Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2020; 26(41): 6335-6345
Published online Nov 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i41.6335
Published online Nov 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i41.6335
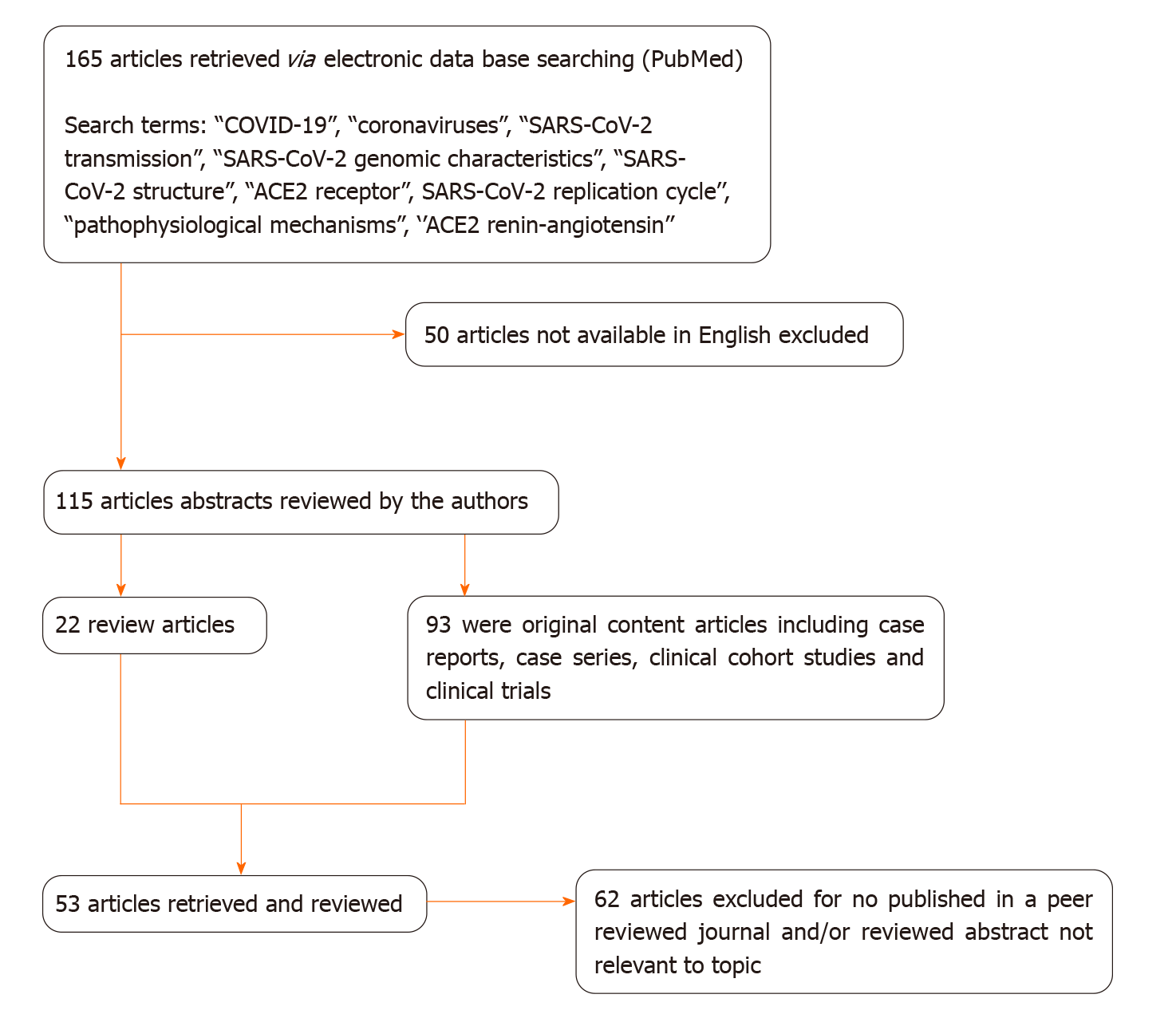
Figure 1 Decision tree for literature research strategy.
COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme type 2.
