Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2019; 25(33): 4835-4849
Published online Sep 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4835
Published online Sep 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4835
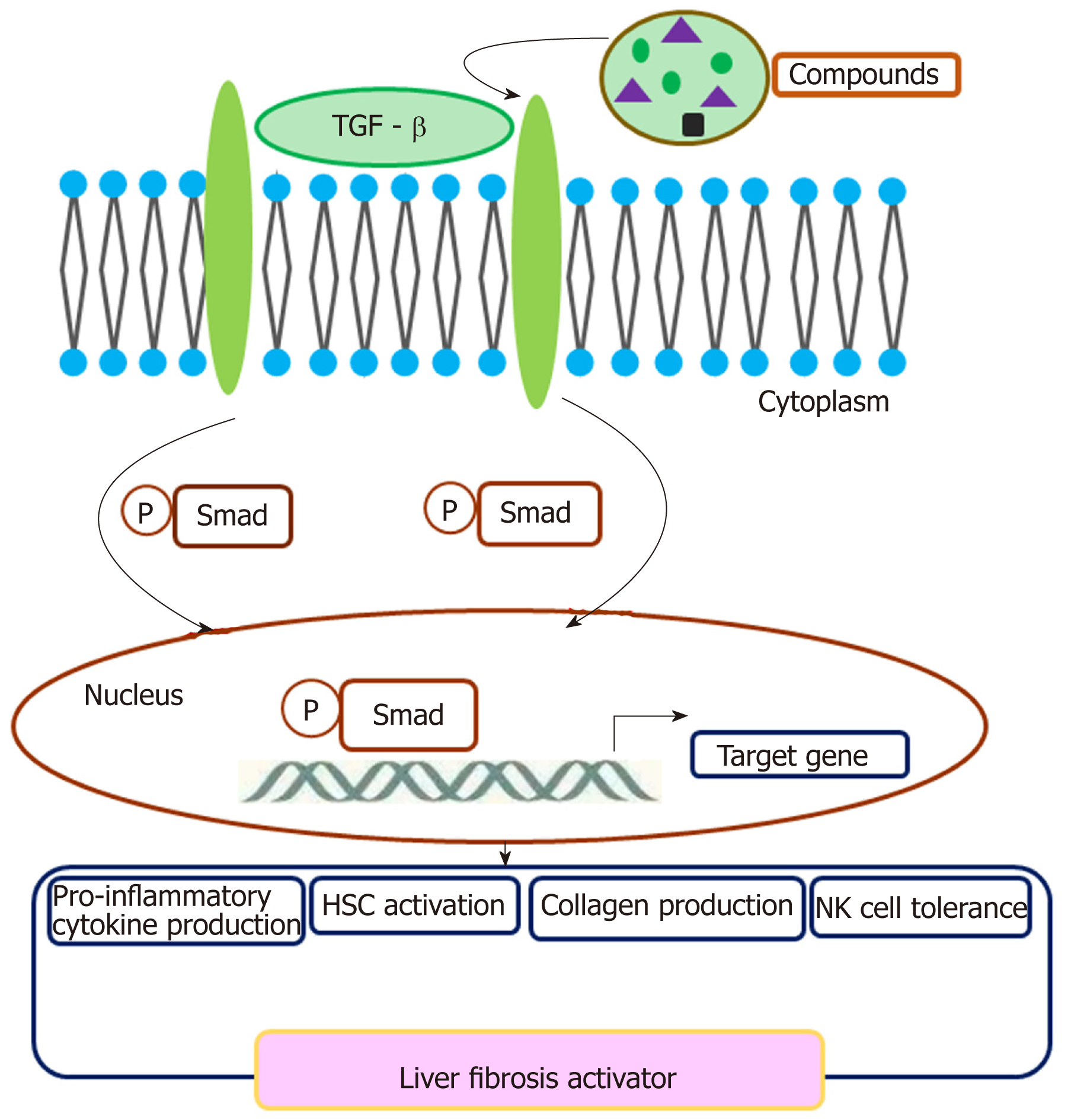
Figure 1 Transforming growth factor-β mediated crosstalk network in liver fibrosis.
TGF-β is primarily signaled by intracellular Smads. TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; NK: Natural killer.
