Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2017; 23(25): 4569-4578
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4569
Published online Jul 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4569
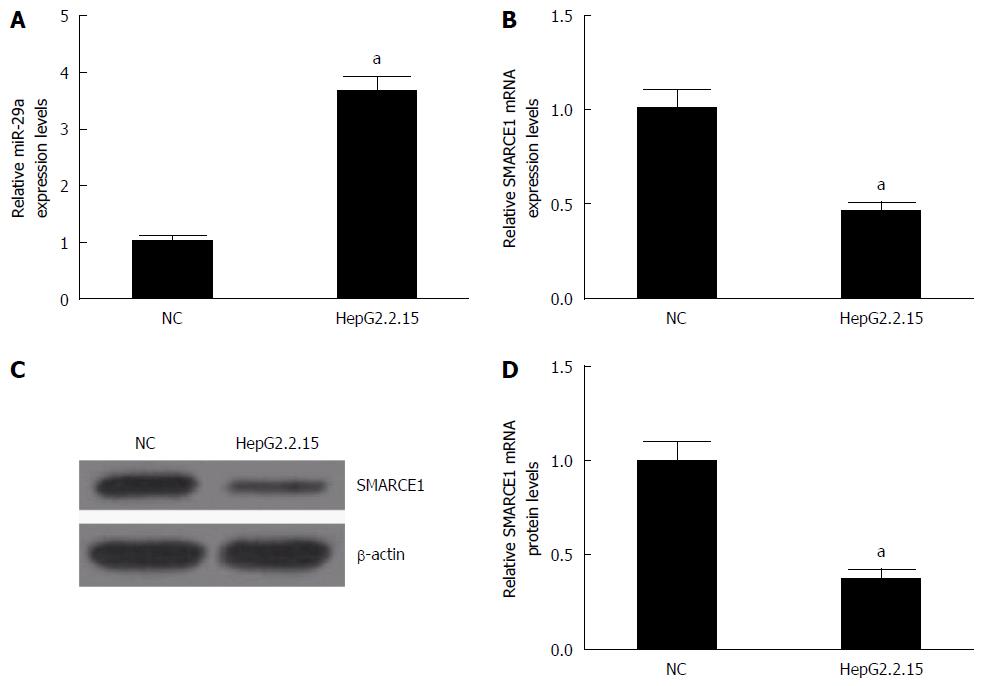
Figure 1 Expression of miR-29a and SMARCE1 in hepatitis B virus-infected HepG2.
2.15 cells (n = 3). A and B: qRT-PCR analysis showed the expression levels of miR-29a and SMARCE1 in HepG2.2.15 cells and HepG2 cells (NC); C and D: The protein level of SMARCE1 was detected and quantified by western blotting of HepG2.2.15 cells and HepG2 cells (NC). Data represent the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs NC.
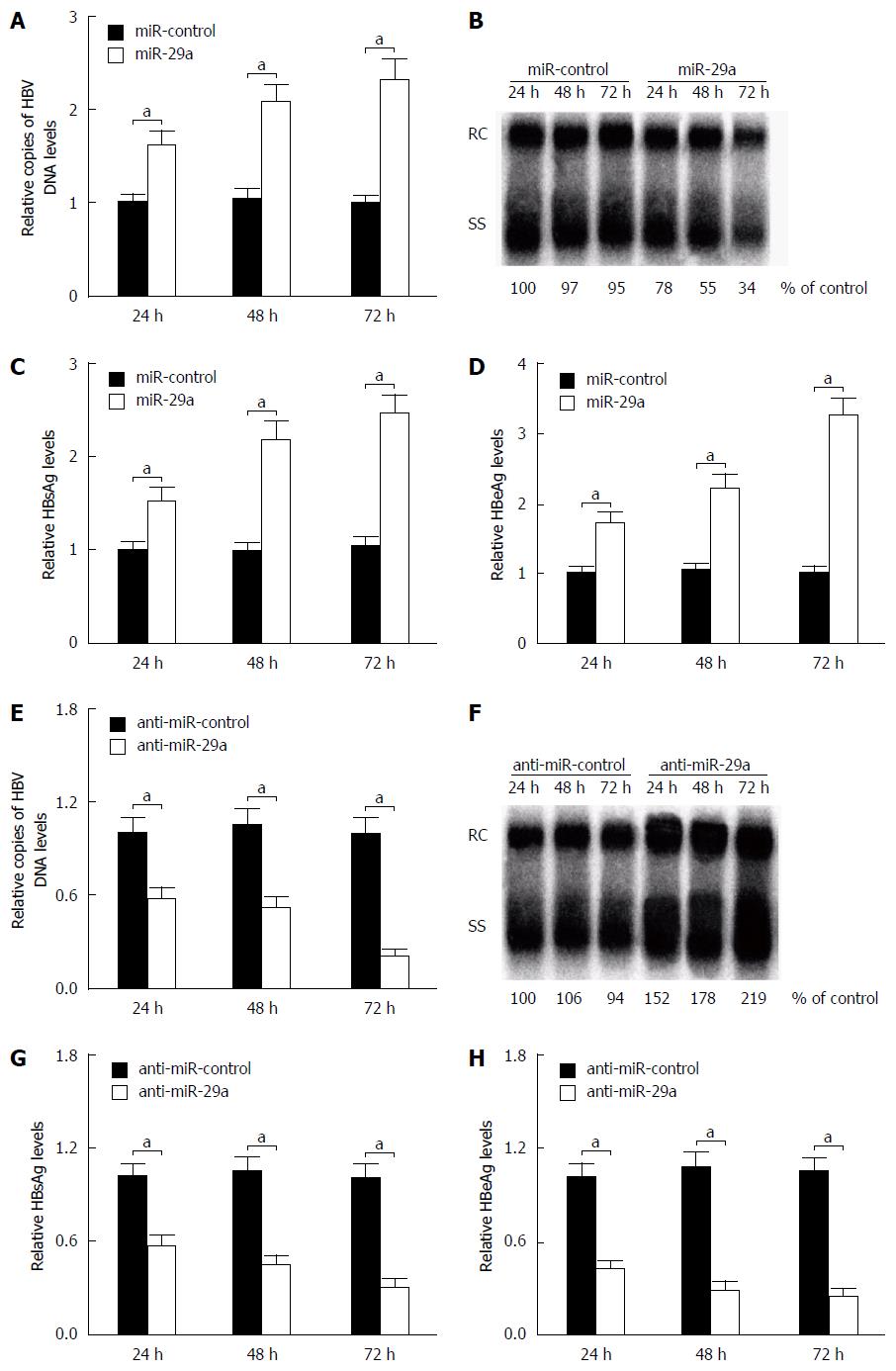