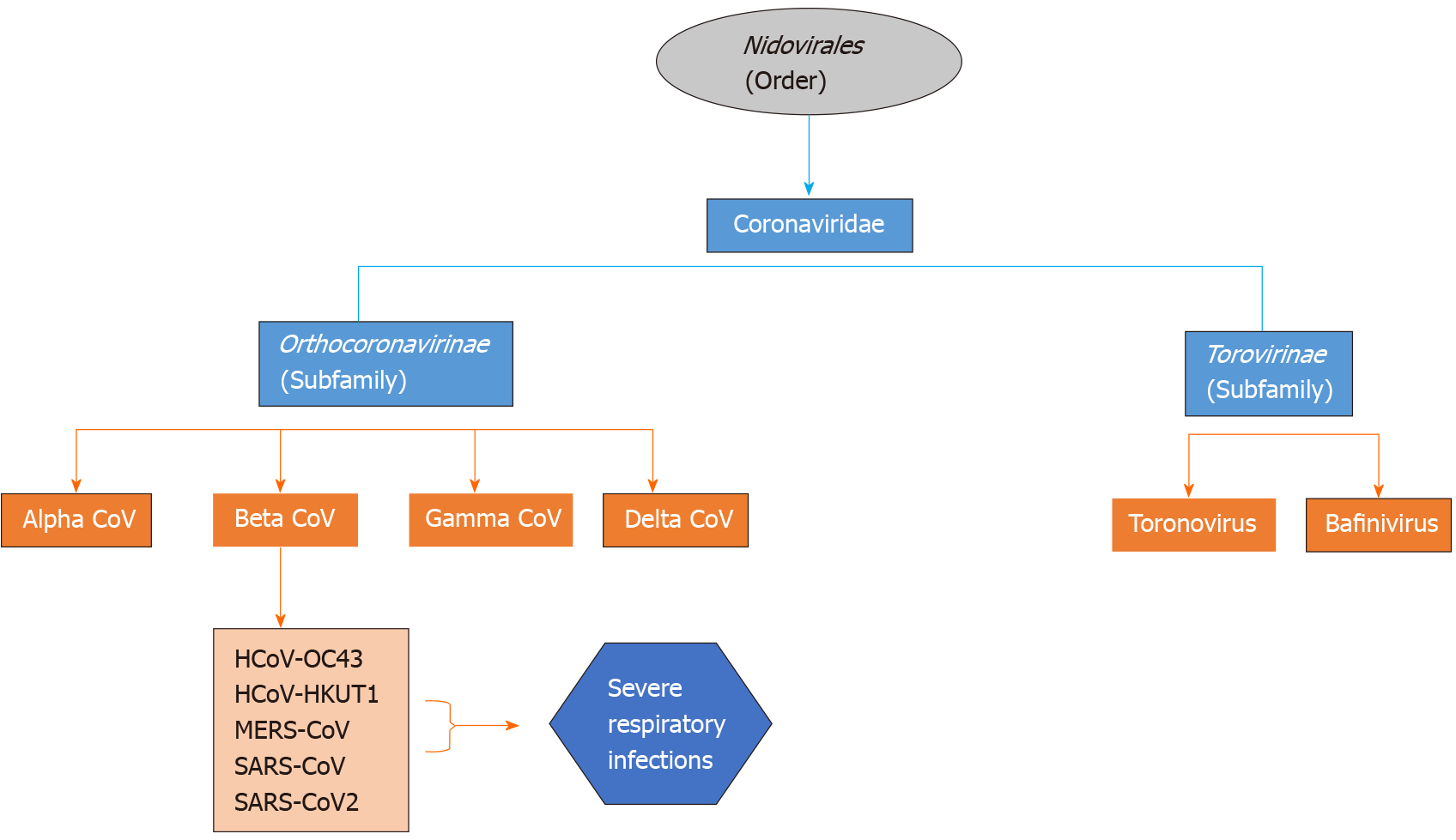
Figure 2 Classification scheme of the various types of coronaviruses within the family Coronaviridae.
SARS-CoV: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus; MERS-CoV: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; HCoV: Human coronavirus; CoV: Coronavirus.