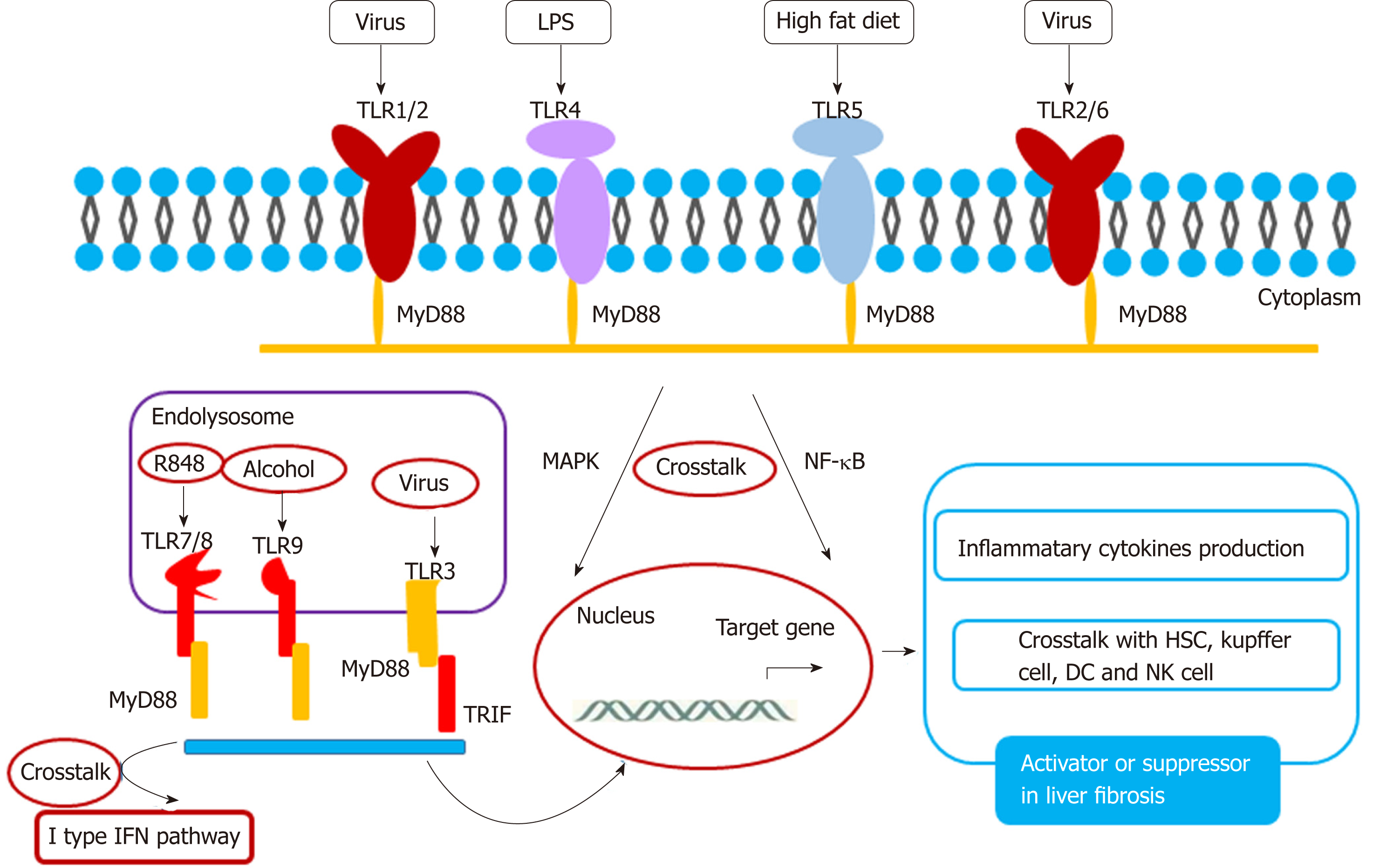
Figure 2 Toll-like receptor mediated crosstalk network in liver fibrosis.
Toll-like receptor is a member of DAMPs that recognize pathogen-associated molecules and thereby transmit inflammatory signals that cause inflammatory responses. TLR: Toll-like receptor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-кB: Nuclear factor-кB; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; DC: Dendritic cells; NK: Natural killer.
