Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2017; 23(23): 4181-4190
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4181
Published online Jun 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4181
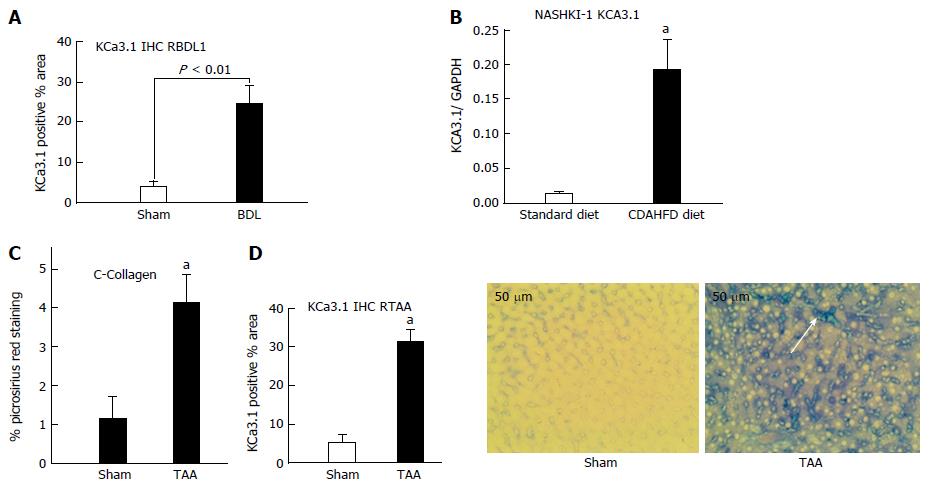
Figure 1 Upregulation of KCa3.
1 expression in diseased livers. A: In rats subjected to biliary occlusion, hepatic KCa3.1 expression, probed with anti-KCa3.1 (SK4, IKCa1) antibody, was several-fold that in of sham operated rats. B: Densitometric analysis was made of Western blots for KCa3.1 expression in liver lysates from mice fed a standard diet or CDAHFD for 8 wk. Compared to its expression in livers from animals on a standard diet, KCa3.1 expression is increased several-fold in livers from the CDAHFD cohort (aP < 0.05 vs standard diet). C: Left: Livers from rats administered TAA for 8 wk exhibited increased fibrosis evidenced by increased picrosirius red staining (aP < 0.05 vs sham). D: Increased KCa3.1 expression significantly (aP < 0.05 vs Sham) (middle). (20 ×), intense blue membranous staining (white arrow and right bottom) was noted in these fibrotic livers.
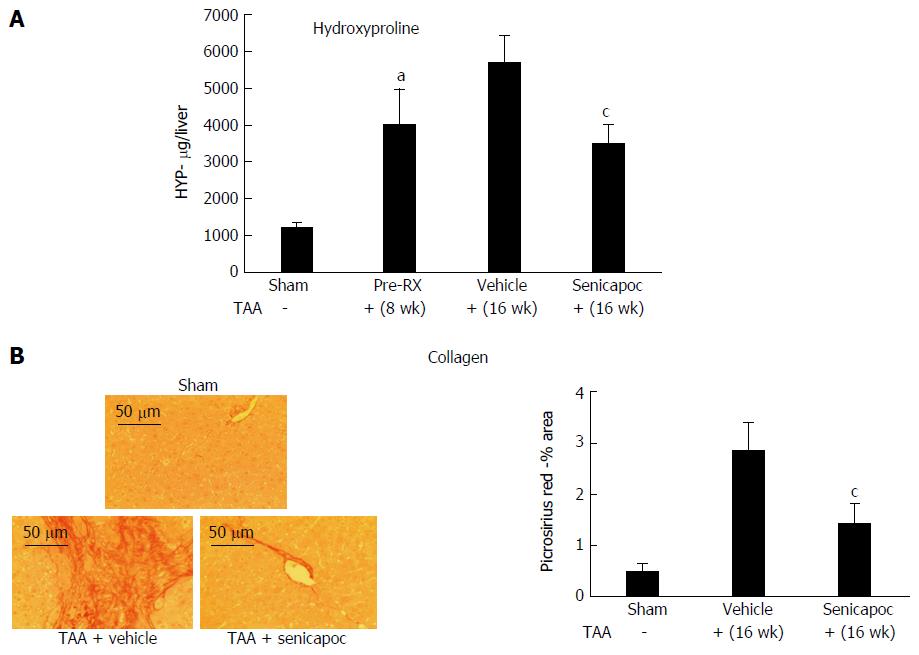
Figure 2 Senicapoc is anti-fibrotic in toxin-induced liver disease.
