Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2020; 26(39): 6087-6097
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.6087
Published online Oct 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.6087
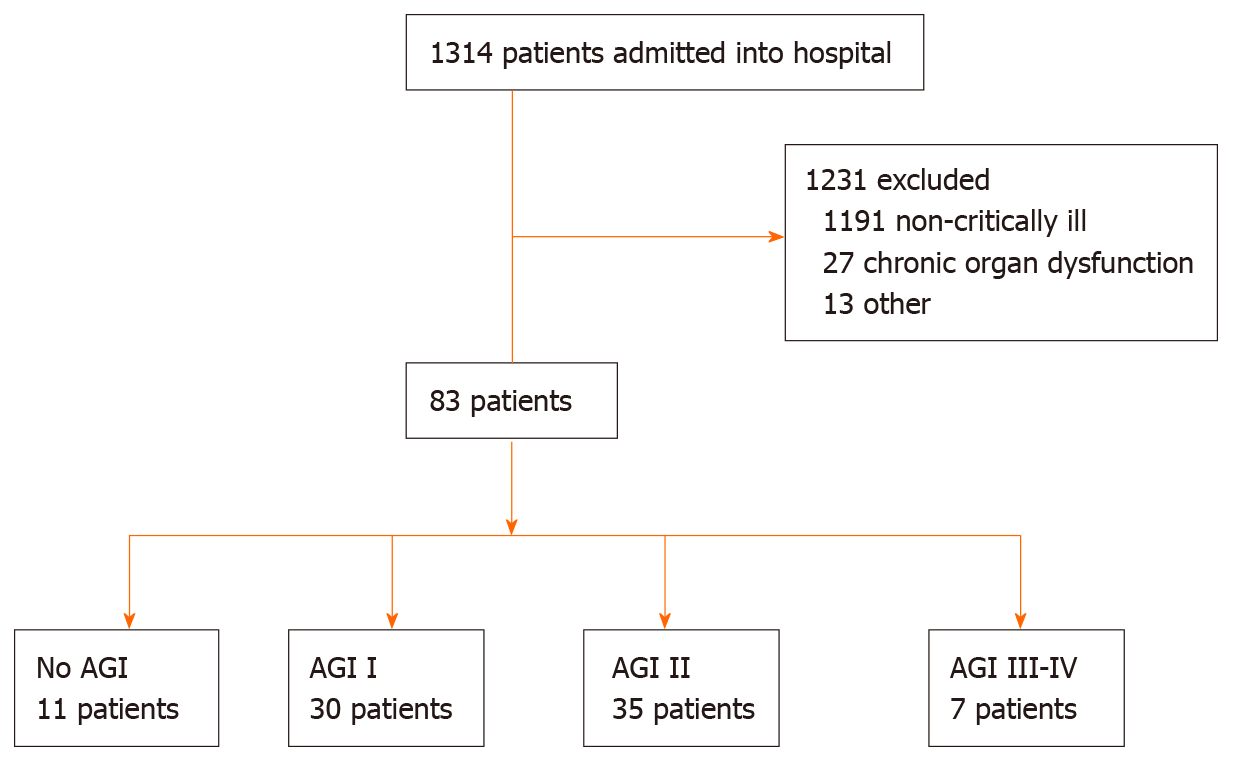
Figure 1 The flow diagram of participants.
AGI: Acute gastrointestinal injury.
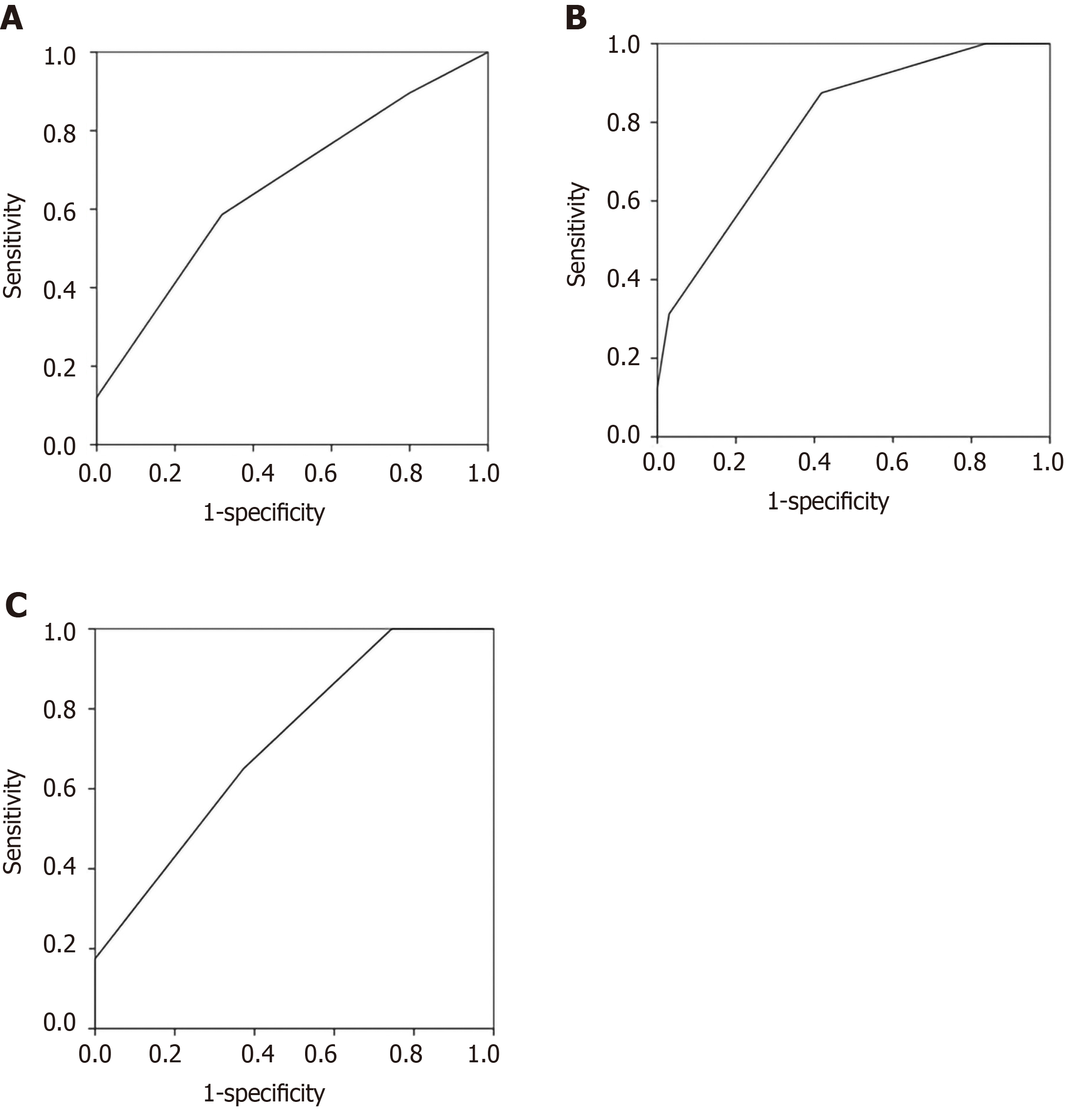
Figure 2 The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves.
