Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2016; 22(9): 2779-2788
Published online Mar 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2779
Published online Mar 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2779
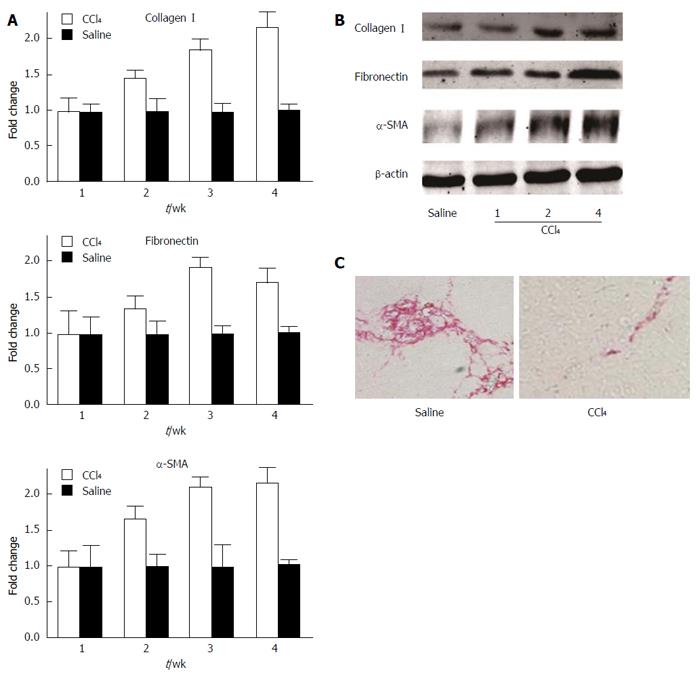
Figure 1 Expression of fibrogenic proteins and extracellular matrix deposition in the liver of mice exposed to CCl4.
A: Relative mRNA expression of collagen I, fibronectin, and α-SMA after 1, 2, 3, and 4 wk of CCl4 treatment, as determined by quantitative RT-PCR; B: Protein expression of collagen I, fibronectin, and α-SMA after 1, 2, and 4 wk of CCl4 treatment, as determined by Western blot; C: Picrosirius red staining shows hepatic collagen deposition in mice treated with CCl4 for 4 wk; saline treatment served as the control group. SMA: Smooth muscle actin.
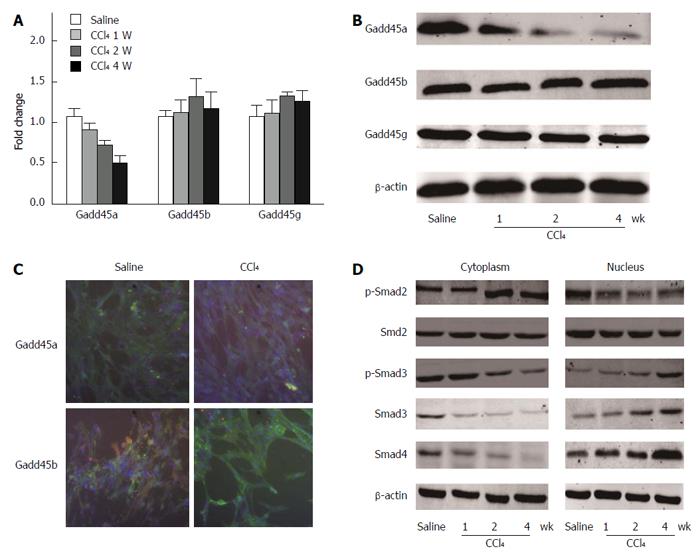
Figure 2 Chronic CCl4 injury suppresses Gadd45a expression and activates TGF-β/Smad signaling.
