Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2017; 23(17): 3030-3042
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3030
Published online May 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3030
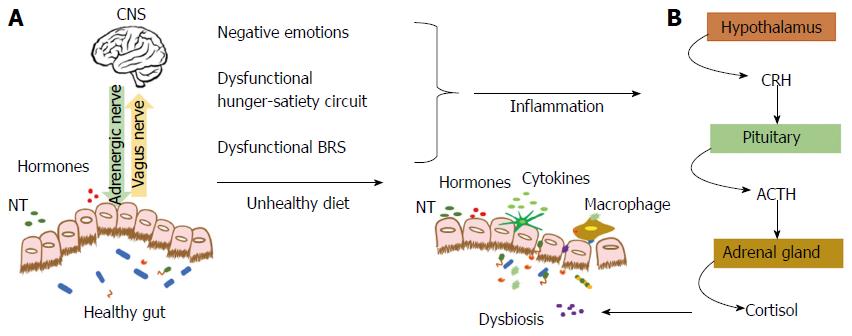
Figure 1 Gut-brain axis and dysbiosis.
A: The gut microbiota maintains a two-way communication with the CNS using hormones, neuropeptides, NT, cytokines and the afferent (vagus nerve) and efferent signals (adrenergic nerve); B: Alterations in the energy balance circuit and BRS that lead to negative emotions chronically activate the HPA axis elevating cortisol levels. Cortisol results in dysbiosis, allowing pathogens to permeate the gut barrier and activate inflammation. Unhealthy dietary patterns also lead to dysbiosis, inflammation and negative emotions. CNS: Central nervous system; BRS: Brain reward system; CRH: Corticotrophin-releasing hormone; ACTH: Adrenocorticotropic hormone; HPA: Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal.
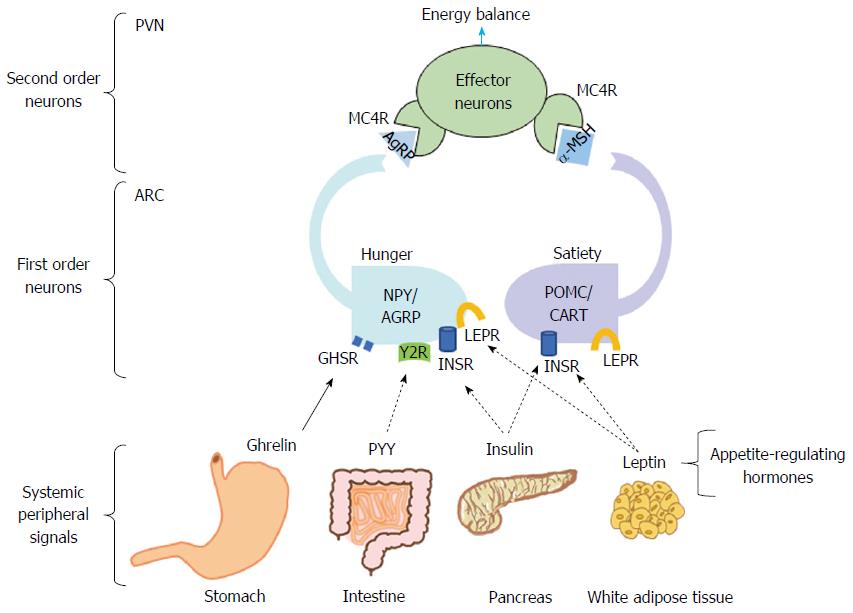
Figure 2 Hunger-satiety circuit and energy balance.
Energy balance depends on the appropriate compensatory signals from the hypothalamic nucleus. Food intake is promoted by the binding of ghrelin to the GHSR in the NPY/AgRP neurons, blocking anorexigenic signaling. Once food consumption occurs, PYY-Y2R binding has an antagonistic effect on the orexigenic pathway. Leptin and insulin bind to their specific receptors in POMC/CART neurons that in turn induces α-MSH to bind to its MC4R, promoting satiety. Furthermore, leptin and insulin in NYP/AGRP neurons inhibit AgRP signaling. GHSR: Growth hormone secretagogue receptor; NPY/AgRP: Neuropeptide Y/Agouti-related receptor protein; PYY: Peptide YY; Y2R: Y2 receptor; POMC/CART: Pro-opiomelanocortin/cocaine and amphetamine regulated transcript; α-MSH: α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone; PVN: Paraventricular nucleus; ARC: Arcuate nucleus.
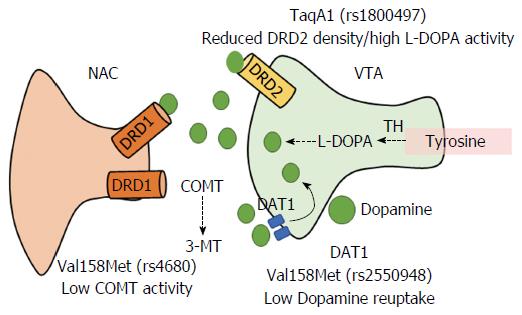
Figure 3 Brain reward dopaminergic signaling between ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens neurons.
Dopamine in the VTA area activates excitatory DRD1 in the NAC. Several genetic polymorphisms in the regulatory proteins DRD2, DAT1, and COMT modify the reward response to dopamine. VTA: Ventral tegmental area; NAC: Nucleus accumbens; DRD1: Dopamine receptor 1; DRD2: Dopamine receptor 2; DAT1: Dopamine transporter 1; COMT: Catechol-O-methyl-transferase; TH: Tyrosine hydroxylase.
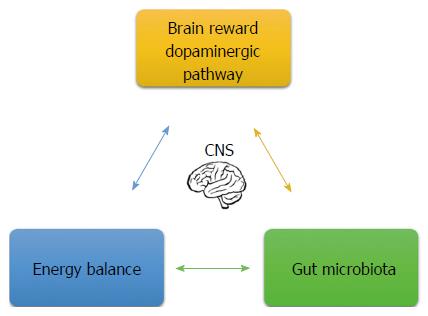
Figure 4 Signals involved in the health/disease process.
Brain dopaminergic pathway and energy balance regulate emotional eating behaviors. Negative emotion contributes to alterations in gut microbiota composition. At the same time, gut microbiota environment and its metabolites communicate to the central to the brain and regulate the brain’s reward system and energy balance. CNS: Central nervous system.
- Citation: Panduro A, Rivera-Iñiguez I, Sepulveda-Villegas M, Roman S. Genes, emotions and gut microbiota: The next frontier for the gastroenterologist. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(17): 3030-3042
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i17/3030.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3030