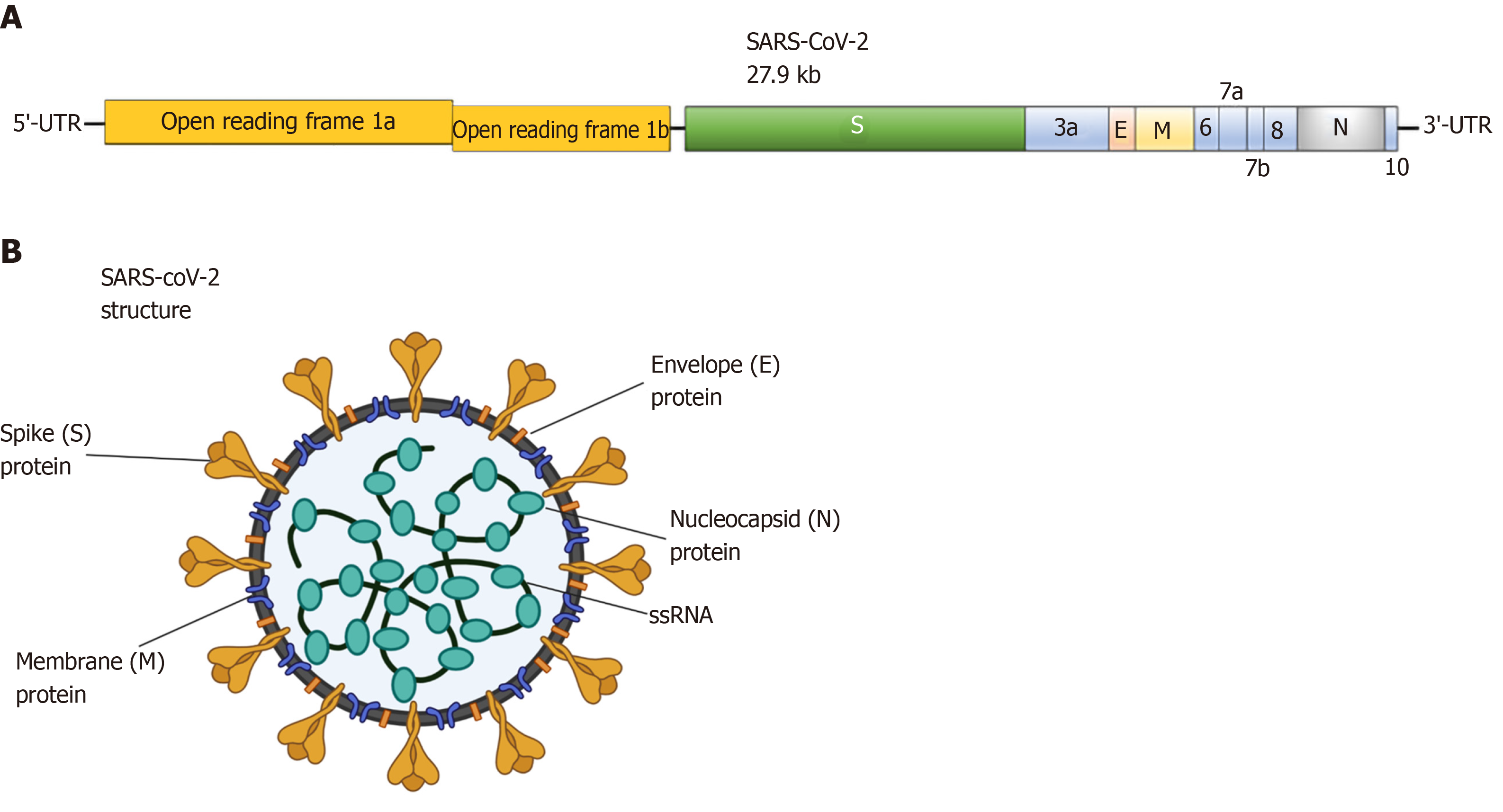
Figure 3 Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 schematic structure.
A: Schematic representation of the genomic organization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2); B: Schematic diagram of the structural features of SARS-CoV-2 and its primary structural proteins. The above diagrams were created with Biorender.com. Kb: kilobase pair; ORF: Open reading frame; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; S: Spike protein; E: Envelope protein; M: Membrane protein; N: Nucleocapsid protein.