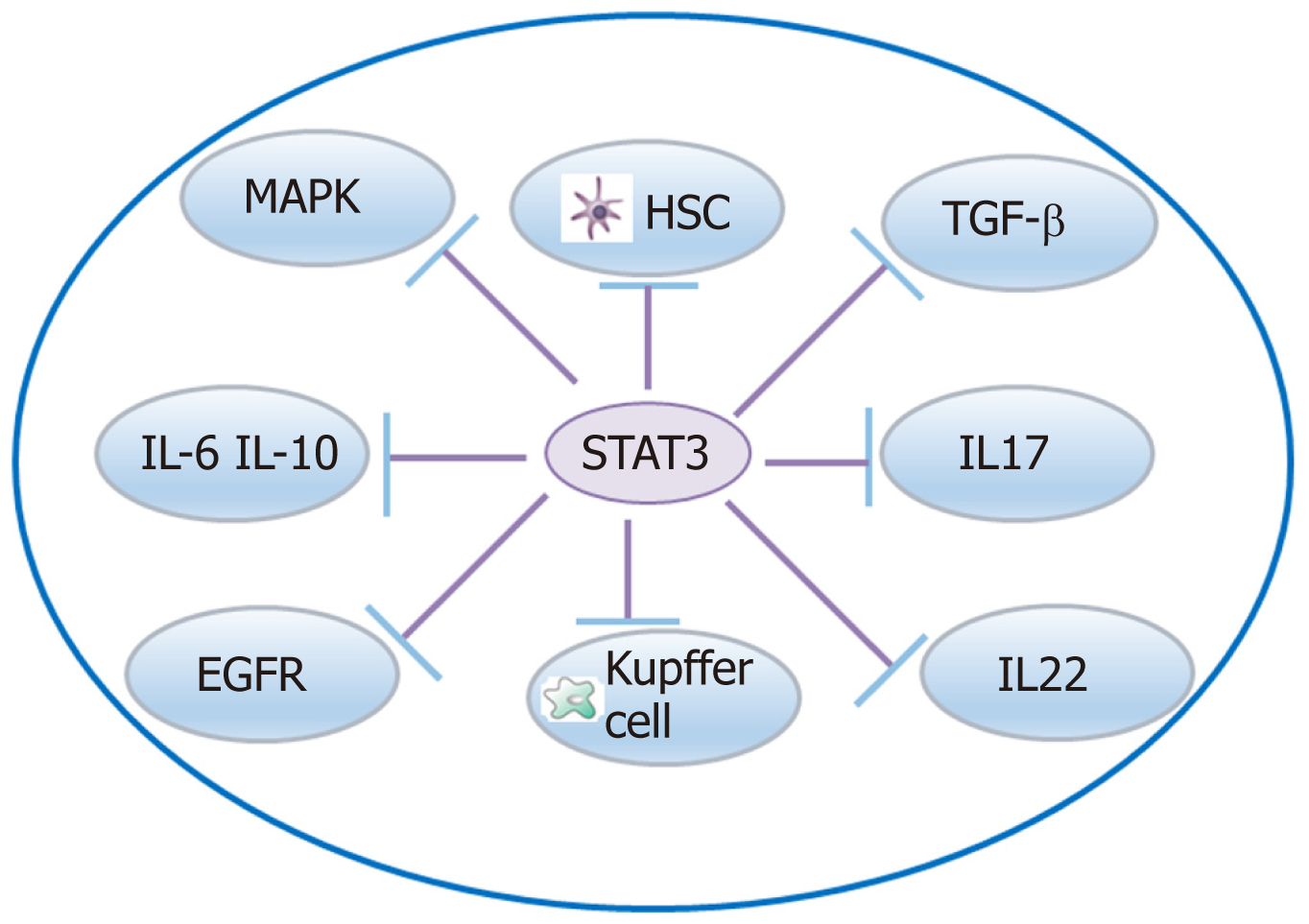
Figure 3 STAT3-mediated inflammatory mediator crosstalk network in liver fibrosis.
EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; IL: Interleukin.
