Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2017; 23(47): 8283-8290
Published online Dec 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8283
Published online Dec 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8283
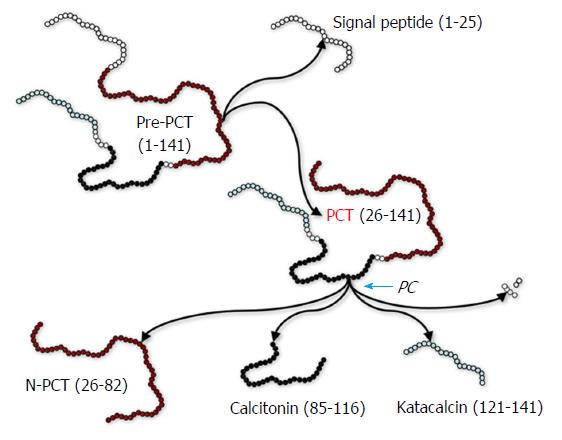
Figure 1 Biochemistry and biology of procalcitonin.
N-PCT: N-terminal procalcitonin; PC: Prohormone convertase; pre-PCT: Pre-procalcitonin; PCT: Procalcitonin.
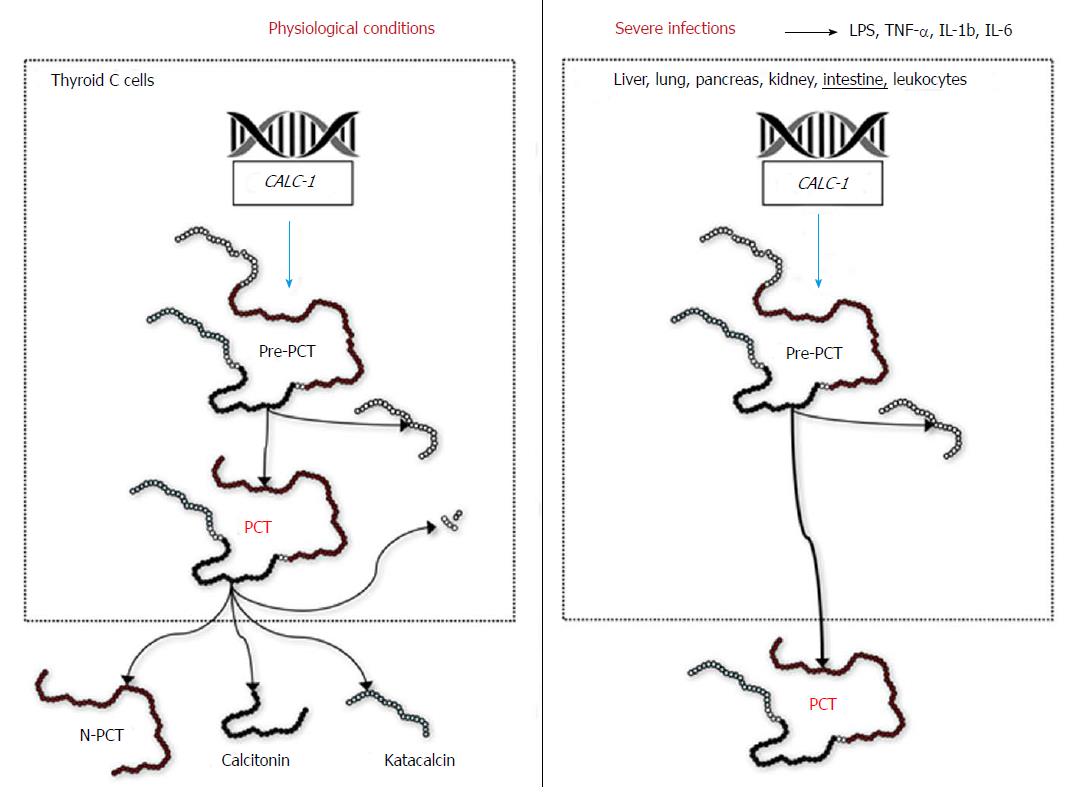
Figure 2 Biology of procalcitonin in normal and infective conditions.
CALC-1: Calcitonin-related polypeptide gene 1; LPC: Lipopolysaccharide; IL-1b: Interleukin-1b; IL-6: Interleukin-6; N-PCT: N-terminal procalcitonin; pre-PCT: Pre-procalcitonin; PCT: Procalcitonin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
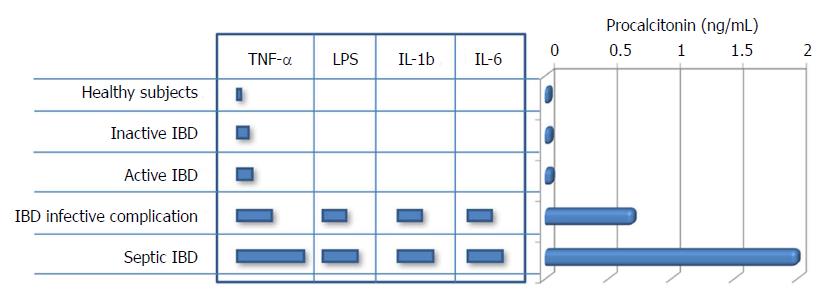
Figure 3 Procalcitonin in inflammatory bowel disease.
CALC-1: Calcitonin-related polypeptide gene 1; LPC: Lipopolysaccharide; IL-1b: Interelukin-1b; IL-6: Interleukin-6; N-PCT: N-terminal procalcitonin; pre-PCT: Pre-procalcitonin; PCT: Procalcitonin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Lippi G, Sanchis-Gomar F. Procalcitonin in inflammatory bowel disease: Drawbacks and opportunities. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(47): 8283-8290
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i47/8283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8283