Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2017; 23(15): 2795-2801
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2795
Published online Apr 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2795
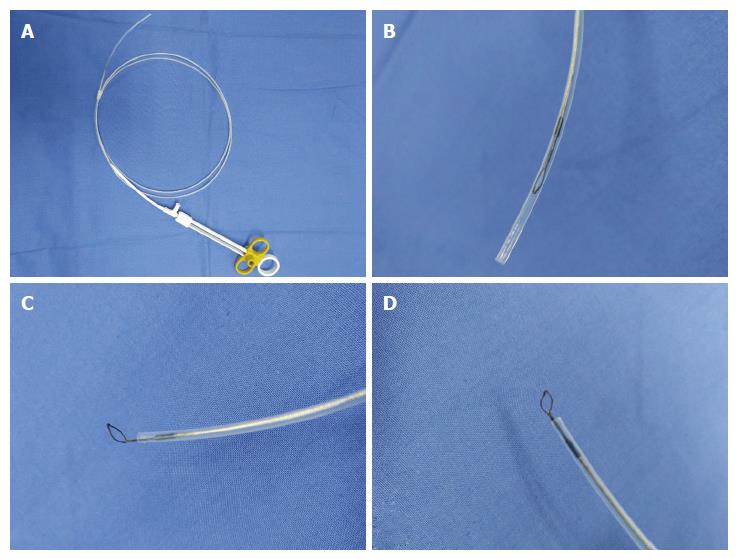
Figure 1 Vertical electrode loop.
A: The vertical electrode loop device; B: The loop is dragged into the sheath when not working; C and D: When working, the small loop that is vertically wielded to the end of the electric metal wire is pushed out of the sheath.
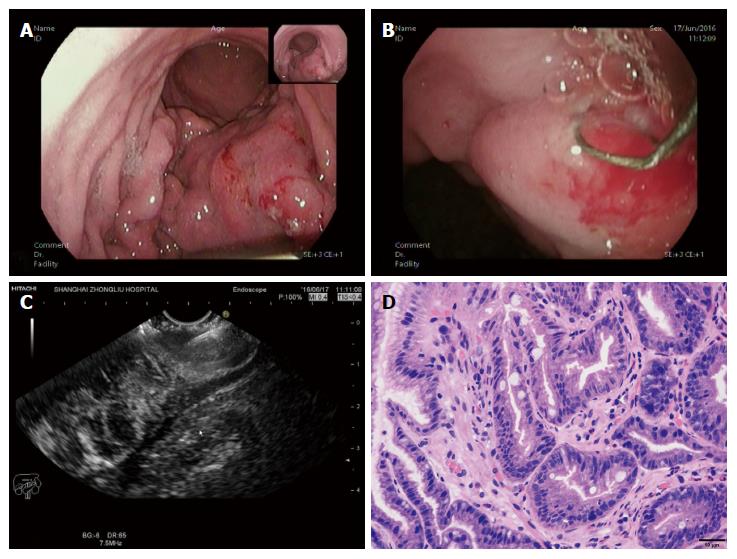
Figure 2 A case diagnosed with gastric linitis plastic.
A: Endoscopic characteristics: thick and rigid gastric duplicature and a narrow cavity; B: The loop was placed on the targeted focus characterized by the obviously thick and rigid wall on the tumor, then the holes were cut; C: A biopsy forceps was poked into the holes to acquire the deep tissue samples under the guidance of EUS; D: The tissue specimen was then analysed histopathologically and shown to be gastric adenocarcinoma.
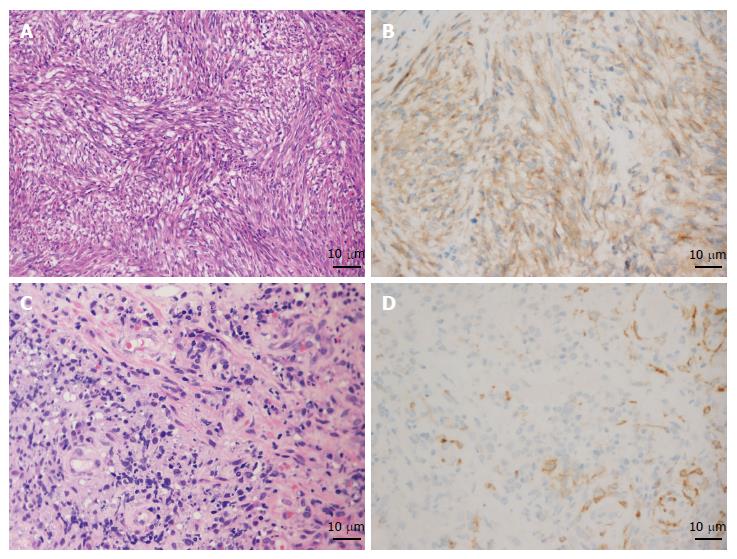
Figure 3 Results of pathology and immunohistochemistry of gastrointestinal stromal tumors and gastric lymphoma.
A and B: The pathology characterized by spindle cells (HE, × 200) and immunohistochemistry showing positive CD117 staining proved the diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST); C and D: Increased and dispersively distributed lymphocytes (HE, × 400) with positive CD10 staining according to the immunohistochemistry results confirmed the diagnosis of gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- Citation: Liu YM, Yang XJ. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided cutting of holes and deep biopsy for diagnosis of gastric infiltrative tumors and gastrointestinal submucosal tumors using a novel vertical diathermic loop. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(15): 2795-2801
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i15/2795.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i15.2795