Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2020; 26(12): 1242-1261
Published online Mar 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i12.1242
Published online Mar 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i12.1242
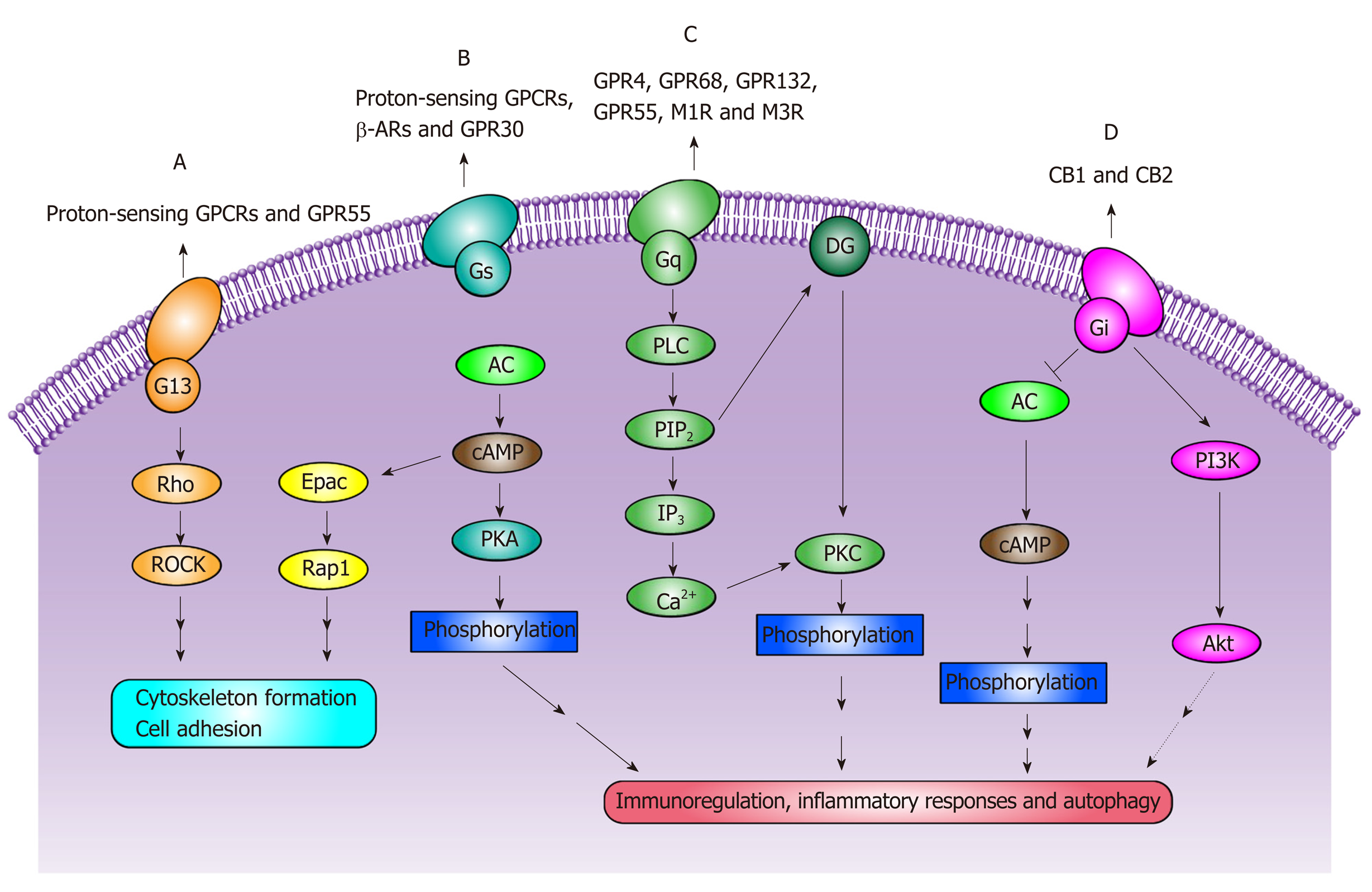
Figure 1 The main signaling pathways of G protein-coupled receptors.
A: Proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors and G protein-coupled receptor 55 are coupled to G13 proteins and are involved in G13/Rho signaling pathways, mediating the modulation of cytoskeleton formation and cell adhesion; B: Proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors, G protein-coupled receptor 30 and β-adrenergic receptors are implicated in Gs/adenylyl cyclase/cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling pathways and multiple phosphorylation events, and then mediate immunoregulation, inflammatory responses and autophagy. In addition, G protein-coupled receptor 4 is also implicated in cAMP/exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac) signaling pathways, and then affects cell adhesion; C: G protein-coupled receptor 4, G protein-coupled receptor 68, G protein-coupled receptor 132, G protein-coupled receptor 55, type 1 muscarinic receptor and type 3 muscarinic receptor bind to Gq proteins and are involved in Gq/phospholipase C/Ca2+ signaling pathways, then phosphorylate target proteins, mediating the regulation of immune response, inflammatory reaction and autophagy; D: Cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 are coupled to Gi proteins and are involved in immunoregulation, inflammatory responses and autophagy through Gi/adenylyl cyclase/cAMP and Gi/phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/Akt signaling pathways. GPCRs: G protein-coupled receptors; GPR55: G protein-coupled receptor 55; ROCK: Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase; GPR30: G protein-coupled receptor 30; β-ARs: β-adrenergic receptors, including β1-, β2- and β3-adrenergic receptor; AC: Adenylyl cyclase; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; GPR4: G protein-coupled receptor 4; Epac: Exchange protein activated by cAMP; Rap1: Ras associated protein 1; PKA: Protein kinase A; GPR68: G protein-coupled receptor 68; GPR 132: G protein-coupled receptor 132; M1R: Type 1 muscarinic receptor; M3R: Type 3 muscarinic receptor; PLC: Phospholipase C; PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; IP3: Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; DG: Diacylglycerol; PKC: Protein kinase C; CB1: Cannabinoid receptor 1; CB2: Cannabinoid receptor 2; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; Akt: Also known as protein kinase B (PKB); Proton-sensing GPCRs: GPR4, GPR68, GPR65 and GPR132; Phosphorylation: nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kB), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) etc.
- Citation: Zeng Z, Mukherjee A, Varghese AP, Yang XL, Chen S, Zhang H. Roles of G protein-coupled receptors in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(12): 1242-1261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i12/1242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i12.1242