Figure 2 Effect of miR-29a on hepatitis B virus replication and expression (n = 3).
HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with miR-control, miR-29a mimics or anti-miR-29a for 24 h. A: Relative HBV DNA copies were measured by qPCR analysis; B: HBV replication was detected by Southern blotting. The positions of relaxed circular (RC) and single-stranded (SS) DNAs are indicated 24 h post transfection. The ELISA assay was conducted to detect the levels of (C) HBsAg and (D) HBeAg 24 h post transfection. Data represent the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs miR-control. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen.
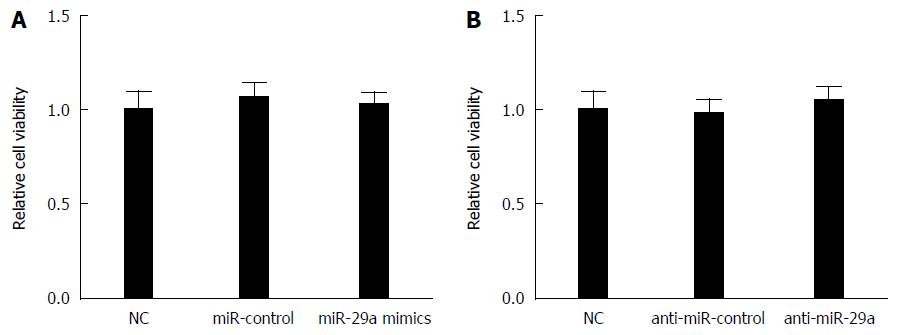
Figure 3 Effect of miR-29a on HepG2.