A: Eight weeks after administration of TAA, livers exhibited increased hydroxyproline (collagen) content (aP < 0.05 vs sham). Animals randomized to Senicapoc between weeks 8 and 16, exhibited reduced liver fibrosis at week 16 (cP < 0.05 vs TAA + vehicle). B: Picosirus red stained livers (20 ×) from representative sham, TAA + vehicle or TAA + Senicapoc-treated animals (16 wk TAA; 8 wk drug) are shown. Intervention with Senicapoc reduced hepatic collagen accumulation (cP < 0.05 vs TAA + vehicle).
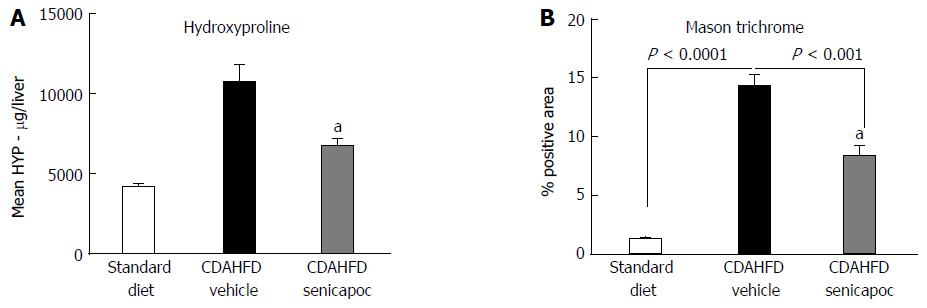
Figure 3 Senicapoc is anti-fibrotic in diet-induced liver disease.
In animals randomized to Senicapoc for 4 wk after 4 wk on CDAHFD (total 8 wk on diet), A: measurement of liver hydroxyproline, a readout of tissue collagen; and B: analysis of Masson’s trichrome showed that Senicapoc decreases liver fibrosis. aP < 0.05 vs vehicle.
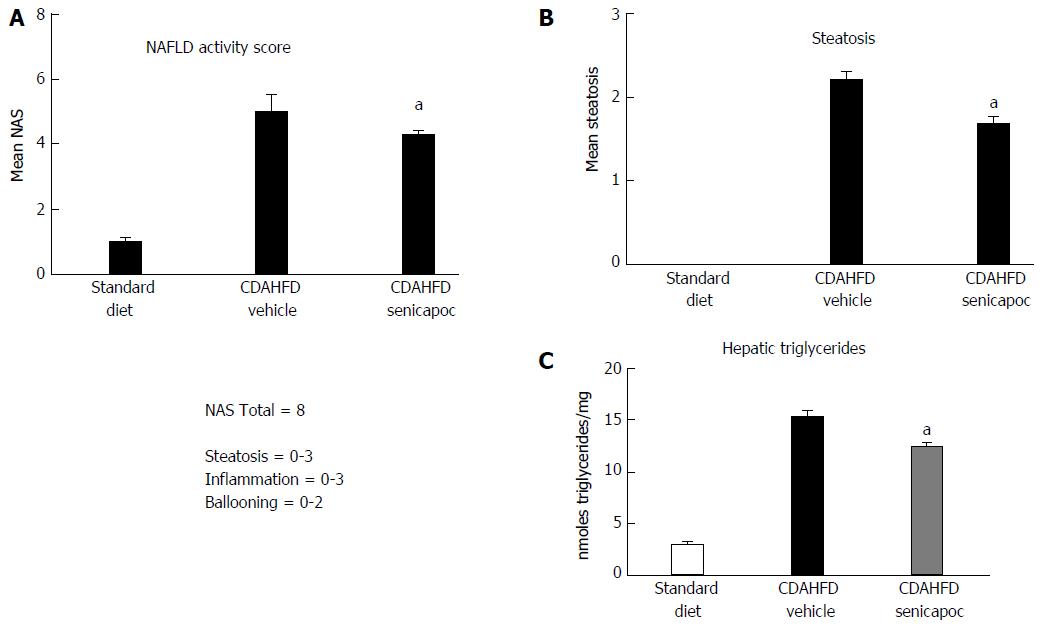
Figure 4 Intervention with Senicapoc is anti-steatotic in the CDAHFD Model.
