Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2020; 26(19): 2403-2415
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2403
Published online May 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2403
Figure 1 Lobo classification and Boix classification of periampullary diverticulum.
A: Lobo classification of periampullary diverticulum; B: Boix classification of periampullary diverticulum. Type I: The papilla is located inside of the diverticulum (Ia: Up; Ib: Left, Ic: Down; Id: Right); type II: The papilla is located in the margin of the diverticulum (IIa: Apical left margin; IIb: Apical right margin; IIc: Center left or right margin; IId: Between 2 diverticula); type III: The papilla is located near the diverticulum. IDP: Intradiverticular papilla; JPD: Juxtapapillary diverticula.
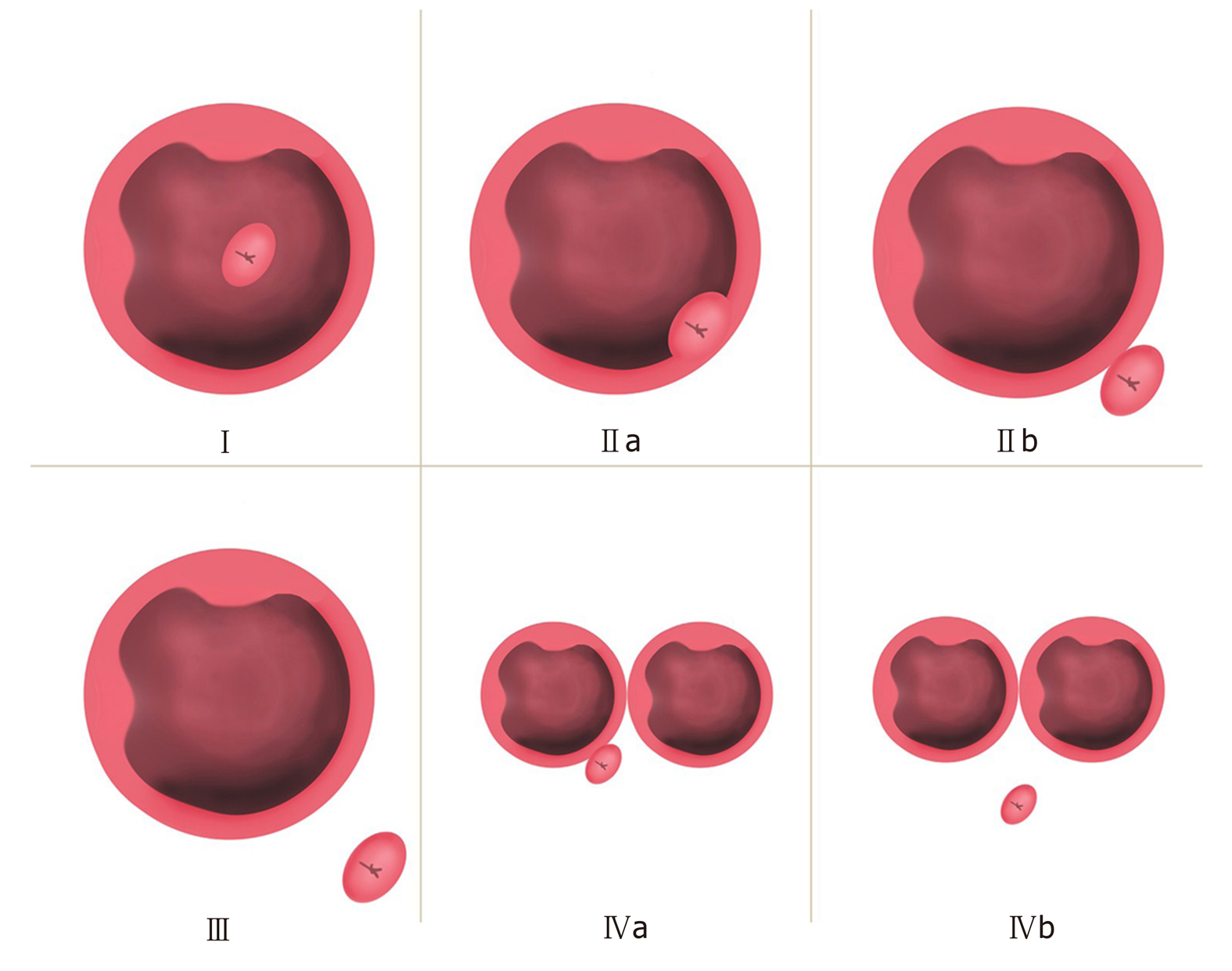
Figure 2 Li-Tanaka classification of periampullary diverticulum.