2.15 cell viability (n = 3). HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with miR-control, miR-29a mimics or anti-miR-29a for 48 h. HepG2 cell viability transfected with (A) miR-29a mimics and (B) anti-miR-29a was determined using the CCK-8 assay. Data represent the mean ± SD.
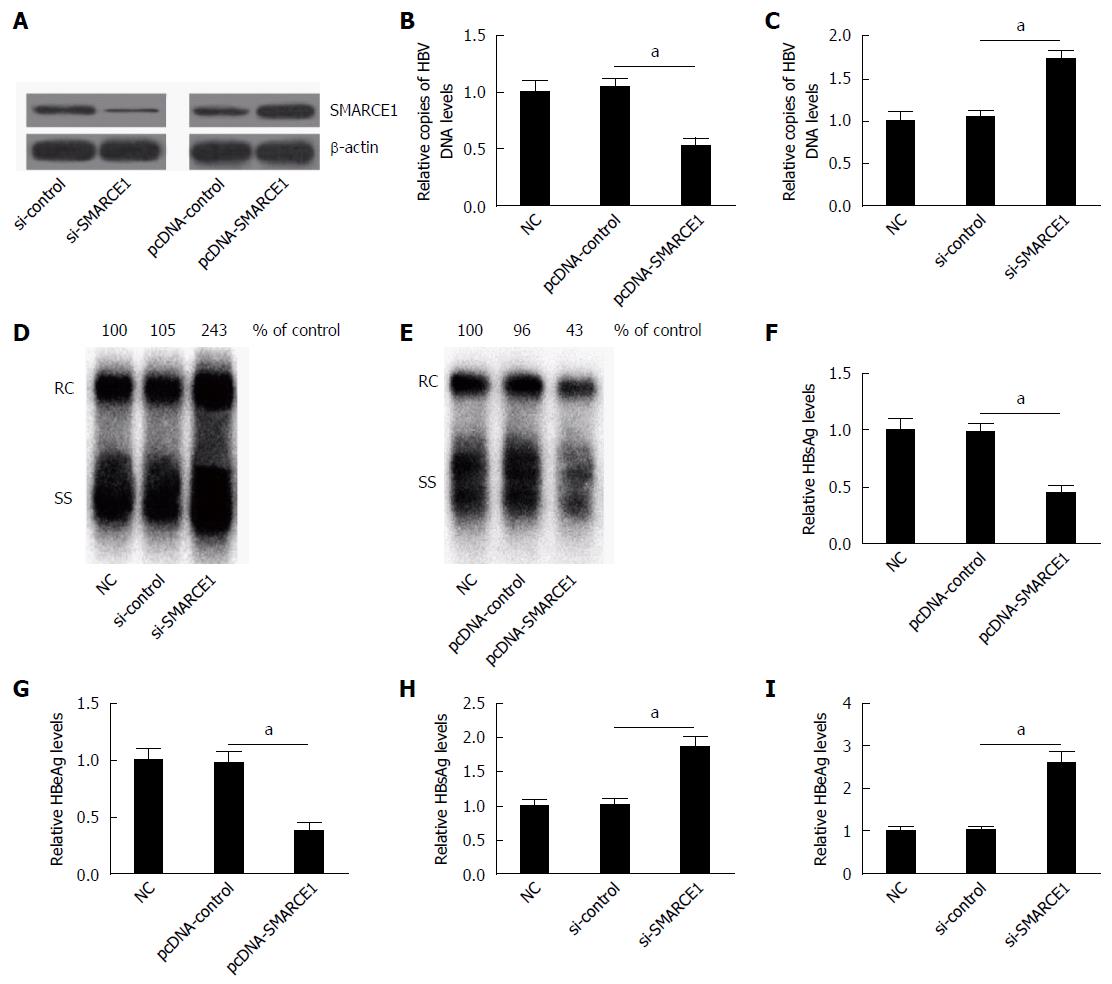
Figure 4 Effect of SMARCE1 on hepatitis B virus replication and expression (n = 3).