In animals randomized to Senicapoc for 4 wk after 4 wk on CDAHFD (total 8 wk on diet), A: Reduced NAS (0-8 scale); B: Reduced steatosis (0-3 scale); and (C) reduced accumulation of hepatic triglycerides was observed. aP < 0.05 vs CDAHFD + vehicle.
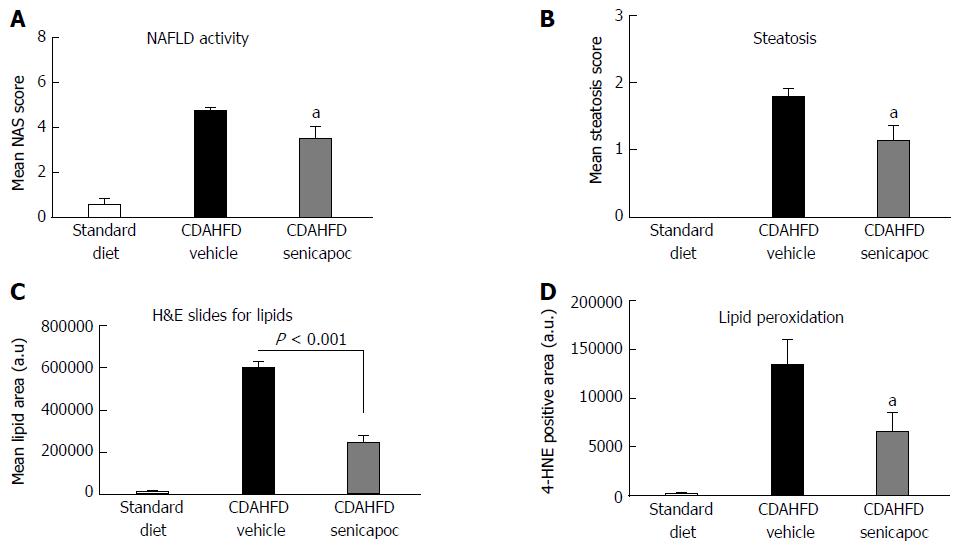
Figure 5 Senicapoc prevents steatosis in the CDAHFD Model.
In animals fed CDAHFD for a week, co-treatment with Senicapoc, A: Decreased NAS (0-8 scale); B: Decreased steatosis (0-3 scale); C: Decreased the lipid vacuole area measured by planimetry in H&E-stained sections; and D: Treatment with Senicapoc reduced hepatic lipid peroxidation (4-HNE) observed in the CDAHFD + vehicle cohort. aP < 0.05 vs vehicle.