Type I: The papilla is located inside the diverticulum and not adjacent to the margin; type II: The papilla is located in the margin of the diverticulum (type IIa: Inside of the margin; type IIb: Outside of the margin, < 1 cm); type III: The papilla is located outside the margin, ≥ 1 cm; type IV: The papilla is located in the margin of the diverticulum, ≥ 2 diverticula (type IVa: The papilla is located outside the margins of at least one diverticulum, < 1 cm; type IVb: The papilla is located outside the margins of all the diverticula, ≥ 1 cm).
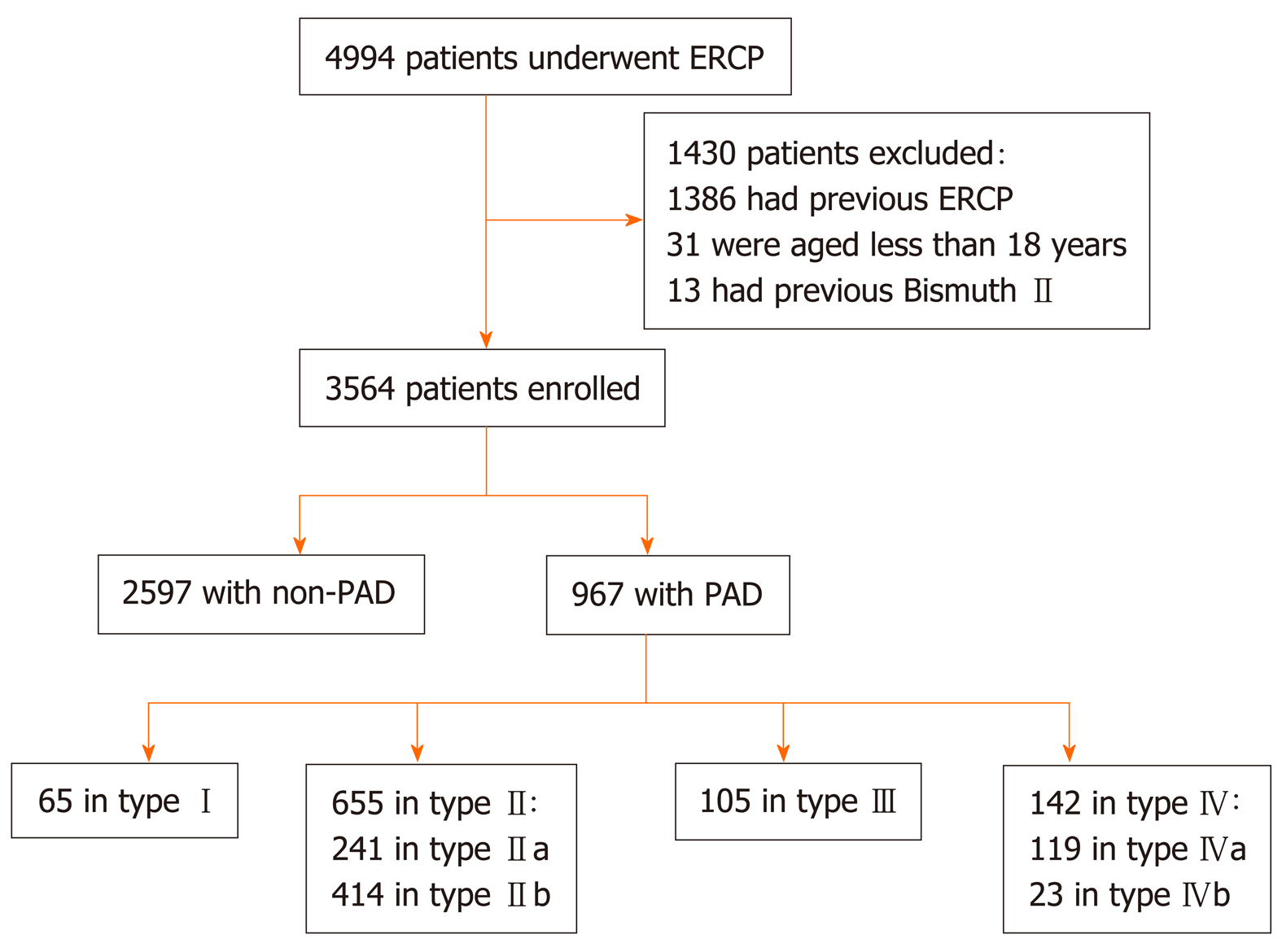
Figure 3 Flow chart (Li-Tanaka classification).
PAD: Periampullary diverticulum; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
- Citation: Yue P, Zhu KX, Wang HP, Meng WB, Liu JK, Zhang L, Zhu XL, Zhang H, Miao L, Wang ZF, Zhou WC, Suzuki A, Tanaka K, Li X. Clinical significance of different periampullary diverticulum classifications for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography cannulation. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(19): 2403-2415
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i19/2403.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2403