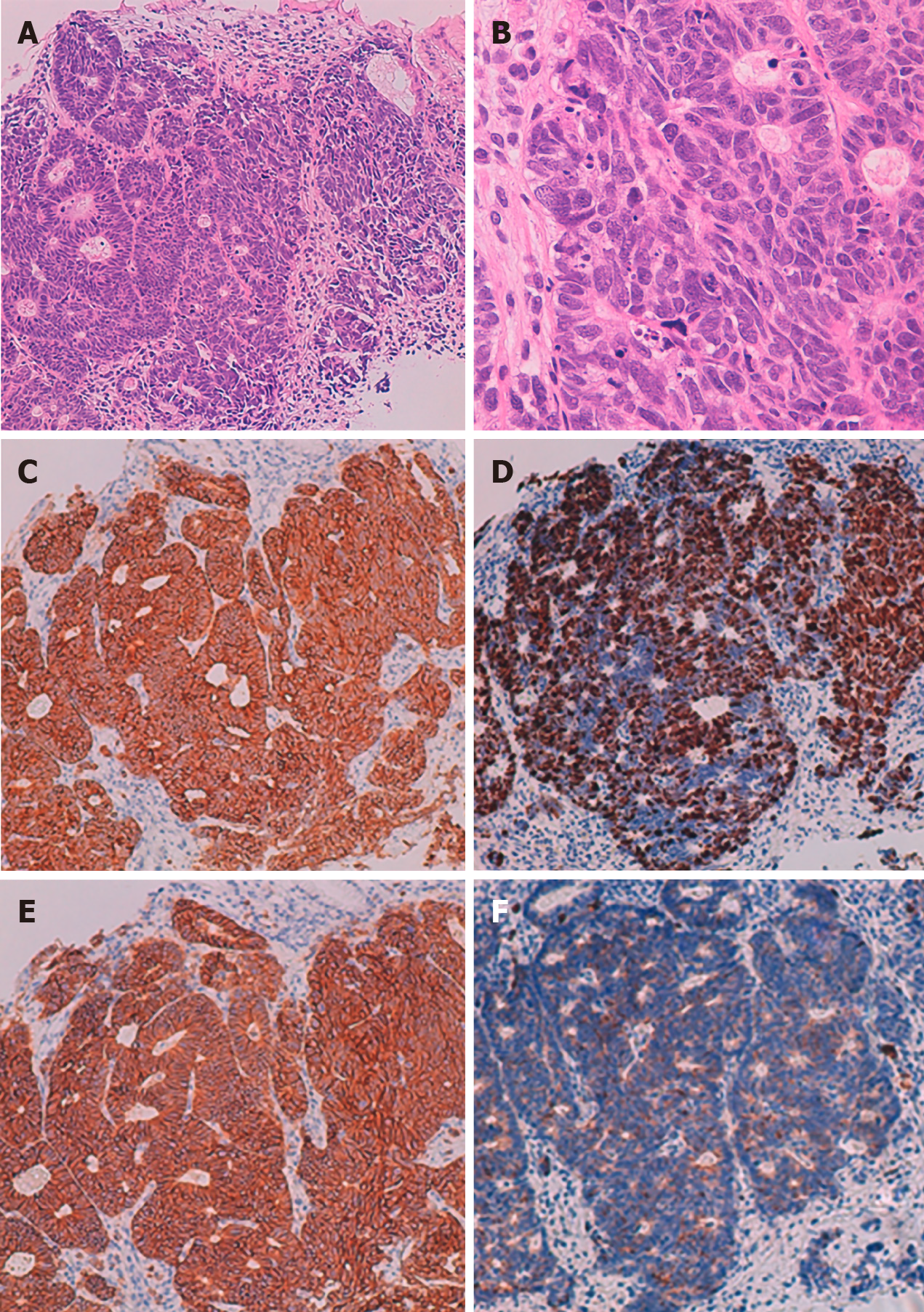
Figure 3 Histological findings of a mucosal lesion.