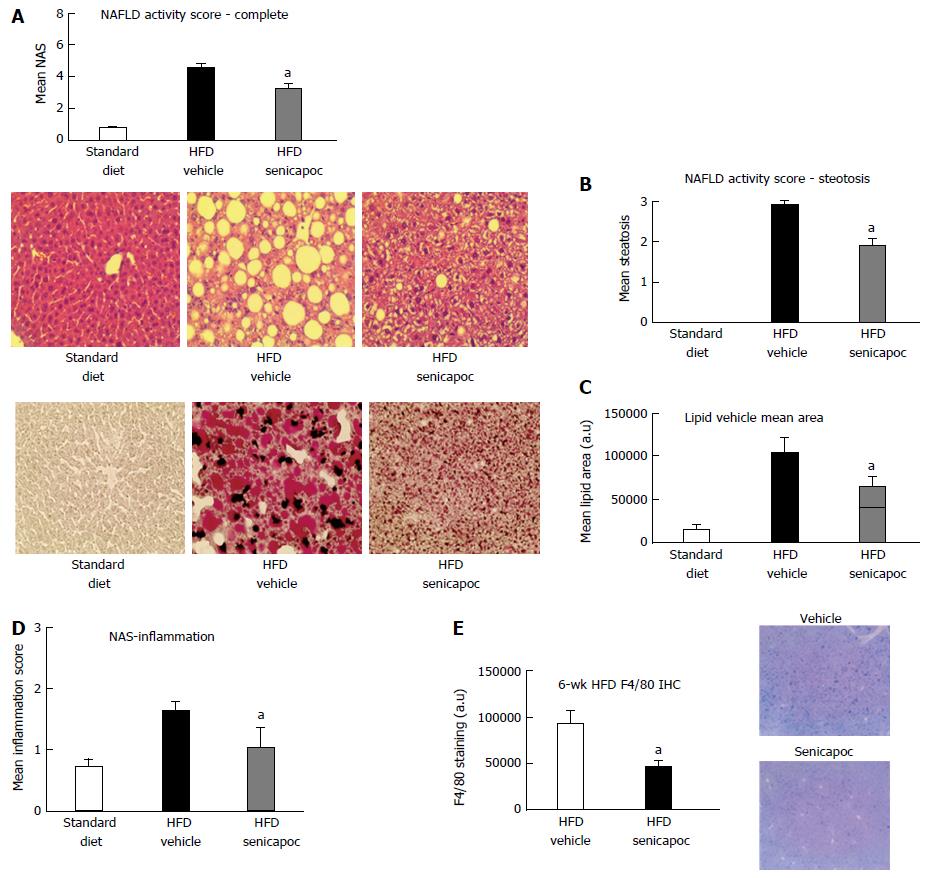
Figure 6 Senicapoc prevents steatosis in the high fat diet Model.
In animals fed a HFD for 6 wk, co-treatment with Senicapoc, A: Reduced NAS (0-8 scale); B: Decreased steatosis [H&E-stained section (40 ×) on left, steatosis score on right]; C: Decreased hepatic lipid content (Oil Red O- stained section (40 ×) on left; lipid vesicular area right); D: Six weeks on HFD is associated with inflammation (0-3 scale) which is mitigated with Senicapoc; and E: Senicapoc reduces F4/80 staining, a marker of macrophage activity, in the liver. aP < 0.05 vs vehicle. HFD: High fat diet.
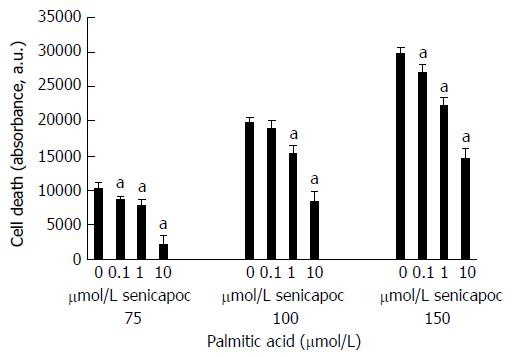
Figure 7 Senicapoc prevents lipid-induced apoptosis.
HepG2 cells were treated with Senicapoc (0-10 μmol/L) and then loaded with palimitic acid (75-150 μmol/L). Following overnight incubation, apoptosis was measured using the Caspase Glo assay. Treatment with Senicapoc decreased palmitic acid-driven HepG2 cell death [aP < 0.05 vs corresponding control (0 μmol/L Senicapoc) at each concentration of palmitic acid].
- Citation: Paka L, Smith DE, Jung D, McCormack S, Zhou P, Duan B, Li JS, Shi J, Hao YJ, Jiang K, Yamin M, Goldberg ID, Narayan P. Anti-steatotic and anti-fibrotic effects of the KCa3.1 channel inhibitor, Senicapoc, in non-alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(23): 4181-4190
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i23/4181.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4181