A: HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with pcDNA-control, pcDNA-SMARCE1, si-control, or si-SMARCE1 for 24 h; B and E: Western blotting was performed to detect the level of SMARCE1 after pcDNA-SMARCE1 or si-SMARCE1 transfection; C and D: qPCR and Southern blotting analysis showed that SMARCE1 overexpression significantly reduced the HBV DNA replication and SMARCE1 knockdown significantly increased the HBV DNA replication; F and G: ELISA assay showed that SMARCE1 overexpression significantly decreased the levels of HBsAg and HBeAg; H and I: Endogenous SMARCE1 inhibition by si-SMARCE1 significantly promoted the levels of HBsAg and HBeAg. aP < 0.05 vs controls. Data represent the mean ± SD.
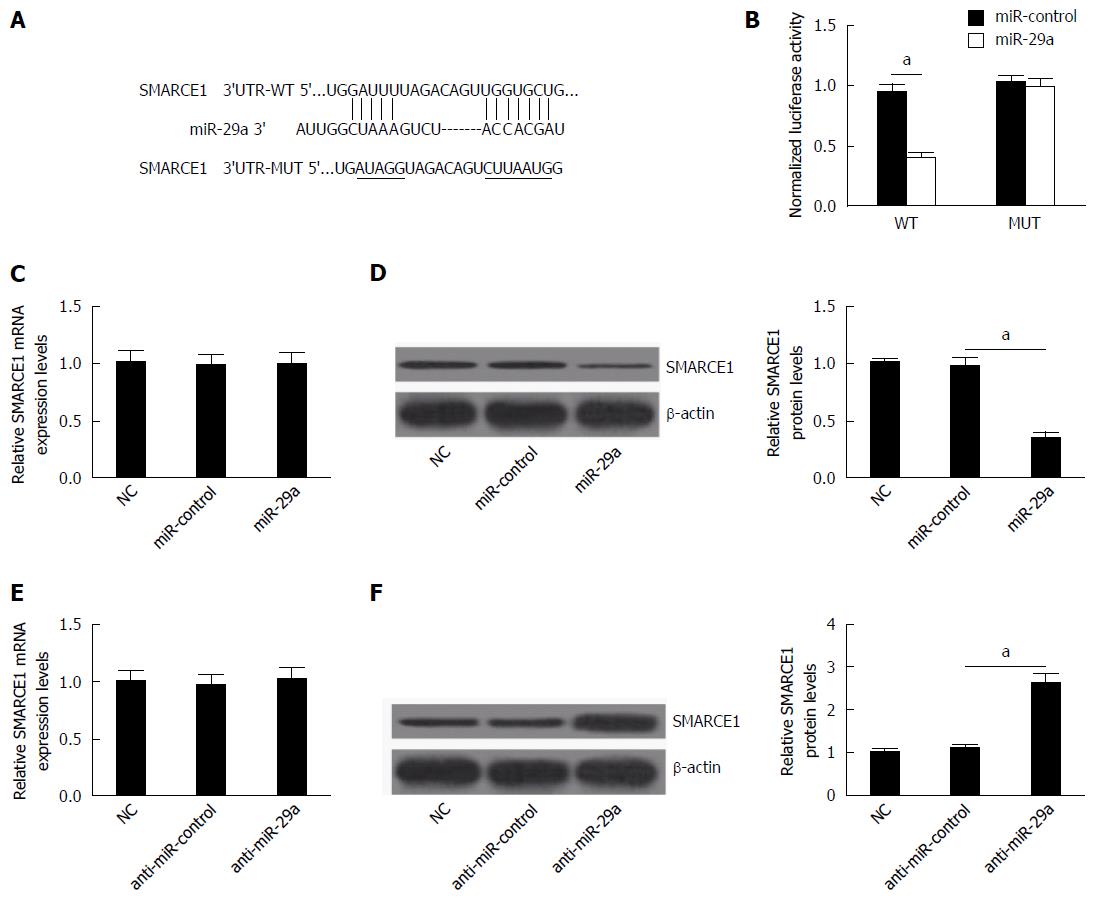
Figure 5 SMARCE1 is a target of miR-29a (n = 3).