A: Relative mRNA expression levels of Gadd45a, Gadd45b, and Gadd45g in the livers of mice treated with CCl4 for 1, 2, and 4 wk; the saline-treated group served as the control group; B: Relative protein expression levels of Gadd45a, Gadd45b, and Gadd45g in the livers of mice treated with CCl4 for 1, 2, and 4 wk; C: Immunofluorescence staining of Gadd45a, Gadd45b, and Gadd45g (in green) in HSCs treated with CCl4 for 4 wk (nuclei are stained blue with DAPI; scale bars = 10 μm); D: Expression levels of p-Smad2, p-Smad3, Smad2, Smad3, and Smad4 were analyzed in HSCs treated with CCl4 for 1, 2, and 4 wk. HSC: Hepatic stellate cells; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
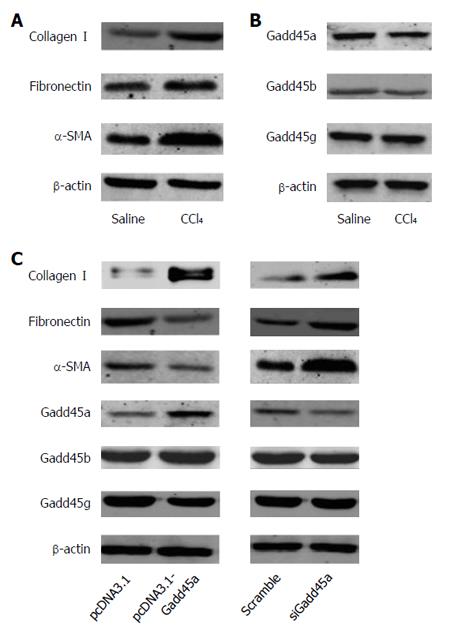
Figure 3 Gadd45a inhibits the expression of extracellular matrix proteins and α-smooth muscle actin in CCl4-treated hepatic stellate cells.
A: Expression of type I collagen, fibronectin, and α-SMA in HSCs treated with CCl4vs saline for 24 h; B: Expression of Gadd45a, Gadd45b, and Gadd45g in HSCs treated with CCl4vs saline for 24 h; C: Expression of type I collagen, fibronectin, α-SMA, Gadd45a, Gadd45b, and Gadd45g in HSCs transfected with pcDNA3.1-Gadd45a or siRNA-Gadd45a. HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; SMA: Smooth muscle actin.
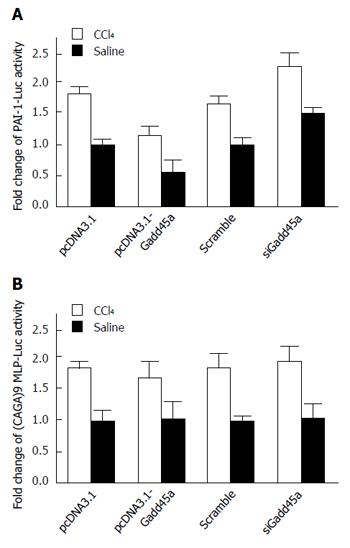
Figure 4 Gadd45a inhibits hepatic fibrosis through the suppression of transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling.