A: Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (0.659, P = 0.022); B: Septic shock (0.793, P < 0.001); C: 28-d mortality (0.716, P = 0.001).
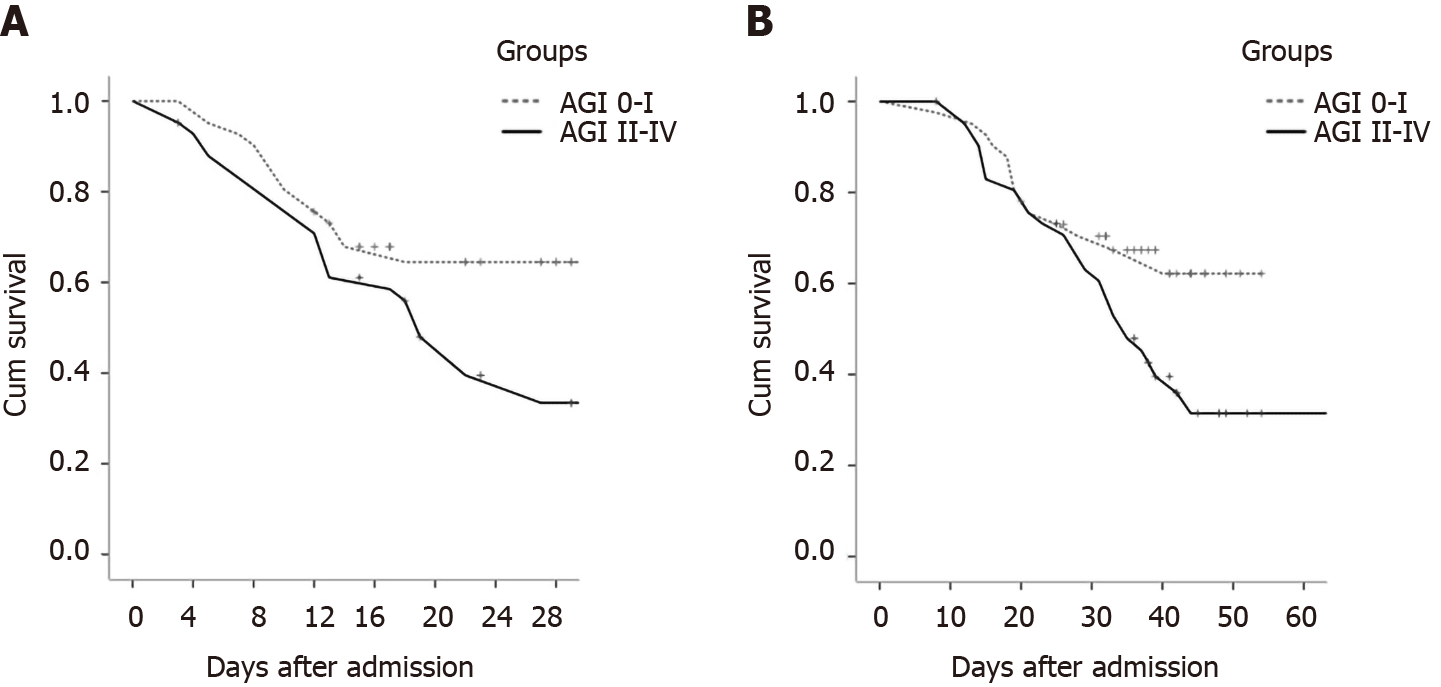
Figure 3 Cumulative survival.
Significant differences in 28-d mortality after admission and 60-d mortality after disease onset were found between the group with acute gastrointestinal injury (AGI) grade I/no AGI (n = 41) and the group with acute gastrointestinal injury grade II to IV (n = 42). A: 28-d mortality after admission (P = 0.037); B: 60-d mortality after disease onset (P = 0.049). AGI: Acute gastrointestinal injury.
- Citation: Sun JK, Liu Y, Zou L, Zhang WH, Li JJ, Wang Y, Kan XH, Chen JD, Shi QK, Yuan ST. Acute gastrointestinal injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(39): 6087-6097
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i39/6087.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i39.6087