A: Wild-type (WT) and mutant (MUT) 3’-UTR binding sites are shown. The mutated bases are labelled with a horizontal line; B: Relative luciferase activity was measured in HEK293 cells co-transfected WT or MUT SMARCE1 3’-UTR with miR-17 mimic or miR-control; C-E: The relative mRNA (C) and protein (D and E) levels of SMARCE1 were measured in HepG2.2.15 cells transfected with miR-29a mimics or anti-miR-29a. Data represent the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs miR-control.
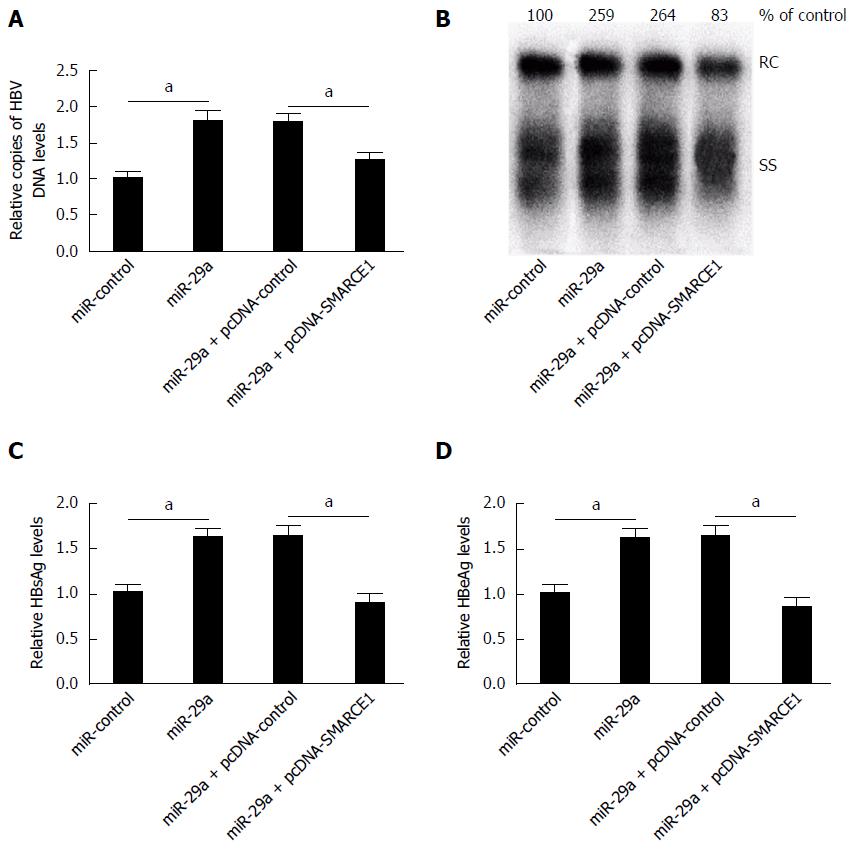
Figure 6 miR-29a promotes hepatitis B virus replication and expression by targeted regulation of SMARCE1 (n = 3).
HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected with miR-control or miR-29a mimics or co-transfected miR-29a mimics with pcDNA-control or pcDNA-SMARCE1. A and B: Restored expression of SMARCE1 by pcDNA-SMARCE1 relieved the increased HBV replication by miR-29a overexpression; C and D: Restored expression of SMARCE1 by pcDNA-SMARCE1 reversed the increased HBsAg and HBeAg expression by miR-29a overexpression. Data represent the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, vs miR-control. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; RC: Relaxed circular; SS: Single-stranded.
- Citation: Wu HJ, Zhuo Y, Zhou YC, Wang XW, Wang YP, Si CY, Wang XH. miR-29a promotes hepatitis B virus replication and expression by targeting SMARCE1 in hepatoma carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(25): 4569-4578
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i25/4569.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i25.4569