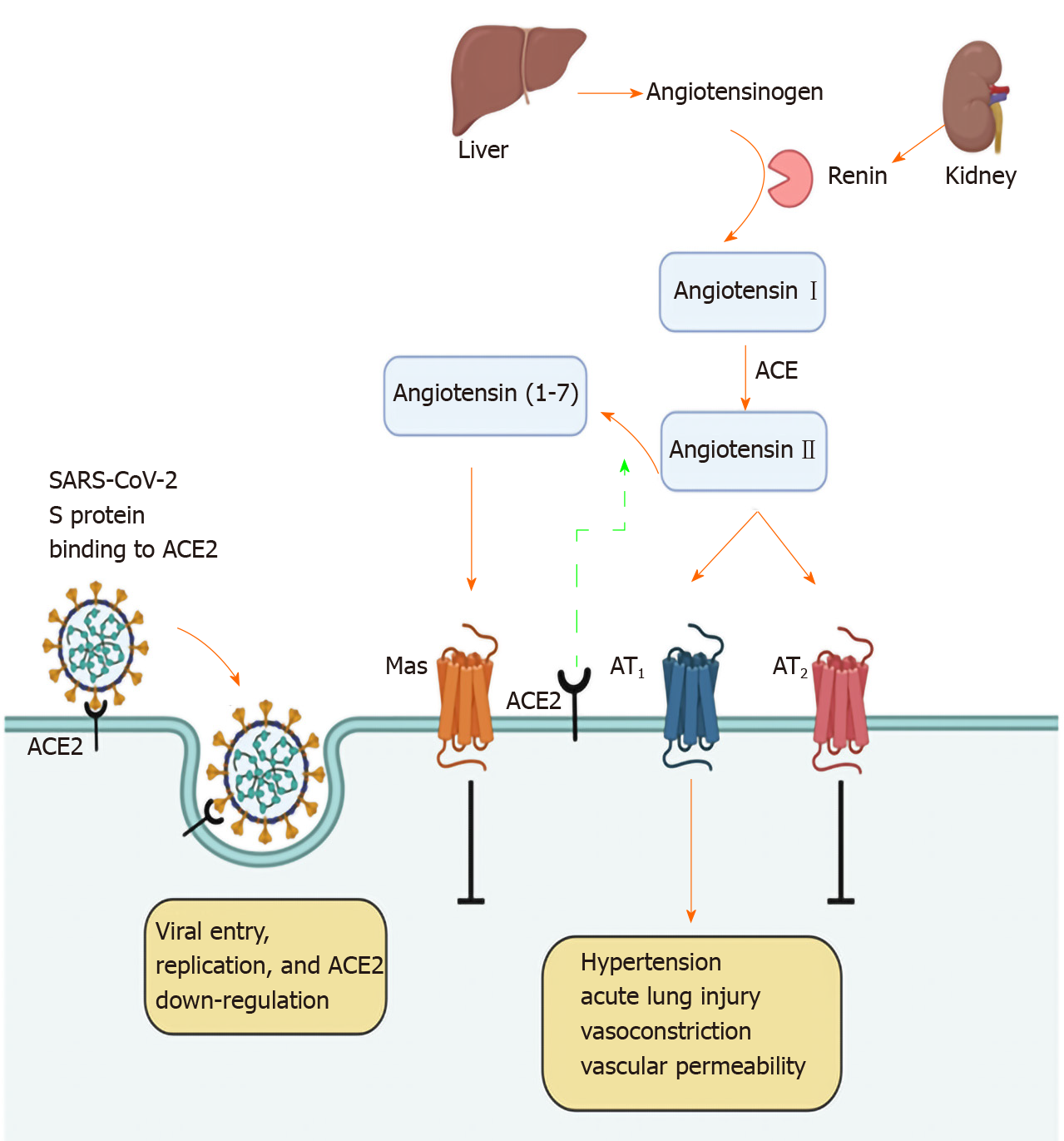
Figure 4 Interaction between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and the renin-angiotensin system.
The above diagram was created with Biorender.com. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; ACE2: Angiotensin converting enzyme type 2; ACE: Angiotensin converting enzyme; AT: Angiotensin II receptor type.
- Citation: Galanopoulos M, Doukatas A, Gazouli M. Origin and genomic characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and its interaction with angiotensin converting enzyme type 2 receptors, focusing on the gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(41): 6335-6345
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i41/6335.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i41.6335