Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2017; 23(23): 4222-4232
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4222
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4222
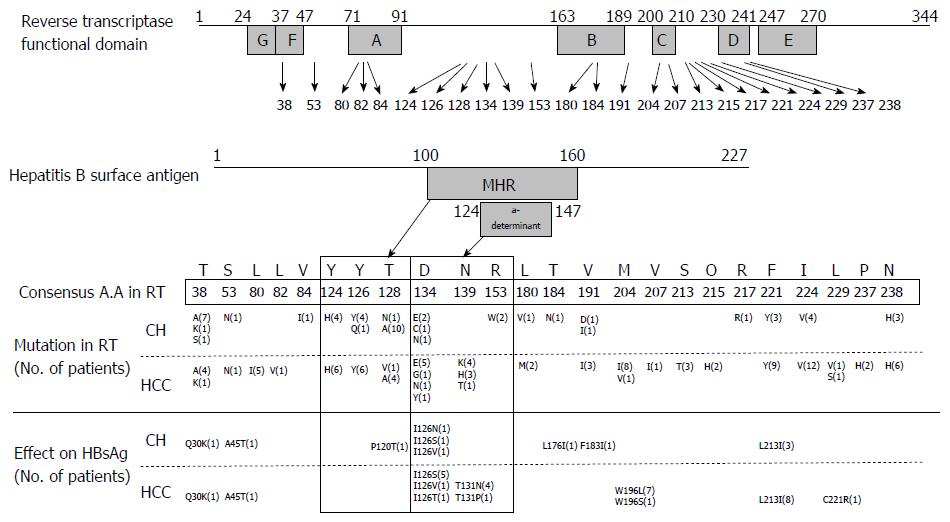
Figure 1 Mutations identified in reverse transcriptase region and the overlapped hepatitis B virus surface antigen.
The identified NAr mutations in this study in the hepatitis B virus (HBV) reverse transcriptase (RT) sequence (1-344 aa) and overlapped HBsAg (1-227 aa) were shown. RT consists of 6 functional domains, G (24-36 aa), F (37-47 aa), A (71-91 aa), B (163-189 aa), C (200-210 aa), D (230-241 aa) and E (247-270 aa). HBsAg contains MHR region (100-160 aa) including “a” determinant region (124-147 aa). Lower box indicated 24 identified NAr mutations in this study and comparison of mutation types between CH and hepatocellular carcinoma patients. CH: Chronic hepatitis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
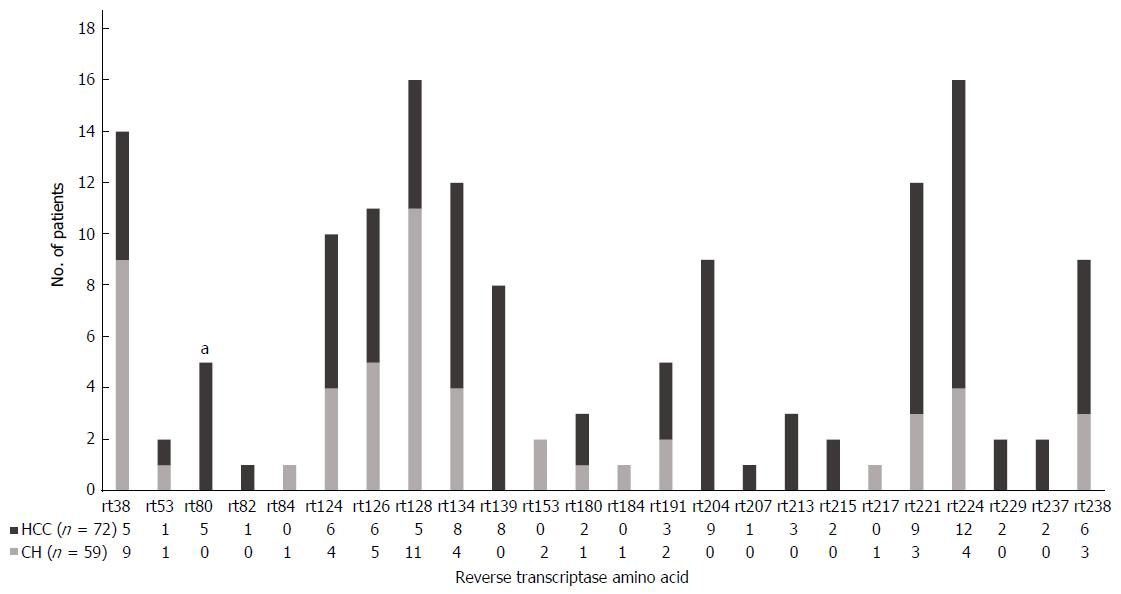
Figure 2 Comparison of nucleos(t)ide analog resistance variants frequency between chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
Of identified 24 mutations, mutation frequency at the 3 sites, rt80, rt139 and rt204 was significantly higher in hepatocellular carcinoma patients than in CH patients. aP < 0.05. CH: Chronic hepatitis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Kim JE, Lee SY, Kim H, Kim KJ, Choe WH, Kim BJ. Naturally occurring mutations in the reverse transcriptase region of hepatitis B virus polymerase from treatment-naïve Korean patients infected with genotype C2. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(23): 4222-4232
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i23/4222.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4222