A: Effects of Gadd45 on PAI-1-Luc activity in HSCs treated with pcDNA3.1, Gadd45a, and Gadd45a siRNA in both the CCl4 and saline groups; B: Effects of Gadd45 on (CAGA)9 MLP-Luc activity in HSCs treated with pcDNA3.1, Gadd45a, and Gadd45a siRNA in both the CCl4 and saline groups. HSC: Hepatic stellate cell; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
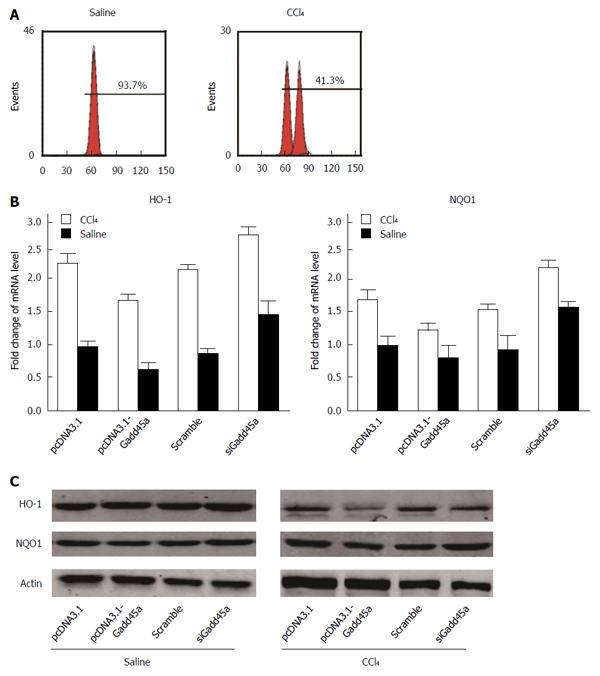
Figure 5 Gadd45a exerts reactive oxygen species scavenging effects by upregulating the expression of antioxidant enzymes.
A: The effects of Gadd45a on ROS generation in CCl4-pretreated HSCs treated with pcDNA3.1, PCDNA3.1-Gadd45a, scrambled siRNA, and Gadd45a siRNA were detected by flow cytometry; B: Effects of Gadd45a on HO-1 and NQO1 RNA expression in CCl4-pretreated HSCs treated with pcDNA3.1, PCDNA3.1-Gadd45a, scrambled siRNA, and Gadd45a siRNA; C: Effects of Gadd45a on HO-1 and NQO1 protein expression in CCl4-pretreated HSCs treated with pcDNA3.1, PCDNA3.1-Gadd45a, scrambled siRNA, and Gadd45a siRNA. HSC: Hepatic stellate cells; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
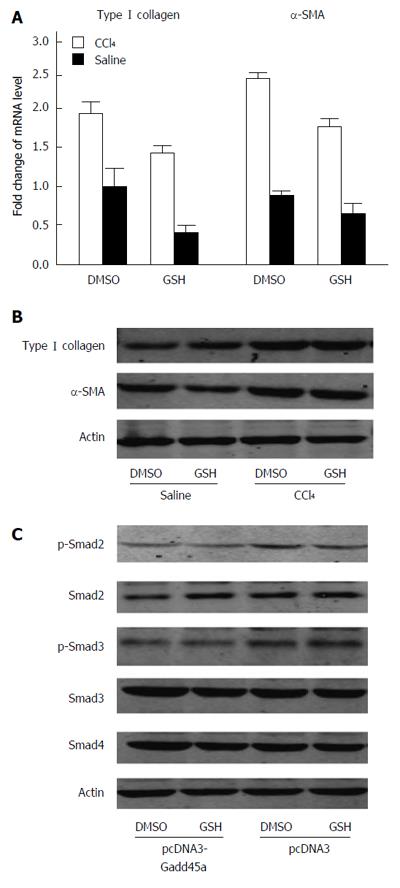
Figure 6 Gadd45a inhibits the transforming growth factor-β/Smad signaling pathways partly due to its antioxidant properties.
A: Relative mRNA expression of type I collagen and α-SMA as determined by quantitative RT-PCR. Hepatic stellate cells were stimulated with CCl4 in the presence or absence of glutathione for 24 h; B: Western blot analyses of type I collagen and α-SMA expression; C: Activation of the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways was measured by Western blot analyses of p-Smad2, p-Smad3, Smd2, Smad3, and Smad4. GSH: Glutathione; SMA: Smooth muscle actin; TGF: Transforming growth factor.
- Citation: Hong L, Sun QF, Xu TY, Wu YH, Zhang H, Fu RQ, Cai FJ, Zhou QQ, Zhou K, Du QW, Zhang D, Xu S, Ding JG. New role and molecular mechanism of Gadd45a in hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(9): 2779-2788
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i9/2779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2779