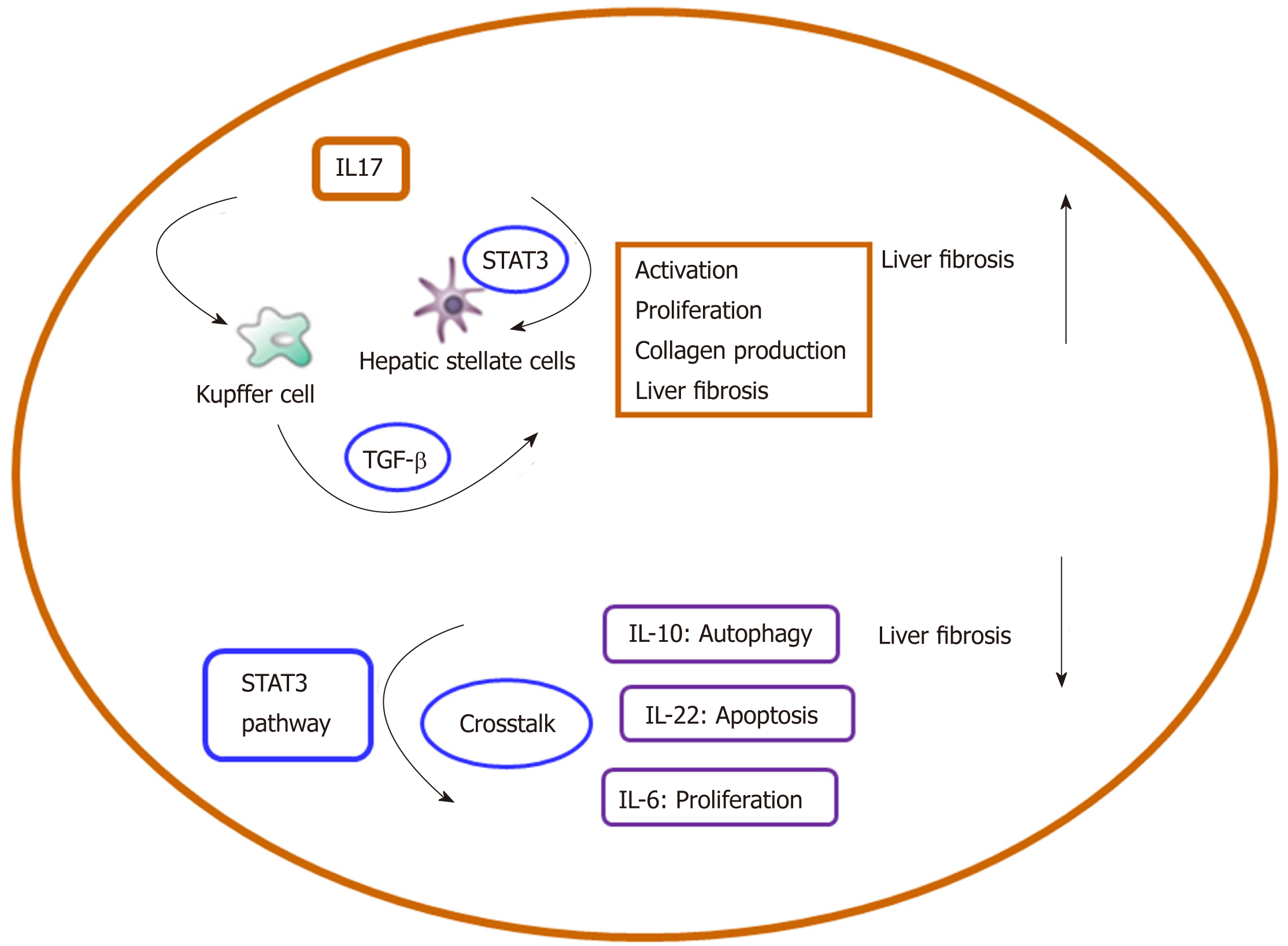
Figure 4 Inflammatory mediator network between cytokines and signaling pathway in liver fibrosis.
TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Zhangdi HJ, Su SB, Wang F, Liang ZY, Yan YD, Qin SY, Jiang HX. Crosstalk network among multiple inflammatory mediators in liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(33): 4835-4849
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i33/4835.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4835