Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2017; 23(12): 2185-2193
Published online Mar 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i12.2185
Published online Mar 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i12.2185
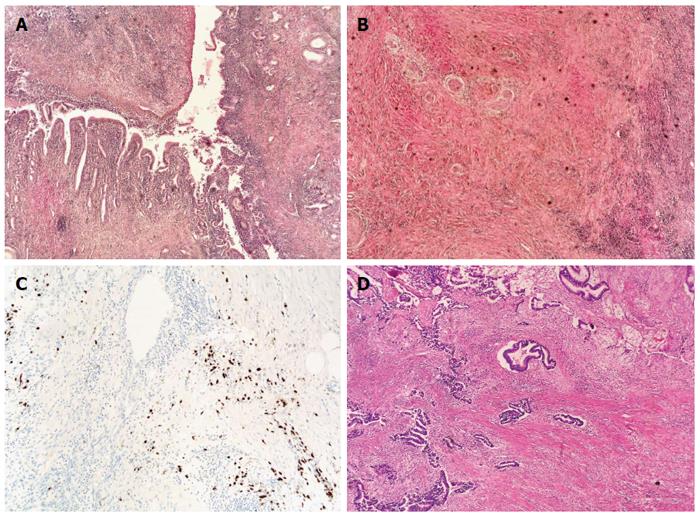
Figure 1 Histological findings in resected pancreatic tissue in a patient with synchronous presence of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
A: Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, original magnification × 40; B: AIP showing storiform fibrosis, HE staining, original magnification × 40; C: AIP with immunohistochemical staining of plasma cells for IgG4; D: Pancreatic cancer, HE staining, original magnification × 40.
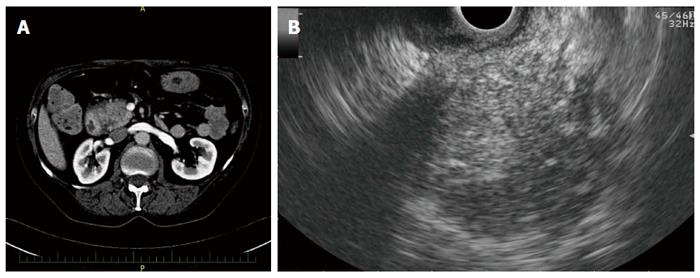
Figure 2 Imaging findings in a patient with autoimmune pancreatitis.
A: Hypodense lesion in the pancreatic head on computed tomography; B: Hypoechoic lesion of the pancreatic head on endoscopic ultrasonography.
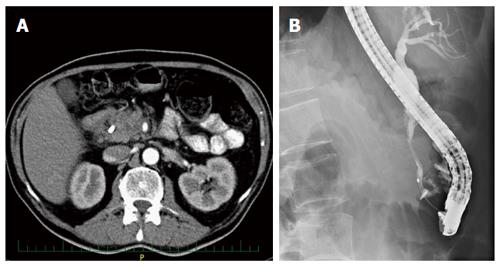
Figure 3 Imaging findings in a patient with autoimmune pancreatitis + pancreatic cancer.
A: Hypodense lesion in the pancreatic head with a common bile duct (CBD) stent on computed tomography; B: Distal CBD stricture on endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography.
- Citation: Macinga P, Pulkertova A, Bajer L, Maluskova J, Oliverius M, Smejkal M, Heczkova M, Spicak J, Hucl T. Simultaneous occurrence of autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in patients resected for focal pancreatic mass. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(12): 2185-2193
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i12/2185.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i12.2185