Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2017; 23(10): 1758-1763
Published online Mar 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1758
Published online Mar 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1758
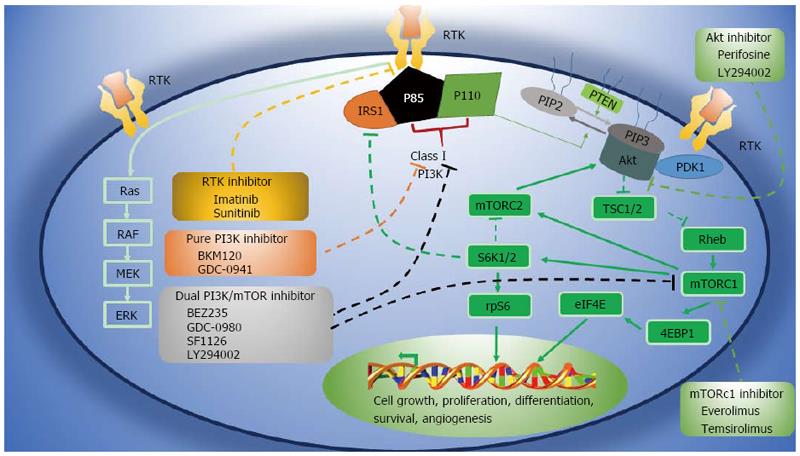
Figure 1 PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and inhibitors in clinical development[29].
Solid lines represent activating actions, and dotted lines represent inhibitory actions. 4EBP1: 4E-binding protein 1; PKB: Protein kinase B; ERK: Extracellular signal-related kinase; IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate 1; MEK: Mitogen-activated protein/ERK kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; mTORC: mTOR complex; PDK1: Pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoamide kinase isozyme 1; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; Rheb: Ras homolog enriched in brain; rpS6: Ribosomal protein S6; RTK: Receptor tyrosine kinase; S6K: Ribosomal S6 kinase; TSC1/2: Tuberous sclerosis protein.
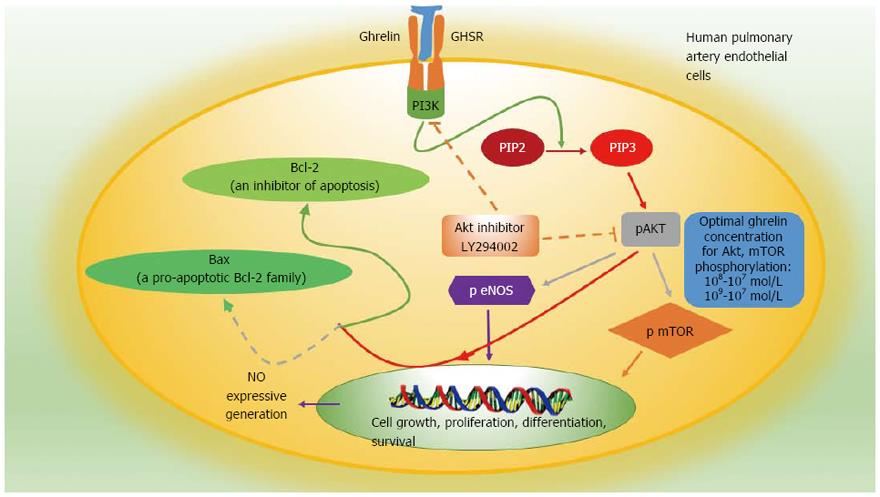
Figure 2 Specific mechanism of ghrelin involved in the protection of pulmonary artery endothelial cells and activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells[44-47].
Solid lines represent activating actions, and dotted lines represent inhibitory actions. PIP2: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate.
- Citation: Zhu CZ, Liu D, Kang WM, Yu JC, Ma ZQ, Ye X, Li K. Ghrelin and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(10): 1758-1763
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i10/1758.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1758