A: Low-power histological view of Hematoxylin and eosin (H-E) stained specimens showing atypical epithelial cells with solid alveolar nests; B: High-power view of H-E stained specimens reveals poorly differentiated atypical cells with large nucleus-cytoplasm ratio; C: Synaptophysin positive; D: Ki 67 index is approximately 70%; E: CD56 positive; F: Chromogranin A positive.
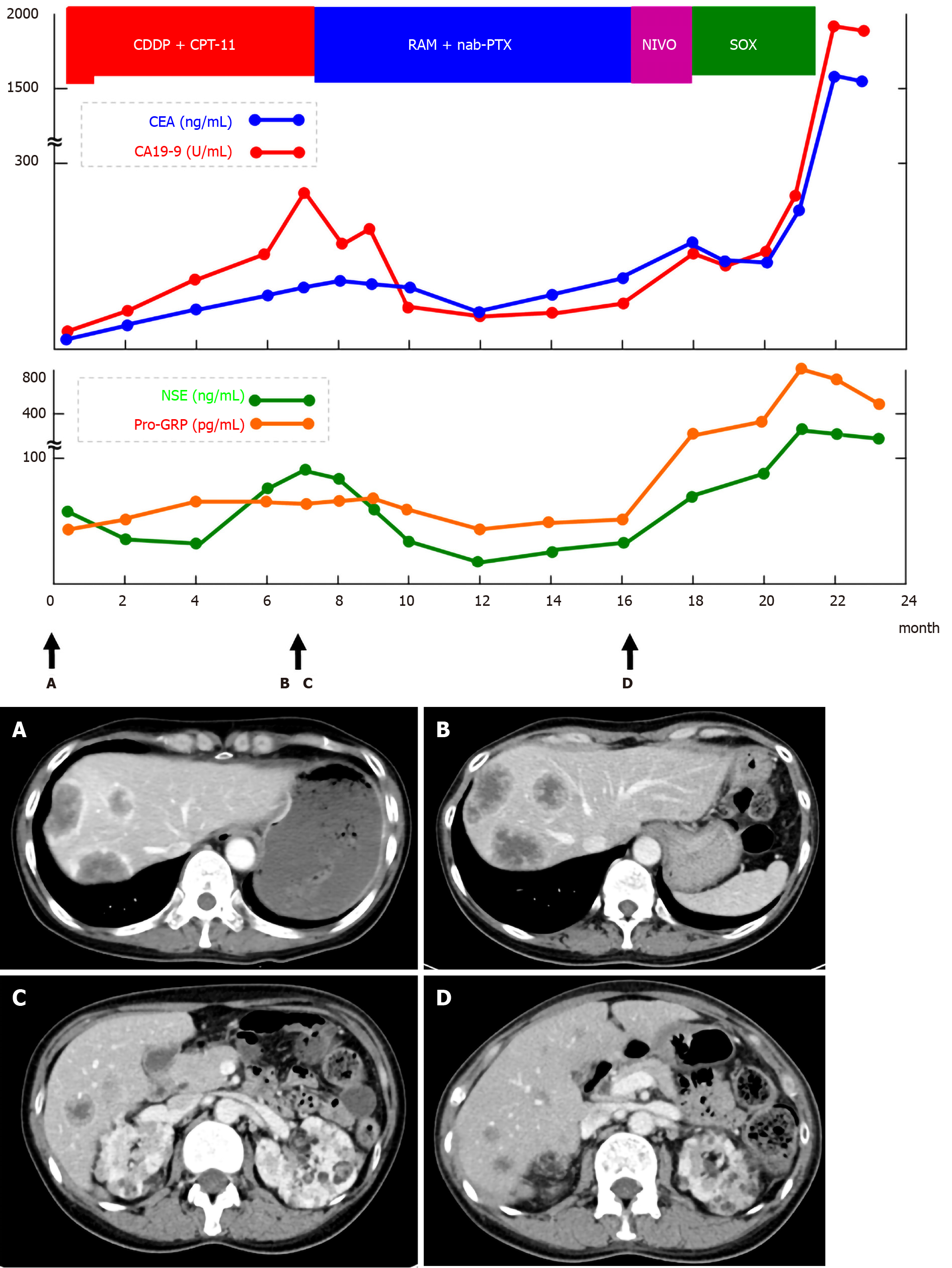
Figure 4 Clinical course of this case.
A-D: Serum tumor markers were elevated. A CT scan after seven courses of chemotherapy revealed increased liver metastasis. CDDP: Cisplatin; CPT-11: Irinotecan; RAM: Ramucirumab; nab-PTX: Nab-Paclitaxel; NIVO: Nivolumab; SOX: S-1 and oxaliplatin; CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen; CA19-9: Carbohydrate antigen 19-9; NSE: Neuron-specific enolase; Pro-GRP: Pro-gastrin-releasing peptide.
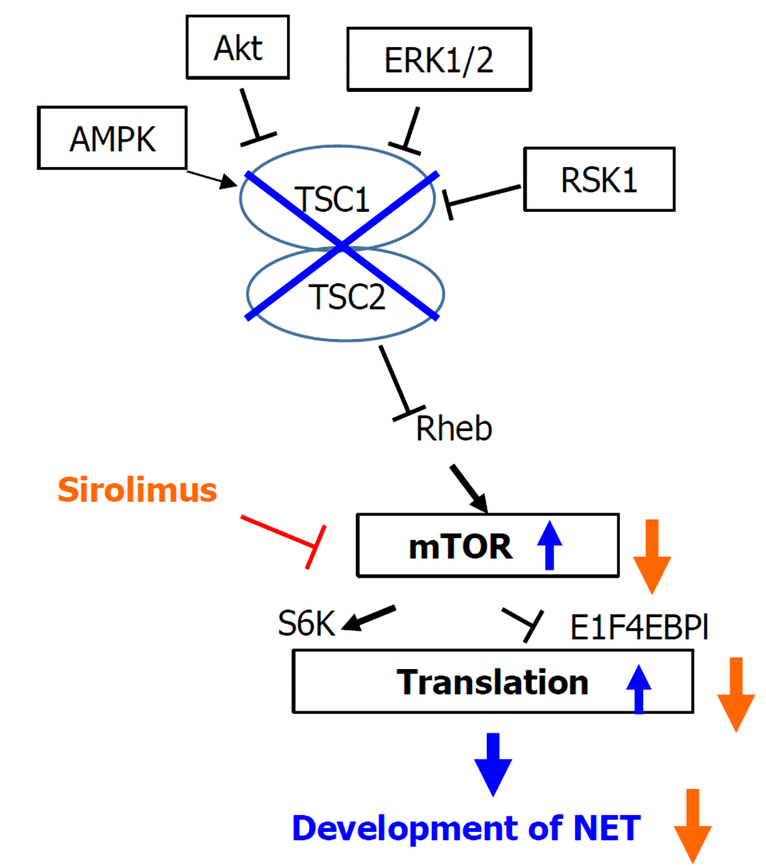
Figure 5 Diagram showing that the mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor suppresses the formation of neuroendocrine tumor by suppressing the AKT-mTOR pathway.
In the AKT-mTOR pathway, mutation of tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)1/TSC2 genes causes mTOR to proliferate and generate neuroendocrine tumor (NET). Sirolimus, an mTOR inhibitor, inhibits the abnormal growth of mTOR, which suppresses the generation of NET. TSC: Tuberous sclerosis complex; AMPK: Adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular regulated protein kinases; RSK: Ribosomal S6 kinase; EBP: Evidence-based practice; NET: Neuroendocrine tumor.
- Citation: Ishida N, Miyazu T, Tamura S, Suzuki S, Tani S, Yamade M, Iwaizumi M, Osawa S, Hamaya Y, Shinmura K, Sugimura H, Miura K, Furuta T, Sugimoto K. Tuberous sclerosis patient with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagogastric junction: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(45): 7263-7271
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i45/7263.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7263